PostgreSQL on Ubuntu
Fresh install of Ubuntu on my MacBook Pro i7 because Apple said the OS X was no longer upgradable. Time to install and configure MySQL Server. These are the steps to install MySQL on the Ubuntu Desktop.
Installation
- Update the Ubuntu OS by checking for, inspecting, and upgrading any available updates with the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt list sudo apt upgrade
- Check for available PostgreSQL Server packages with this command:
sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib
- Connect as the postgres user with the following command:
sudo -i -u postgres
Then, you can connect to PostgreSQL with this command:
psql
It displays your connection as the root user. Then, you can use the show data_directory; command to find the data directory:
psql (14.8 (Ubuntu 14.8-0ubuntu0.22.04.1)) Type "help" for help. postgres=# show data_directory; data_directory ----------------------------- /var/lib/postgresql/14/main (1 row)\q
- At this point, you have some operating system (OS) stuff to setup before configuring a PostgreSQL sandboxed videodb database and student user.
- Assume the role of the root superuser on Ubuntu with this command:
sudo sh
As the root user, navigate to /etc/postgresql/14/main directory and edit the pg_hba.conf file. Add lines for the postgres and student users, as shown below:
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD # "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only local all all peer local all postgres peer local all student peer # IPv4 local connections: host all all 127.0.0.1/32 scram-sha-256 # IPv6 local connections: host all all ::1/128 scram-sha-256 # Allow replication connections from localhost, by a user with the # replication privilege. local replication all scram-sha-256 host replication all 127.0.0.1/32 scram-sha-256 host replication all ::1/128 scram-sha-256
- As the root user, navigate to the /var/lib/postgresql/14 directory, and make the video_db directory with the following command:
mkdir video_db - Change the video_db ownership and group to the respective postgres user and primary group:
chown postgres:postgres video_db - Change the video_db permissions to read, write, and execute for only the owner with this syntax as the postgres user:
chmod 700 video_db
- Assume the role of the root superuser on Ubuntu with this command:
- Connect to the postgres account and perform the following commands:
- Connect as the postgres user with the following command:
sudo -i -u postgres
- After connecting as the postgres superuser, you can create a video_db tablespace with the following syntax:
CREATE TABLESPACE video_db OWNER postgres LOCATION '/var/lib/postgresql/14/video_db';
This will return the following:
CREATE TABLESPACE
You can query whether you successfully create the video_db tablespace with the following:
SELECT * FROM pg_tablespace;
It should return the following:
oid | spcname | spcowner | spcacl | spcoptions -------+------------+----------+--------+------------ 1663 | pg_default | 10 | | 1664 | pg_global | 10 | | 16389 | video_db | 10 | | (3 rows)
-
You need to know the PostgreSQL default collation before you create a new database. You can write the following query to determine the default correlation:
postgres=# SELECT datname, datcollate FROM pg_database WHERE datname = 'postgres';
It should return something like this:
datname | datcollate ----------+------------- postgres | en_US.UTF-8 (1 row)
The datcollate value of the postgres database needs to the same value for the LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE parameters when you create a database. You can create a videodb database with the following syntax provided you’ve made appropriate substitutions for the LC_COLLATE and LC_CTYPE values below:
CREATE DATABASE videodb WITH OWNER = postgres ENCODING = 'UTF8' TABLESPACE = video_db LC_COLLATE = 'en_US.UTF-8' LC_CTYPE = 'en_US.UTF-8' CONNECTION LIMIT = -1;
You can verify the creation of the videodb with the following command:
postgres# \l
It should show you a display like the following:
List of databases Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | ICU Locale | Locale Provider | Access privileges -----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------- postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | =c/postgres + | | | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | =c/postgres + | | | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres videodb | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | (4 rows)Then, you can assign comment to the database with the following syntax:
COMMENT ON DATABASE videodb IS 'Video Store Database';
- Create a Role, Grant, and User:
In this section you create a dba role, grant privileges on a videodb database to a role, and create a user with the role that you created previously with the following three statements. There are three steps in this sections.
- The first step creates a dba role:
CREATE ROLE dba WITH SUPERUSER;
- The second step grants all privileges on the videodb database to both the postgres superuser and the dba role:
GRANT TEMPORARY, CONNECT ON DATABASE videodb TO PUBLIC; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE videodb TO postgres; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE videodb TO dba;
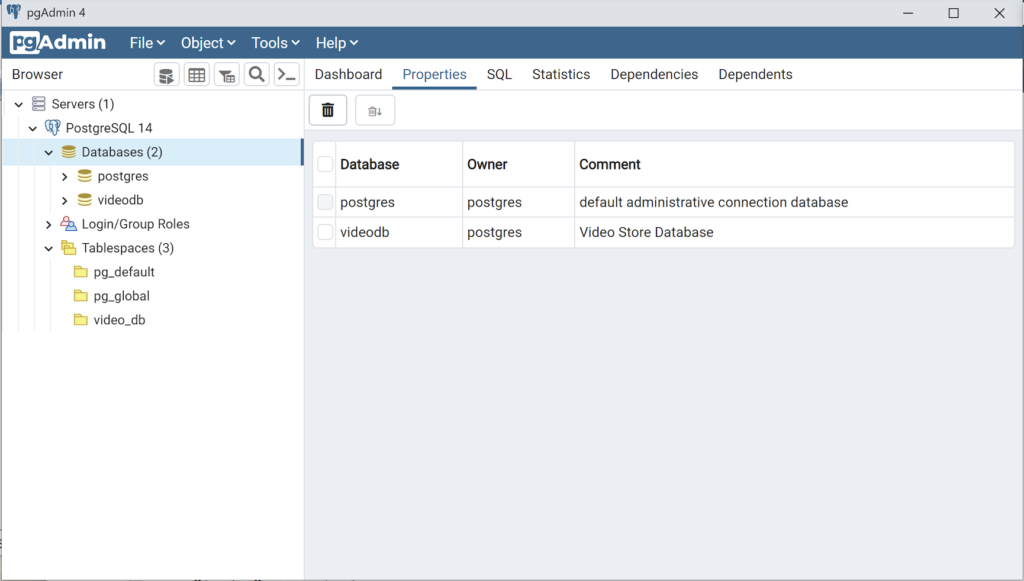
Any work in pgAdmin4 requires a grant on the videodb database to the postgres superuser. The grant enables visibility of the videodb database in the pgAdmin4 console as shown in the following image.
- The third step creates a student user:
CREATE USER student WITH ROLE dba ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'student';
- The fourth step changes the ownership of the videodb database to the student user:
ALTER DATABASE videodb OWNER TO student;
You can verify the change of ownership for the videodb from the postgres user to student user with the following command:
postgres# \l
It should show you a display like the following:
List of databases Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | ICU Locale | Locale Provider | Access privileges -----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------+----------------------- postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | =c/postgres + | | | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | =c/postgres + | | | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres videodb | student | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | =Tc/student + | | | | | | | student=CTc/student + | | | | | | | dba=CTc/student (4 rows)
Installation of PGAdmin4
These are the steps to install pgAdmin4. They include some preconditions.
You need to install the curl utility as a precondition.
sudo apt install curl
Install the public key for the repository (if not done previously):
curl -fsSL https://www.pgadmin.org/static/packages_pgadmin_org.pub | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/pgadmin.gpg
- The first step creates a dba role:
- Connect as the postgres user with the following command: