Archive for the ‘HTML’ Category
Popular Programming Languages
First of all, Happy New Year!
IEEE Spectrum published a ranking of the most popular programming languages. Computational journalist Nick Diakopoulos wrote the article. While it may surprise some, I wasn’t surprised to find SQL in the top ten.
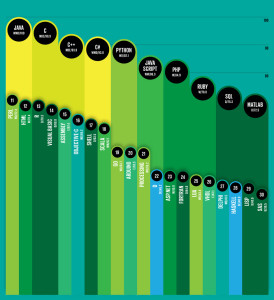 Nick weighted and combined 12 metrics from 10 sources (including IEEE Xplore, Google, and GitHub) to rank the most popular programming languages.
Nick weighted and combined 12 metrics from 10 sources (including IEEE Xplore, Google, and GitHub) to rank the most popular programming languages.
- Compiled programming languages (Java [#1], C [#2], C++ [#3], C# [#4], Objective-C [#16])
- Interpreted programming languages (Python [#5], JavaScript [#6], PHP [#7], Ruby [#8], Perl [#11], HTML [#12])
- Data languages (SQL [#9], MATLAB [#10], R [#13])
I couldn’t resist including Objective-C because it shows how the iPhone, iPad, and Mac OS impact our daily lives. At the same time, Assembly [#15] is actually more popular than Objective-C. Shell [#17] follows Objective-C. While the Visual Basic [#14] programming language still remains very popular.
There are many “why” questions raised by this list of popular programming languages. The “why” from my perspective deals with what are the market drivers for their popularity. The money drivers I see are as follows:
- Business software: Java, C++, C#, and AIDE – Android IDE (works with Java and C++ source code)
- OS X and iOS Development: Objective-C
- Development Tools: Java, C, C++, and Python
- System Admin/Utilities Tools: C, Perl, and Shell
- Web Development: Python, PHP, Ruby, and Perl
- Data Analysis: SQL, MATLAB, and R
Business Intelligence (BI) software manages most high-level data analysis tools and they’ll continue to get better over time. However, if SQL has shown us anything over 30 years it’s that ultimately we revert to it to solve problems. The conclusion from the reality of BI probably means the programming languages that develop those tools will continue to rise and so will the underlying data languages.
It’s also interesting to note that nine out of ten of the popular programming languages work with databases, like Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server. While JavaScript doesn’t access the database typically, it’s JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is supported in all the databases.
Common Lookup Tables 2
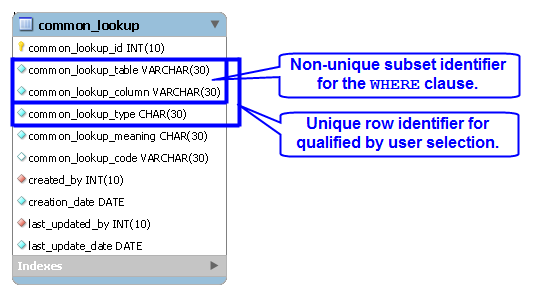
Last October I posted an example and description of a common_lookup table. It was intended to show how common_lookup tables support drop down selections in web forms. However, it wasn’t adequate to show how they work with existing data, and the function only supported fresh queries.
This post goes to the next level, and shows how to use foreign keys to preselect values for display in web forms. It also rewrites the prior function so that it supports querying existing data and inserting new data.
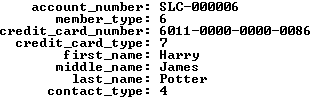
Let’s start with data stored in join between two tables – the member and contact tables. The internal lookup uses the customers name from the contact table to find the membership account information in the member table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | SELECT m.account_number , m.member_type -- A fk to common_lookup table. , m.credit_card_number , m.credit_card_type -- A fk to common_lookup table. , c.first_name , c.middle_name , c.last_name , c.contact_type -- A fk to common_lookup table. FROM member m INNER JOIN contact c ON m.member_id = c.member_id WHERE c.first_name = 'Harry' AND c.middle_name = 'James' AND c.last_name = 'Potter'\G |
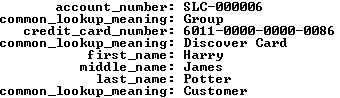
It returns the results on the left, while a set of joins against the common_lookup table returns the results on the right (both use the \G in SQL Monitor to display the data vertically).
The member_type, credit_card_type, and contact_type columns in the data set on the left hold foreign key values. They’re copies of values found in the primary key column of the common_lookup table. You have the option of using these values to connect the data through a join or through function calls. A join requires three copies of the common_lookup table and yields the data displayed on the right above. The query to get the meaningful business information from the common_lookup table is:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | SELECT m.account_number , cl1.common_lookup_meaning , m.credit_card_number , cl2.common_lookup_meaning , c.first_name , c.middle_name , c.last_name , cl3.common_lookup_meaning FROM member m INNER JOIN contact c ON m.member_id = c.member_id INNER JOIN common_lookup cl1 ON cl1.common_lookup_id = m.member_type INNER JOIN common_lookup cl2 ON cl2.common_lookup_id = m.credit_card_type INNER JOIN common_lookup cl3 ON cl3.common_lookup_id = c.contact_type WHERE c.first_name = 'Harry' AND c.middle_name = 'James' AND c.last_name = 'Potter'\G |
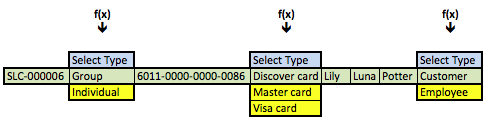
The data returned from any query is symmetrical, which means all columns return the same number of rows. The results of the preceding query are the business results. Although, they’re not what you’d want to display in a web form that presents the ability to change values, like the member, credit card, or contact types. You need to get that information by using the foreign key as a parameter to a function call, and in this case three function calls. One for each of the foreign keys from the original query results. The result is an asymmetric collection of data would look like the following conceptually with Lily Luna Potter as the customer (note the green row is the symmetrical return set from the preceding query):
The f(x) represents a generic function call where the x substitutes for the foreign key value as a lookup key to the primary key value of the common_lookup table. The function in this case is a query that returns a two column list. One column holds the primary key value of the (common_lookup_id) and the other holds the customer facing description (from the common_lookup_meaning column).
These steps describe the process:
- Use the natural key (the user name) to find the data in the
contacttable. - Use the
member_idforeign key column in thecontacttable to link to the same name column primary key in themembertable by joining the two rows. - Use the foreign keys in the new row (combining columns from the
contactandmembertables) as call parameters to a PHP function that returns all possible foreign key values and their business descriptions in a web form.
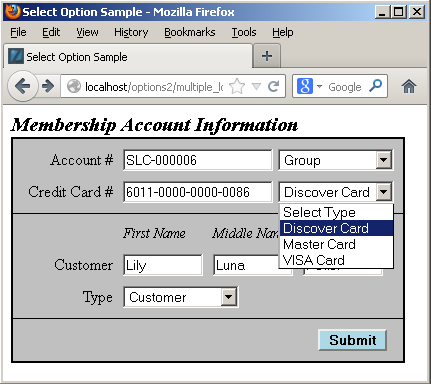
The vertical choices displayed above map to OPTION tag elements of an HTML SELECT tag. The blue highlighted value contains an instruction, Select Type, in the display of an HTML OPTION tag, and it holds a null as the value of the VALUE attribute for the OPTION tag. The other displayed rows are the possible values. The green highlighted value is the currently selected value and the yellow highlighted values are alternate possibilities for an end-user to select. The logic for that process is in the PHP get_common_lookup function below.
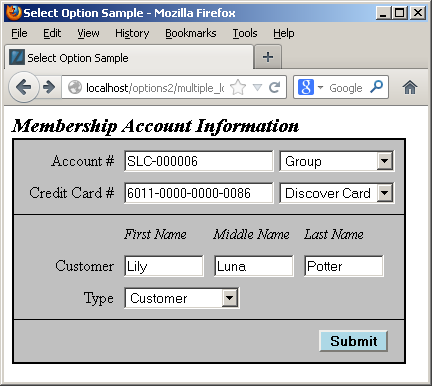
Having discussed the structure of the data and problem, we’ll present the result in a dynamically constructed web form below. The display form shows a member account with customer information.
You should note that the primary and foreign keys aren’t displayed because they’re irrelevant to the business process. Primary and foreign keys only serve to support relationships when we use surrogate keys as the primary key of a table. Only the meaningful information from the common_lookup table are displayed in the preceding form. Behind the web form, the primary and foreign key values are critical to maintaining anomaly free table data.
Each of the drop downs contains the full selection of possibilities from the common_lookup table, and an end-user could choose a new value by clicking on any of the drop down fields. For example, the following displays the selection of a type of credit card:
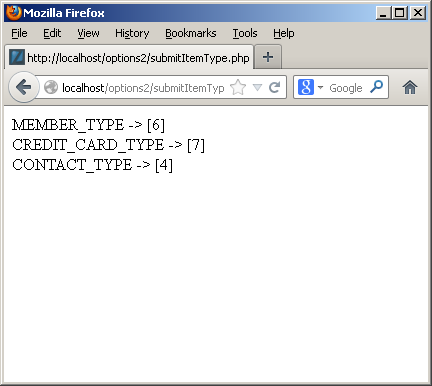
The user can click on the drop down, and then navigate from the selection to a new selection. Assuming we don’t change anything, submitting the form should transmit the foreign key column values. The following shows that’s exactly what it does:
As you can see from the screen shot it works easily. Below is the PHP code for a MySQL credentials file and the get_lookup function. The function lets you find an existing value or returns a set of unique values for you to choose from.
You should rename the following credentials.php file as MySQLCredentials.inc for it to work in the file below it.
Assuming you’ve implemented the credentials.php file as the MySQLCredentials.inc file, you can now implement the following file. The get_common_lookup function returns a <SELECT> tag with a list embedded of <OPTION> tags with values; one <OPTION> tag is selected when the foreign key matches a valid primary key value in the common_lookup table; and no <OPTION> tag is selected when the foreign key doesn’t match a a valid primary key value in the common_lookup table. The last possibility means a user must choose a new valid value for the foreign key column when the foreign key column is constrained as a mandatory or not null column.
The code for the web form is a bit more complex, as shown below. It contains three separate calls to the modified get_common_lookup function (on lines 104, 111, and 126). Each call to the get_common_lookup function selects the list of possible values and highlights the value associated with the foreign key value.
Here’s the web form code. You should note that it only returns a single row of data from the query by using a natural key from the contact table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 | <html>
<header>
<title>Select Option Sample</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* Class tag element styles. */
.box {border:1px solid;padding:0px;width:392px;background-color:silver;}
.bottomBox {border-left:1px solid;border-right:1px solid;border-bottom:1px solid;padding:5px;width:380px;background-color:silver;}
.middleBox {border:1px solid;padding:5px;width:380px;background-color:silver;}
.topBox {border-left:1px solid;border-right:1px solid;border-top:1px solid;padding:5px;width:380px;background-color:silver;}
.button {margin:5px;background-color:lightblue;font-weight:bold;align:right;}
.clear {clear:left;}
.dropDown {min-width:50px;display:block;float:left;text-align:left;color:black;}
.formDownLabel {width:90px;display:block;float:left;margin:5px;text-align:right;vertical-align:bottom;color:black;}
.formAcrossLabel {width:80px;display:block;float:left;padding-bottom:0px;margin:5px 5px 0px;text-align:left;vertical-align:bottom;font-style:italic;font-size:90%;color:black;}
.formInput {min-width:150px;margin:5px;text-align:left;}
.formShortInput {width:80px;margin:5px;text-align:left;}
.title1 {margin-left:0px;font-weight:bold;font-style:italic;font-size:125%;color:black;}
.title2 {margin-left:5px;font-weight:bold;font-style:italic;font-size:105%;color:black;}
</style>
</header>
<body>
<?php
// Include libraries.
include_once("MySQLCredentials.inc");
include_once("library.inc");
// Define a HTML page string.
$out = '';
// Declare input variables.
$first_name = (isset($_GET['first_name'])) ? $_GET['first_name'] : $first_name = "Harry";
$middle_name = (isset($_GET['middle_name'])) ? $_GET['middle_name'] : $middle_name = "James";
$last_name = (isset($_GET['last_name'])) ? $_GET['last_name'] : $last_name = "Potter";
// Declare output variables.
$member_account_number = null;
$credit_card_number = null;
// Declare lookup input and output (initialized as nulls to suppress warnings) variables.
$member_table = 'member';
$member_type = 'member_type';
$member_type_id = null;
$credit_card_type = 'credit_card_type';
$credit_card_type_id = null;
$contact_table = 'contact';
$contact_type = 'contact_type';
$contact_type_id = null;
// Assign credentials to connection.
$mysqli = new mysqli(HOSTNAME, USERNAME, PASSWORD, DATABASE);
// Check for connection error and print message.
if ($mysqli->connect_errno) {
print $mysqli->connect_error."<br />";
print "Connection not established ...<br />";
}
else {
// Initial statement.
$stmt = $mysqli->stmt_init();
// Declare a static query.
$sql = "SELECT m.account_number\n"
. ", m.member_type\n"
. ", m.credit_card_number\n"
. ", m.credit_card_type\n"
. ", c.first_name\n"
. ", c.middle_name\n"
. ", c.last_name\n"
. ", c.contact_type\n"
. "FROM member m INNER JOIN contact c\n"
. "ON m.member_id = c.member_id\n"
. "WHERE c.first_name = ?\n"
. "AND c.middle_name = ?\n"
. "AND c.last_name = ?\n";
// Prepare statement.
if ($stmt->prepare($sql)) {
$stmt->bind_param("sss",$first_name,$middle_name,$last_name); }
// Attempt query and exit with failure before processing.
if (!$stmt->execute()) {
// Print failure to resolve query message.
print $mysqli->error."<br />";
print "Failed to resolve query ...<br />";
}
else {
// This query only returns one row, and an empty block follows the while logic.
$stmt->bind_result($member_account_number, $member_type_id, $credit_card_number, $credit_card_type_id, $first_name, $middle_name, $last_name, $contact_type_id);
while ($stmt->fetch()) {}
}
}
// Print the query form.
$out .= '<form method="post" name="myForm" action="submitItemType.php">';
$out .= '<label class="title1">Membership Account Information</label><br />';
$out .= '<div class="box">';
$out .= '<div class="topBox">';
$out .= '<label class="formDownLabel">Account #</label><input class="formInput" type="text" value="'.$member_account_number.'" />';
$out .= '<select name="member_type" size="1" onChange="change(this.form.member_type)">';
// Get dynamic membership type lookup string fragment.
$out .= get_common_lookup($member_table, $member_type, $member_type_id);
$out .= '</select><br />';
$out .= '<label class="formDownLabel">Credit Card #</label><input class="formInput" type="text" value="'.$credit_card_number.'" />';
$out .= '<select name="credit_card_type" size="1" onChange="change(this.form.credit_card_type)">';
// Get dynamic credit card type lookup string fragment.
$out .= get_common_lookup($member_table, $credit_card_type, $credit_card_type_id);
// Print the closing HTML table tag.
$out .= '</select><br />';
$out .= '</div>';
$out .= '<div class="middleBox">';
$out .= '<label class="formDownLabel"> </label>';
$out .= '<label class="formAcrossLabel">First Name</label><label class="formAcrossLabel">Middle Name</label><label class="formAcrossLabel">Last Name</label><br class="clear" />';
$out .= '<label class="formDownLabel">Customer</label><input class="formShortInput" type="text" value="'.$first_name.'" />';
$out .= '<input class="formShortInput" type="text" value="'.$middle_name.'" />';
$out .= '<input class="formShortInput" type="text" value="'.$last_name.'" /><br />';
$out .= '<label class="formDownLabel">Type</label>';
$out .= '<select style="margin:5px" name="contact_type" size="1" onChange="change(this.form.contact_type)">';
// Get dynamic membership type lookup string fragment.
$out .= get_common_lookup($contact_table, $contact_type, $contact_type_id);
$out .= '</select><br />';
$out .= '</div>';
$out .= '<div class="bottomBox">';
$out .= '<input class="button" style="margin-left:300px" name="submit" type="submit" value="Submit">';
$out .= '</div>';
$out .= '</form>';
$out .= '</body>';
$out .= '</html>';
print $out;
?>
</body>
</html> |
The submit button simply runs another web page that prints the actual values for the drop down selections. Here’s the code to print that:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | <html> <head> </head> <body> <?php // Print the surrogate key values for the common_lookup_id column. print "MEMBER_TYPE -> [".$_POST['member_type']."]<br />"; print "CREDIT_CARD_TYPE -> [".$_POST['credit_card_type']."]<br />"; print "CONTACT_TYPE -> [".$_POST['contact_type']."]<br />"; ?> </body> </html> |
I hope this helps those who are interested in sorting how to implement a common_lookup table.
Common Lookup Tables 1
My students wanted an example of how to use a lookup table in the database. I thought it would be a great idea to create a simple example like this one. You can read further on my second post about common lookup tables.
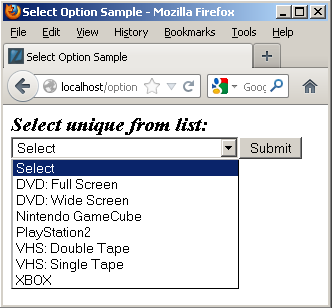
A lookup table is a generalization that holds lists of values that support end-user selections. The following example uses a combination of the common_lookup_table and common_lookup_column columns to identify sets of value for drop down lists. The end-user selects a value from the list to identify a unique row, and returns a common_lookup_id surrogate key value.
The sample code uses the table defined in the previous illustration. It uses a simple HTML drop down list, a PHP library.inc file, and an HTML display form. Below is the drop down selection set for a table and column value.
The drop down list code uses an insecure and trivial GET method to keep the example simple, as shown below:
<html>
<header>
<title>Select Option Sample</title>
<style type="text/css">
/* Class tag element styles. */
.label {min-width:200px;text-align:left;}
.title {font-weight:bold;font-style:italic;font-size:125%;}
</style>
</header>
<body>
<?php
// Include libraries.
include_once("library.inc");
// Declare input variables.
$table_name = (isset($_GET['table_name'])) ? $_GET['table_name'] : $table_name = "item";
$column_name = (isset($_GET['column_name'])) ? $_GET['column_name'] : $column_name = "item_type";
// Call function.
get_lookup($table_name, $column_name);
?>
</body>
</html> |
The library.inc file contains the logic to use a PHP prepared statement to read and render a SELECT HTML tag. It uses OPTION tags for all values in the drop down list. The values for the OPTION tag are the surrogate key values from the common_lookup_id column of the common_lookup table, and text elements are the descriptive values from the common_lookup_meaning column.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 | <?php /* || Program Name: library.inc */ function get_lookup($table_name, $column_name) { // Assign credentials to connection. $mysqli = new mysqli("localhost", "student", "student", "studentdb"); // Check for connection error and print message. if ($mysqli->connect_errno) { print $mysqli->connect_error."<br />"; print "Connection not established ...<br />"; } else { // Initial statement. $stmt = $mysqli->stmt_init(); // Declare a static query. $sql = "SELECT cl.common_lookup_id\n" . ", cl.common_lookup_meaning\n" . "FROM common_lookup cl\n" . "WHERE common_lookup_table = ?\n" . "AND common_lookup_column = ?\n" . "ORDER BY 2"; // Prepare statement. if ($stmt->prepare($sql)) { $stmt->bind_param("ss",$table_name,$column_name); } // Loop through a result set until completed. do { // Attempt query and exit with failure before processing. if (!$stmt->execute()) { // Print failure to resolve query message. print $mysqli->error."<br />"; print "Failed to resolve query ...<br />"; } else { // Fetch a row for processing. $result = $stmt->get_result(); // Print the opening select tag. print '<form method="post" name="myForm" action="submitItemType.php">'; print '<div class="title">Select unique from list:</div>'; print '<select name="item_type" size="1" onChange="change(this.form.item_type)">'; print "<option class=label value='' selected>Select </option>"; // Read through the rows of the array. while( $row = $result->fetch_array(MYSQLI_NUM) ) { print "<option class=label value='".$row[0]."'>".$row[1]."</option>"; } } } while($stmt->next_result()); // Print the closing HTML table tag. print '</select>'; print '<input name="submit" type="submit" value="Submit">'; print '</form>'; // Release connection resource. $mysqli->close(); } } ?> |
The display form action calls the submitItemType.php program, which displays the value from the OPTION tag selected in the prior form. The code for the display is:
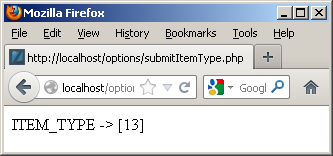
<html> <head> </head> <body> <?php print "ITEM_TYPE -> [".$_POST['item_type']."]"; ?> </body> </html> |
It generates:
Hope this helps illustrate the value of and mechanics of lookup tables. As mentioned above, there’s a newer post on how to leverage common_lookup tables with more working code.