MySQL and Java Tutorial
This demonstrates how to create an Java infrastructure for reading and writing large text files to a MySQL database. The example provides:
- A
FileIO.jarlibrary that lets you enter MySQL connection parameters through aJOptionPane, and a customizedJFileChooserto filter and read source files from the file system. - A
mysql-connector-java-3.1.14-bin.jarfile, which is MySQL’s library for JDBC communication with the MySQL Databases.
The steps to compiling and testing this code are qualified below:
- Download and install the Java Software Development Kit (JSDK) for Java 6.
- Create a
C:\JavaTestfolder on Windows, or a/JavaTestdirectory from some mount point of your choice. - Download and position the
mysql-connector-java-3.1.14-bin.jarandFileIO.jarfiles in theJavaTestdirectory. - Create a batch file to source your environment path (%PATH% on Windows and $PATH on Linux or Mac OS X) and the two Java Archive (JAR) files. A sample batch file is noted below:
set PATH=C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_07\bin;%PATH% set CLASSPATH=C:\JavaDev\Java6\mysql-connector-java-3.1.14-bin.jar;C:\JavaDev\Java6\FileIO.jar;. |
You can run this file by simply typing the files first name. On Linux or Mac OS X, you first need to grant it privileges with the chmod command as 755.
- Copy the
WriteReadCLOBMysql.javacode from the bottom of this posting and also put it into theJavaTestdirectory. - Compile the
WriteReadCLOBMysql.javasource code with thejavacutility, as shown below:
javac WriteReadCLOBMysql.java |
After you compile it, you should run it as follows:
java WriteReadCLOBMysql |
- Before running the code, you’ll need to seed (
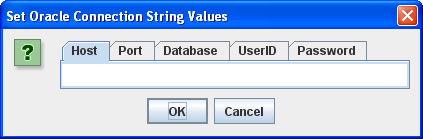
INSERT) a row that meets the desired hard coded criteria. It requires anITEM_TITLEvalue of'The Lord of the Rings - Fellowship of the Ring'and anITEM_SUBTITLEof'Widescreen Edition'in theITEMtable. - When it runs, you’ll see the following tabbed
JOptionPane.
You need to enter the following values before clicking the OK button:
- Host: The
localhostkey word, orhostnameof your physical machine running the database. - Port: The
portthat the MySQL Listener is running on (the default value is3306). - Database: The Oracle TNS Alias, which is
sampledbfor the full database sample database. - UserID: The
username with permissions to the database entered that can access anITEMtable. - Password: The
passwordfor the user’s account.
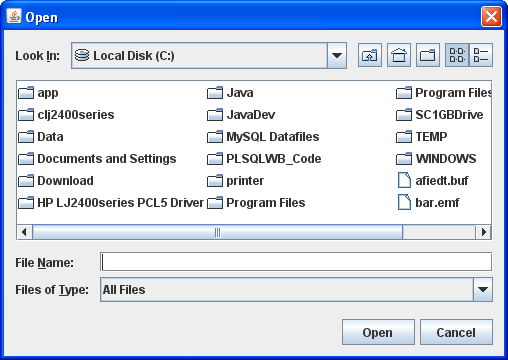
In the JFileChooser, select a file to upload to the database.
You should see what you uploaded displayed in a JFrame.
Java Source Code Program ↓
The drop down unfolds the WriteReadCLOB.java source code.
The following program has dependencies on the FileIO.jar file. You need to download it and put it in your $CLASSPATH for Linux or Mac OS X or %CLASSPATH% for Windows.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 | // -------------------------------------------------------------------- // WriteReadCLOBMysql.java // by Michael McLaughlin // // This code demonstrates reading an image file and displaying // the image in a JLabel in a JFrame. // // The UPDATE and SELECT statements have dependencies on the // create_store.sql script. // -------------------------------------------------------------------- // Java Application class imports. import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.io.Reader; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JOptionPane; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; // Generic JDBC imports. import java.sql.*; // Mysql JDBC import. import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.*; import java.io.File; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; // Include book libraries (available at publisher website). import plsql.jdbc.DataConnectionPane; import plsql.fileio.FileIO; // -------------------------------------------------------------------/ public class WriteReadCLOBMysql extends JFrame { // Define database connections. private String host; private String port; private String dbname; private String userid; private String passwd; // Define data connection pane. private DataConnectionPane message = new DataConnectionPane(); // Construct the class. public WriteReadCLOBMysql (String s) { super(s); // Get database connection values or exit. if (JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(this,message ,"Set Oracle Connection String Values" ,JOptionPane.OK_CANCEL_OPTION) == 0) { // Set class connection variables. host = message.getHost(); port = message.getPort(); dbname = message.getDatabase(); userid = message.getUserID(); passwd = message.getPassword(); // Print connection to console (debugging tool). message.getConnection(); // Create a JPanel for data display. ManageCLOB panel = new ManageCLOB(); // Configure the JPanel. panel.setOpaque(true); setContentPane(panel); // Configure the JFrame. setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); setLocation(100,100); pack(); setVisible(true); } else System.exit(1); } // -------------------------------------------------------------------/ private class ManageCLOB extends JPanel { // Define display variables. private String clobText; private JScrollPane scrollPane; private JTextArea textArea; // -----------------------------------------------------------------/ public ManageCLOB () { // Set layout manager. super(new GridLayout(1,0)); // Assign file read to String. clobText = FileIO.openFile(FileIO.findFile(this)); // Insert record before querying it. if (clobText.length() > 0) { if (insertClob(host,port,dbname,userid,passwd,clobText)) clobText = getQuery(host,port,dbname,userid,passwd); else clobText = null; } else System.exit(2); // Construct text area and format it. textArea = new JTextArea(clobText); textArea.setEditable(false); textArea.setFont(new Font(Font.SANS_SERIF,Font.PLAIN,14)); textArea.setLineWrap(true); textArea.setRows(10); textArea.setSize(400,100); textArea.setWrapStyleWord(true); // Put the image in container, and add label to panel. scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea); add(scrollPane); } // ---------------------------------------------------------------/ private Boolean insertClob(String host,String port,String dbname ,String user,String pswd,String fileString) { try { // Define connection. DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver()); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://" + host + ":" + port + "/" + dbname, user, pswd); // Create statement. PreparedStatement prest; String sql = "UPDATE item SET item_desc = ? WHERE item_title = 'The Lord of the Rings - Fellowship of the Ring' AND item_subtitle = 'Widescreen Edition'"; prest = conn.prepareStatement(sql); prest.setString(1,fileString); // Execute query. if (prest.execute()) conn.commit(); // Close resources. prest.close(); conn.close(); // Return CLOB as a String data type. return true; } // End of connection try-block. catch (SQLException e) { if (e.getSQLState() == null) { System.out.println( new SQLException("mysql Client Net8 Connection Error.", "mysql-" + e.getErrorCode() + ": Incorrect Net8 thin client arguments:\n\n" + " database name [" + dbname + "]\n", e.getErrorCode()).getSQLState()); // Return an empty String on error. return false; } else { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // Return an empty String on error. return false; }}} // -----------------------------------------------------------------/ private String getQuery(String host,String port,String dbname ,String user,String pswd) { // Define method variables. char[] buffer; int count = 0; int length = 0; String data = null; String[] type; StringBuffer sb; try { // Define connection. DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver()); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://" + host + ":" + port + "/" + dbname, user, pswd); // Define metadata object. DatabaseMetaData dmd = conn.getMetaData(); // Create statement. Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); // Execute query. ResultSet rset = stmt.executeQuery( "SELECT item_desc " + "FROM item " + "WHERE item_title = " + "'The Lord of the Rings - Fellowship of the Ring'"+ "AND item_subtitle = 'Widescreen Edition'"); // Get the query metadata, size array and assign column values. ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rset.getMetaData(); type = new String[rsmd.getColumnCount()]; for (int col = 0;col < rsmd.getColumnCount();col++) type[col] = rsmd.getColumnTypeName(col + 1); // Read rows and only CLOB data type columns. while (rset.next()) { for (int col = 0;col < rsmd.getColumnCount();col++) { if (type[col] == "CLOB") { // Assign result set to CLOB variable. Clob clob = rset.getClob(col + 1); // Check that it is not null and read the character stream. if (clob != null) { Reader is = clob.getCharacterStream(); // Initialize local variables. sb = new StringBuffer(); length = (int) clob.length(); // Check CLOB is not empty. if (length > 0) { // Initialize control structures to read stream. buffer = new char[length]; count = 0; // Read stream and append to StringBuffer. try { while ((count = is.read(buffer)) != -1) sb.append(buffer); // Assign StringBuffer to String. data = new String(sb); } catch (Exception e) {} } else data = (String) null; } else data = (String) null; } else { data = (String) rset.getObject(col + 1); }}} // Close resources. rset.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close(); // Return CLOB as a String data type. return data; } catch (SQLException e) { if (e.getSQLState() == null) { System.out.println( new SQLException("mysql Client Net8 Connection Error.", "mysql-" + e.getErrorCode() + ": Incorrect Net8 thin client arguments:\n\n" + " database name [" + dbname + "]\n", e.getErrorCode()).getSQLState()); // Return an empty String on error. return data; } else { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); return data; }} finally { if (data == null) System.exit(1); }}} // -----------------------------------------------------------------/ public static void main(String[] args) { // Define window. WriteReadCLOBMysql frame = new WriteReadCLOBMysql("Write & Read CLOB Text"); }} |