Archive for the ‘MySQL Workbench’ Category
Oracle OpenWorld 2013
I registered yesterday for Oracle OpenWorld 2013, and I’ll look forward to seeing friends there. Having worked in the Oracle 12c beta for a year, I’ll be interested in the presentations. Also, hearing more about Java 7 at JavaOne. On the downside, I’m missing MySQL Connect this year.

Cloud computing offers many possibilities, and container and pluggable databases are a great solution. We’ve two new acronyms with the Oracle 12c release. A containerized database is a CDB, and a pluggable database is a PDB. I’m looking forward to seeing more about the provisioning of PDBs during the conference. If you’re new to the changes, check out CDBs and PDBs in Chapter 17 in the Oracle 12c Concepts manual.
A couple of my favorite new features are Identity and Invisible Columns. If you’re unfamiliar with the new features for application development, let me recommend this Oracle White Paper. Also, for reference I’ve covered identity and invisible columns thoroughly in the Oracle Database 12c PL/SQL Programming book, which will be available in December.
Missing the MySQL Connect 2013 Bus

Unfortunately, travel budgets preclude me attending MySQL Connect 2013 this year (alas, I’ll miss the bus). 🙁 It was hard because I’d like to see what’s up with MySQL (since I was a closet MySQL user at Oracle before they acquired it). Anyway, if you’re there, make sure you check out MySQL Workbench 6 for me. Also, I’d like to thank Dave Stokes for the AWESOME review he wrote on Amazon.com for my MySQL Workbench: Data Modeling & Development book. Maybe, I’ll get to go to MySQL Connect 2014 next year.
MySQL 5.6 Install Steps
My install instructions on the web site were old, somebody wanted me to publish another set of screen capture for the MySQL 5.6 install and configuration. This is it for Windows 7 using the downloadable MSI file.
Installation Steps
The installation from MySQL’s perspective is actually the installation and configuration of MySQL. For your convenience and reference, I’ve already installed the pre-requisites for MySQL. They’re:
- Visual Studio Tools for Office 20120 Runtime
- Microsoft .NET Framework 4 Client Profile
- Microsoft Excel 2007 or greater
- Microsoft .NET Framework 4 Client Profile
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 32-bit runtime
- Microsoft .NET Framework 4 Client Profile
Below are the installation steps after you download the current release .msi file. The icon should look like the one to the right. For this example, I”m using the
The icon should look like the one to the right. For this example, I”m using the mysql-installer-community-5.6.11.0.msi. Double-click the icon on your desktop or from your C:\Users\username\Downloads folder. While working through the steps, you can launch any of the small images to the left if you’d like to see what your screen should look like (generally with a right click to open in a new window).
- The first screen is a Windows 7 dialog box. Click the Run button to install launch the MySQL 5.6 Installer.
- The second screen is a Windows 7 dialog box. It advises you that the MySQL Installer is working and lets you cancel that operation. Don’t click the Cancel button unless you want to stop the MySQL 5.6 Installer.
- The third screen is a MySQL Installer message box. It closes when ready to proceed. Ignore it, unless it’s there for more than a couple minutes. If that occurs you’ve got something wrong with your Windows installation or a very slow computer. If the former, kill the installation process; if the latter, wait patiently.
- The fourth screen in the process is the first MySQL Installer screen. Here you choose what you want to do. You can install MySQL products, inquire about MySQL, or check physical resource components. Provided you installed the prerequisites listed above, you should be prepared to install MySQL Products. Click the Install MySQL Products link to proceed or one of the others to explore.
- The second MySQL Installer screen is the license form. You must check the I accept the license terms checkbox to enable the Next button. Once the Next button is enabled, click it to proceed.
- The third MySQL Installer screen connects to the Internet and finds the latest product update. You can check the Skip the check for updates (not recommended) checkbox to skip this but for the example we’ll check anyway. Click the Execute button to proceed.
- The fourth MySQL Installer screen connects to the Internet and finds the latest product update. You can check the Skip the check for updates (not recommended) checkbox to skip this but for the example we’ll check anyway. Click the Execute button to proceed.
- The fifth MySQL Installer screen acknowledges the latest update is what you’re installing. Click the Next button to proceed.
-
The sixth MySQL Installer screen gives you five choices for the installation, which are listed below. You most likely want to install the Developer Default, so click the Developer Default radio button and then, click the Next button to proceed.
- MySQL Server
- Both the client and server software for the MySQL Server
- MySQL Workbench
- The GUI application to develop for and manage the server.
- MySQL Visual Studio Plugin
- To work with the MySQL Server from VS.
- MySQL Connectors
- Connector/Net, Java, C/C++, OBDC and others.
- Examples and tutorials
- To help you get started with your development.
- Documentation
- Allows you to read the documentation offline.
- The seventh MySQL Installer screen performs a system check for the pre-requisites, which I listed before the installation. Assuming you installed them, you should see a screen that confirms your system configuration is ready for installation. Click the Next button to proceed.
-
The eighth MySQL Installer screen performs displays the products that it’ll install, which are listed below and available in the full image to the left. Click the Execute button to install the products.
- MySQL Server 5.6.11
- MySQL Workbench CE 5.2.47
- MySQL Notifier 1.0.3
- MySQL for Excel 1.1.1
- Connector/ODBC 5.2.4
- Connector/C++ 1.1.2
- Connector/C++ 1.1.2
- Connector/J 5.1.24
- Connector/NET 6.6.5
- MySQL Documentation 5.6.11
- Samples and Examples 5.6.11
- The nineth MySQL Installer screen shows the installation by product and it can take a couple minutes. The screen to the left displays progress more than halfway complete. You don’t need to do anything in this step until all products are complete.
- The tenth MySQL Installer screen shows the completed installation. Everything should install successfully, as shown in the image. Click the Next button to proceed.
This concludes the installation of the MySQL products. The next section shows you how to configure MySQL.
Configuration Steps
You have two basic options, the simple one and the advanced one. These steps will show you how to perform an advanced configuration. I’ve opted to maintain the step numbering from the beginning of the installation. Here are the steps:
- The eleventh MySQL Installer screen is the first MySQL Configuration screen. You can click the Show Details button or begin the configuration. Click the Next button to proceed.
- The second MySQL Configuration screen sets the server configuration type, enables TCP/IP networking (as opposed to a socket model), and lets you enable Advanced Configuration. For this installation, we enable the Show Advanced Options checkbox before you click the Next button.
-
The third MySQL Configuration screen sets the password and lets you create MySQL User Accounts. It’s much easier to let the install proceed and use MySQL Workbench to create databases, users, and roles; plus grant permissions through the GUI environment. Enter the
rootpassword twice, a trivial and unsecure passwordcangetinis what I recommend to my students who won’t have any meaningful information in the database. Make sure you can remember the password you enter. Clearly, a better password is required for real environments. After entering the password twice, click the Next button to proceed.
-
The fourth MySQL Configuration screen sets the Windows Service Name, and you should probably make sure there isn’t another MySQL56 service on the machine before you proceed. You have the choice of running the Windows Service using the Standard System Account or a Customer User account. Unless you’re an expert at Windows 7 administration, you should probably choose the Standard System Account as the one running the Windows 7 service. Click the Next button.
-
The fifth MySQL Configuration screen sets the logging options. You only need Show Query Log typically, but the Error Log is helpful. Make the choices and click the Next button.
- The sixth MySQL Configuration screen explains the next step. It installs the sample files and example databases. You can see what you’ve installed when you click the Show Details button, which is what I did to get the image at the left. The default choice installs the samples and example databases, which can’t hurt. You’ll need the test database if you install DBD::mysql for Perl. If you don’t want them, you can drop them from the database.
-
The seventh MySQL Configuration screen explains you’ve completed configuring the MySQL Server. Click the Next button to proceed.
-
The eighth MySQL Configuration screen explains you’ve finished everything. You can copy the log file to clipboard, which allows you to see everything that was done. Click the Finish button to complete the installation and configuration.
Just one caveat (that’s a warning), this installation doesn’t put the MySQL executable into your System %PATH% variable. You’ll need to do that, and if I get a chance I’ll put a post together for that. I know one or two of my students may need it later.
I hope this helps those you are using the new installer for the first time. It’s a superior tool to the old one, which was also a good tool.
MySQL Auto Increment
Somebody ran into a problem after reading about the MySQL CREATE statement and the AUTO_INCREMENT option. They couldn’t get a CREATE statement to work with an AUTO_INCREMENT value other than the default of 1. The problem was they were using this incorrect syntax:
CREATE TABLE elvira ( elvira_id int unsigned PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT=1001 , movie_title varchar(60)) ENGINE=InnoDB CHARSET=utf8; |
It raises this error:
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '=1001 , movie_title varchar(60)) ENGINE=InnoDB CHARSET=utf8' at line 2 |
They concluded that MySQL requires you to assign a default value of 1 as the initial automatic numbering value; then you use the ALTER statement to change the initial sequence value. That assumption is incorrect. The problem was with their assignment of an overriding AUTO_INCREMENT value inside the parenthetical list of columns. That assignment needs to occur after the list of columns and constraints, like
CREATE TABLE elvira ( elvira_id int unsigned PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT , movie_title varchar(60)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1001 CHARSET=utf8; |
It’s not an unlikely mistake since there’s no clear example on either of the referenced web pages (at the time of writing). It would be nice if they were added but I’m of the opinion some of the reference manual pages are too sparse.
After creating the table, you have the generic fix that seems to appear most often as an answer to setting or re-setting the auto numbering sequence of a MySQL table:
ALTER TABLE elvira AUTO_INCREMENT=1001; |
Why would you set the auto numbering sequence to something other than 1? Some designers consider it a best practice to increment from a set point like 101 or 1,001 for your Application Programming Interface (API) and they leave a readily identifiable sequence number set for pre- or post-seeded data in tables. The region of preallocated numbers are typically only used in a few of the tables, in any application, but consistently managing sequences across all tables does sometimes simplifies data diagnostics.
Hope this helps somebody looking for a syntax fix. By the way, you can find it on Page 162 of the Oracle Database 11g & MySQL 5.6 Developer Handbook.
MySQL Workbench Book
 Finally, I finished writing the MySQL Workbench book. It’ll be available next spring. Now it’s time to leave for the plane, fly to San Francisco, and see everyone at MySQL Connect.
Finally, I finished writing the MySQL Workbench book. It’ll be available next spring. Now it’s time to leave for the plane, fly to San Francisco, and see everyone at MySQL Connect.
I look forward to meeting folks, I’ll be presenting after MySQL Connect for those staying for Oracle Open World. My presentation is at Oracle Develop on Monday, 10/1/12 from 16:45 – 17:45, in the Marriott Marquis – Foothill F. As I mentioned in an earlier post, you can probably catch me in Moscone West at the bookstore. The publisher requests we attend book signings. 😉
Unfortunately as a speaker I need to convert my Keynote to Powerpoint, and had to purchase, install, and update Microsoft Office 2011 on my Mac. Open Office and Keynote weren’t on the approved list, alas …
Update: The book published 4/9/2013 (a bit of a delay from completing the write, eh?). It’s available on Safari as of yesterday.
MySQL 5.0 migration bug
At present, you can’t use the MySQL Workbench migration tool to migrate MySQL 5.0 to MySQL 5.5, as documented in Bug 66861. The only documentation reference that I could find that references the mysql.proc table. Since the physical definition of the mysql.proc table changes across the MySQL 5.0, 5.1, and 5.6 releases, I modified my documentation Bug 66886 to suggest providing online documentation (as a feature request) for the mysql, information_schema, and performance_schema tables across all releases.
The actual definition of the mysql.proc table for MySQL 5.0.91 holds 16 columns not 20 columns as presently expected by the MySQL Workbench migration tool, and is summarized below:
| Field | Type | Null | Key |
|---|---|---|---|
| db | char(64) | NO | PRI |
| name | char(64) | NO | PRI |
| type | enum(‘FUNCTION’,’PROCEDURE’) | NO | PRI |
| specific_name | char(64) | NO | |
| language | enum(‘SQL’) | NO | SQL |
| sql_data_access | enum(‘CONTAINS_SQL’,…) | NO | CONTAINS_SQL |
| is_deterministic | enum(‘YES’,’NO’) | NO | NO |
| security_type | enum(‘INVOKER’,’DEFINER’) | NO | DEFINER |
| param_list | blob | NO | |
| returns | char(64) | NO | |
| body | longblob | NO | |
| definer | char(77) | NO | |
| created | timestamp | NO | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
| modified | timestamp | NO | 0000-00-00 00:00:00 |
| sql_mode | set(‘REAL_AS_FLOAT’,…) | NO | |
| comment | char(64) | NO |
I found out about the issue through a comment on my blog from Marc, who was trying to migrate his production instance. I hope this provides a heads-up to anybody else attempting to migrate a MySQL 5.0 database to a MySQL 5.5. The good news is that the MySQL Workbench team appears to be actively working the issue.
Bulk Transfer Works
As many already know, I’ve been trying to get the MySQL Workbench migration feature working between Microsoft SQL Server 2012 and MySQL 5.5. There are a number of features added to the 5.2.43 point release, and one led me to believe that the Migration tool expects to find the data in a schema of its own, as opposed to the dbo schema. Having made that change in Microsoft SQL Server, it did appear to have a positive impact on the migration and when I corrected a character set mismatch it worked perfectly!
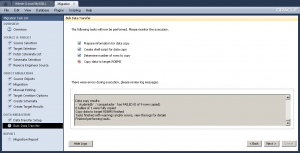 MySQL Workbench successfully migrated the schema and table but failed to migrate the data because of a character set mismatch. I updated Bug 66516 the log file from the character set mismatch before I retyped all 9 test rows to make sure they were in a
MySQL Workbench successfully migrated the schema and table but failed to migrate the data because of a character set mismatch. I updated Bug 66516 the log file from the character set mismatch before I retyped all 9 test rows to make sure they were in a latin1 character set.
I shortened the original log file because the actual log had over 2,000 blanks line :-(. That’s probably something that should be fixed in the code too.
Starting... Prepare information for data copy... Prepare information for data copy done Create shell script for data copy... Table copy script written to C:\Users\McLaughlinM\Desktop\copy_migrated_tables.cmd Create shell script for data copy done Determine number of rows to copy.... Counting number of rows in tables... wbcopytables.exe --count-only --passwords-from-stdin --odbc-source=DSN=SQL Server ODBC;DATABASE=;UID=sa --table [studentdb] [studentdb].[conquistador] 18:29:13 [INF][ copytable]: Opening ODBC connection to 'DSN=SQL Server ODBC;DATABASE=;UID=sa;PWD=XXX' 18:29:14 [INF][ copytable]: ODBC connection to 'DSN=SQL Server ODBC;DATABASE=;UID=sa;PWD=' opened 9 total rows in 1 tables need to be copied: - [studentdb].[studentdb].[conquistador]: 9 Determine number of rows to copy finished Copy data to target RDBMS.... Migrating data... wbcopytables.exe --odbc-source=DSN=SQL Server ODBC;DATABASE=;UID=sa --target=student@mclaughlinsql:3306 --progress --passwords-from-stdin --thread-count=1 --table [studentdb] [studentdb].[conquistador] `studentdb` `conquistador` [conquistador_id], [conquistador], [actual_name], [nationality] `studentdb`.`conquistador`:Copying 4 columns of 9 rows from table [studentdb].[studentdb].[conquistador] ERROR: `studentdb`.`conquistador`:Inserting Batch: Incorrect string value: '\x9Acak' for column 'actual_name' at row 7 `studentdb`.`conquistador`:Finished copying 0 rows in 0m00s 29:15 [INF][ copytable]: Opening ODBC connection to 'DSN=SQL Server ODBC;DATABASE=;UID=sa;PWD=XXX' 29:16 [INF][ copytable]: ODBC connection to 'DSN=SQL Server ODBC;DATABASE=;UID=sa;PWD=' opened 29:16 [INF][ copytable]: Connecting to MySQL server at mclaughlinsql:3306 with user student 29:16 [INF][ copytable]: Connection to MySQL opened Copy helper has finished Data copy results: - `studentdb`.`conquistador` has FAILED (0 of 9 rows copied) 0 tables of 1 were fully copied Copy data to target RDBMS finished Tasks finished with warnings and/or errors, view the logs for details Finished performing tasks. |
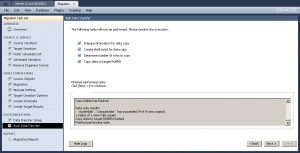 Originally, I thought the failure was due to the extended ASCII characters in the Microsoft SQL Server table. It still failed when I took all of the extended characters out. However, Alfredo suggested it was a character set issue, which is obvious when I looked more closely at the log –
Originally, I thought the failure was due to the extended ASCII characters in the Microsoft SQL Server table. It still failed when I took all of the extended characters out. However, Alfredo suggested it was a character set issue, which is obvious when I looked more closely at the log – '\x9Acak' is clearly an incorrect string. I retyped the INSERT statement for the nine rows and it worked perfectly. Naturally, I’ve updated open Bug 66516 with the log file.
If you’re curious about the Microsoft SQL Server configuration check this post.
Trying to Migrate Data
Getting the MySQL Workbench’s Database Migration has been interesting, and at present incomplete. While I can now successfully connect to the SQL Server 2012 source database and capture a schemata list, migrating the data from SQL Server doesn’t work. Actually, the connection doesn’t work without modifying a Python library in the current MySQL Workbench release.
I blogged about the SQL Server 2012 installation and Windows SQL Server DSN setup last night because the development manager requested them to create a repeatable test case to help resolve Bug 66516. The existing blog post on the MySQL Workbench blog provides step-by-step instructions, so I passed on providing them. This post documents how far I’ve been able to get with the database migration and where I’m stuck.
MySQL Workbench 5.2.42, which is the current release at time of writing, doesn’t retrieve a schemata list from SQL Server 2008 or 2012 unless you edit one of the Python libraries. The instructions for the change are in Bug 66030.
You need to edit the db_mssql_grt.py source file and include the fix from the bug. While the bug lists where to find the file on Mac OS X, you find the db_mssql_grt.py source and compiled files are in the following Windows directory (on a 64-bit OS). Then, you delete the db_mssql_grt.pyc file, which is recompiled the next time you launch MySQL Workbench and there’s a call to a function in the module (or library).
C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Workbench 5.2 CE\modules |
You need to edit line 173, and add the CAST function call before you attempt the migration.
170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 | def getServerVersion(connection): """Returns a GrtVersion instance containing information about the server version.""" version = grt.classes.GrtVersion() ver_string = execute_query(connection, "SELECT CAST(SERVERPROPERTY('ProductVersion') AS VARCHAR)").fetchone()[0] ver_parts = [ int(part) for part in ver_string.split('.') ] + 4*[ 0 ] version.majorNumber, version.minorNumber, version.releaseNumber, version.buildNumber = ver_parts[0:4] return version @ModuleInfo.export(grt.LIST, grt.classes.db_mgmt_Connection) |
After editing the file and saving it, you need to delete the compiled version and start MySQL Workbench to generate the db_mssql_grt.pyc. If MySQL Workbench is running you need to shut it down after deleting the compiled Python file and restart it to generate a new compiled file.
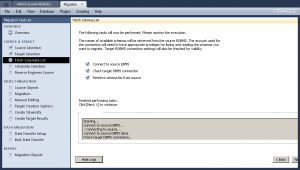 Having fixed the error, you should see verification of your connection to the Microsoft SQL Server. If it fails at this point, you have made an error installing or configuring the Microsoft SQL Server or Windows DSN, or you haven’t made the change to the
Having fixed the error, you should see verification of your connection to the Microsoft SQL Server. If it fails at this point, you have made an error installing or configuring the Microsoft SQL Server or Windows DSN, or you haven’t made the change to the db_mssql_grt.py file.
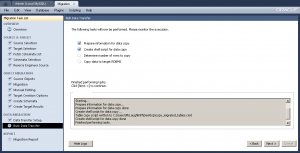 All the other steps work except for copying the data from the Microsoft SQL Server to the MySQL Server. The failure occurs in Bulk Data Transfer segment of the Database Migration wizard. The first error occurs on the Determine number of rows to copy step. The error log didn’t help very much, so I generated the manual script file.
All the other steps work except for copying the data from the Microsoft SQL Server to the MySQL Server. The failure occurs in Bulk Data Transfer segment of the Database Migration wizard. The first error occurs on the Determine number of rows to copy step. The error log didn’t help very much, so I generated the manual script file.
Testing the generated script manually it fails to connect to the SQL Server instance. It appears the command syntax in the generated script is incorrect or one or more of the choices made during the installation of SQL Server or definition of the Windows SQL Server DSN is incorrect.
Here’s the generated script file:
REM Workbench Table Data copy script REM REM Execute this to copy table data from a source RDBMS to MySQL. REM Edit the options below to customize it. You will need to provide passwords, at least. REM REM Source DB: Mssql@SQL Server ODBC (Microsoft SQL Server) REM Target DB: Mysql@mclaughlinsql:3306 REM Source and target DB passwords REM set arg_source_password= REM set arg_target_password= REM Uncomment the following options according to your needs REM Whether target tables should be truncated before copy REM set arg_truncate_target=--truncate-target REM Enable debugging output REM set arg_debug_output=--log-level=debug3 wbcopytables.exe '--odbc-source=DSN=SQL Server ODBC;DATABASE=studentdb;UID=sa' --target=student@mclaughlinsql:3306 --source-password=%arg_source_password% --target-password=%arg_target_password% %arg_truncate_target% %arg_debug_output% --table '[dbo].[ORGANIZATION]' '`studentdb`' '`ORGANIZATION`' |
You need to add the following directory to your %PATH% environment variable to test a call to wbcopytables executable:
SET PATH=%PATH%;C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Workbench 5.2 CE |
The following call to the wbcopytables executable requires you unremark the source and target password statements or set them externally from the script. This call should connect and migrate data from the Microsoft SQL Server database to the MySQL Workbench.
wbcopytables.exe --odbc-source='[DSN=SQL Server ODBC;DATABASE=studentdb;UID=sa]' --target=student@mclaughlinsql:3306 --source-password=cangetin --target-password=student --table '[dbo].[ORGANIZATION]' '`studentdb`' '`ORGANIZATION`' |
However, running it in my environment generates the following error:
wbcopytables.exe: Invalid option '--odbc-source=DRIVER={.\SQLEXPRESS};DSN=SQL |
This was resolved by development in MySQL Workbench 5.2.43; and you can reference Bug 66516 for more information. Although, you need to watch out for character set mismatches, as qualified in this later post.
SQL Server ODBC DSN
 You must install and then configure a Windows Data Source Name (DSN) for SQL Server’s ODBC before you can connect MySQL Workbench to a SQL Server and migrate data. If you fail to set it up, you can’t complete the first step of the MySQL Workbench migration wizard, as shown in the image to the right.
You must install and then configure a Windows Data Source Name (DSN) for SQL Server’s ODBC before you can connect MySQL Workbench to a SQL Server and migrate data. If you fail to set it up, you can’t complete the first step of the MySQL Workbench migration wizard, as shown in the image to the right.
For MySQL readers, this was posted as part of a replicateable test case for Alfredo’s MySQL Workbench team. A Windows OS version of Bug 66516.
You configure a Windows Data Source Name (DSN) for Microsoft SQL Server 2012 after a successful installation (shown in this related blog post), by performing the following steps.
- You need to create a data source in the operating system. You should open the Control Panel and click on the Administrative Tools menu item to begin the installation of a new data source.
- Click the Data Sources (ODBC) menu item to start the process.
- This is where you add a new User Data Source. Click the Add button on the right of the dialog box.
- The Create New Data Source dialog box should show the SQL Server Native Client 11.0 that was installed when you installed the database. Click on it in the selection box, and then click the Finish button.
- The first dialog of the Create a New Data Source to SQL Server process presents the following dialog, which prompts you for a Data Source Name (DSN), a description, a target server. I’ve entered
SQL Server ODBCas the DSN and description, and chosen thelocaldatabase server. The local database server is the server running on thelocalhostmachine. Click the Next button to continue the process.
- The second dialog of the Create a New Data Source to SQL Server process prompts with the following dialog, which lets you opt for integrated Windows authentication or user credential authentication. The easiest set up when you’re running a test case on a single instance selects integrated windows authentication. Click the Next button to continue the process.
- The third dialog of the Create a New Data Source to SQL Server process prompts with the following dialog, which lets you change the default database, attach a database filename, set ANSI rules, the application intent, and multi-subnet failover. The default options are selected in the dialog. Click the Next button to continue the process.
- The fourth dialog of the Create a New Data Source to SQL Server process prompts with the following dialog, which lets you change the language, encryption, character translation, regional settings, and long query execution. The default options are selected in the dialog. Click the Next button to continue the process.
- The next dialog displays the settings for the ODBC SQL Server Setup. You should always confirm that things work by clicking the Test Data Source button.
- The next dialog displays success when you made working choices and failure when something is misconfigured. Click the OK button to continue the process.
- The OK button concludes the Create a New Data Source to SQL Server process, and returns you to the list of valid ODBC Data Sources. Click the OK button to conclude the process.
Hopefully, this helps those learning how to set up Microsoft SQL Server to work with MySQL Workbench’s migration tool.
SQL Server 2012 Install
While testing the MySQL Workbench migration tool, I needed to install Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Express (the free one up to 8 GB of data). These are my notes on installing the product, and you can click on any image to see the full size resolution and details. (The approach using small snapshots on the left was suggested from somebody who uses the blog and felt these would be easier than large but slightly reduced image files.)
For MySQL readers, this was posted as part of a replicateable test case for Alfredo’s MySQL Workbench team. A Windows OS version of Bug 66516.
Installation Steps
For reference, I’ve already installed the pre-requisites of Windows PowerShell 2.0 and Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5. You’ll see that when you get to step #6.
- The first screen gives you the appearance of a wizard format with the list of tasks on the left and the details on the right. Click the New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation to install a copy of SQL Server 2012 Express with a sample database.
- The Microsoft SQL Server 2012 installation firsts checks the rules for the installation. This screen lasts for about 20-30 seconds before you get the licensing dialog box.
- There’s not much choice with this dialog but you must confirm you’ve read the license terms. If you want to keep Microsoft apprise about your platform leave the button check box enabled. It’s unchecked in my installation. 😉 After you address the check boxes, click the Next button to proceed with the installation.
- This dialog should quickly scan for any product updates, which are minimal if you’ve downloaded the file from Microsoft’s download site. Mine was up to date and skipped downloading and extracting tasks. It does take a small amount of time to install the setup files, and you’re parked on this screen while that happens. Click the Install button to continue with the installation.
- A second rule check runs to make sure anything from the software update is completed. Click the Next button to proceed.
- This page presents the Features that you want installed. It installs everything but a local database by default. If you’re building a stand alone instance you should check the LocalDB check box.
- After you check the LocalDB check box, the Features display shows that all features are selected. Click the Next button to continue.
- This dialog lets you choose whether you install a default or named instance. You also provide the instance unique identifier (ID), and root directory. After making sure that’s completed, click the Next button ton continue.
- This section lets you name and set Microsoft Service names for the database engine, reporting services, full-text filter daemon launche, and browser. My settings enable the database engine and reporting services as automatic, which means they start when the operating systems wakes. Click the Next button to continue with the install.
- This dialog lets you set the authentication mode of Microsoft SQL Server. By default, Microsoft SQL Server uses Windows authentication mode. I recommend you opt for Mixed Mode by clicking the radio button and entering a password twice.
- After entering the SQL Server Administrators’ password in the Server Configuration tab view, click the Data Directories tab to check the data directories.
- On the Data Directories tab verify the installation directories. The 64-bit directory default root directory is:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\
- After inspecting the Data Directories, click the User Instances tab and enable the Users are allowed to run a separate instance of the Database Engine check box.
- Clicking the FILESTREAM tab, you click the Enable FILESTREAM for Transact-SQL access check box. This enables FILESTREAM for Transact-SQL. Click the Next button to proceed.
- This dialog of the wizard lets you configure the reporting services. Click the Install and configure radio button and then the Next button to proceed.
- This dialog lets you set the error reporting. Click the Send Windows and SQL Server Error Reports to Microsoft if you want to advise them of errors. After making your notification decision, click the Next button to proceed.
- The installation program takes several minutes to run, and this is a copy of the progress dialog. After the installation completes, the program automatically advances to the completion dialog.
- When everything succeeds you’ll see a dialog like the one on the left. Click the Close button to complete the installation.
- Click on the Start button, choose All Programs, choose Microsoft SQL Server 2012, and choose the SQL Server Management Studio that launches the SQL Server 2012 login screen.
- This launches the Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio as an Administrator. This base image only displays the Object Explorer view.
- Click the View Query button and it displays the SQL Query and Properties view.
Post Installation Configuration Step
After installing the Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Express Edition, I discovered that the pipe definition was incorrect and had to fix it, which was exactly like the fix for Microsoft SQL Server 2008 that I blogged about 3 years ago here.
If you want to set up databases that hold tables of their own as opposed to deploying everything in the dbo schema, you should read this post on configuring SQL Server 2012. It shows you how to create a database, user, and schema.
You’ll need to configure a Windows Data Name Source (DSN) for SQL Server, when you’re planning to connect Microsoft Excel to SQL Server or migrate data from SQL Server using MySQL Workbench.
Hostname Change Error
While staging to rebuild the Oracle DB Console (Oracle Enterprise Manager – OEM), I needed to check something in my MySQL instance and ran into the following error after changing the machine’s hostname for that OEM test. The message basically says that MySQL Workbench can’t resolve the connection.
The dialog error provides an excellent note, which lists the actual error as the first thing to check. The dialog follows:
This lists the text of the error dialog:
Your connection attempt failed for user '<user_name>' from your host to server at <server_name>:3306: Unknown MySQL server host '<server_name>' (0) Please: 1 Check that mysql is running on server <server_name> 2 Check that mysql is running on port 3306 (note: 3306 is the default, but this can be changed) 3 Check the student has rights to connect to <server_name> from your address (mysql rights define what clients can connect to the server and from which machines) 4 Make sure you are both providing a password if needed and using the correct password for <server_name> connecting from the host address you're connecting from |
Navigate to Database -> Manage Connections… in the menu. This opens a dialog where you can manage the details of a connection.
It opens the following dialog page:
The Test button lets you retest whether the connection works. The error message raised by the test, noted below, is not nearly as detailed as the previous error message.
Inspecting the Parameters tab below, you see the hostname value McLaughlinMySQL. The actual hostname is mclaughlinsql. You need to replace the displayed value with the correct value.
After making the change, click the Test Connection button. A correct change prompts you for the user’s password and when successfully entered yields the following dialog.
Hope this helps a few folks resolve the problem when the machine hostname changes.























































