Archive for March, 2024
Ubuntu Pro Upgrade?
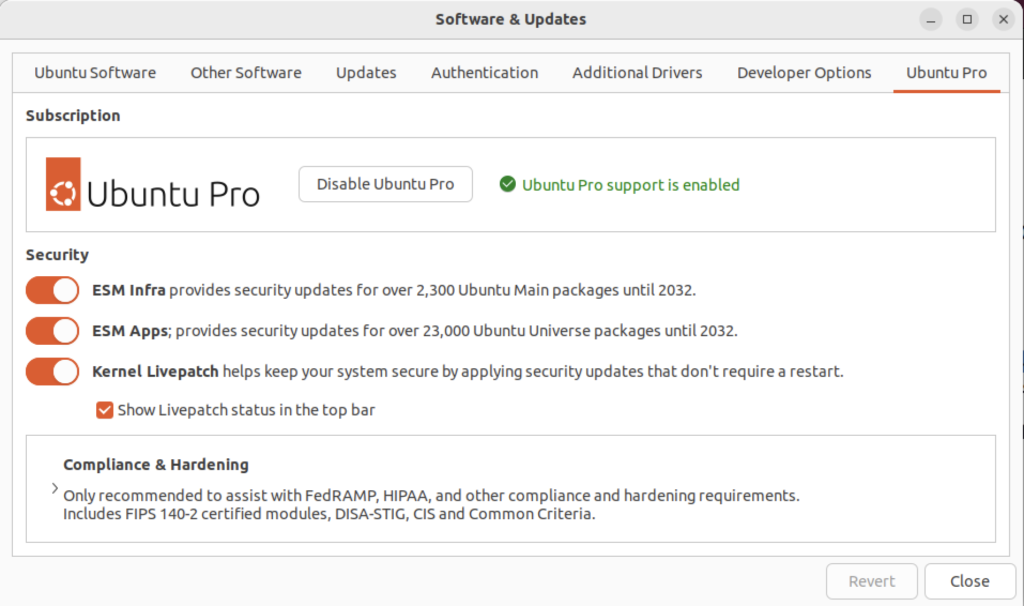
There wasn’t a choice when I chose to update the Ubuntu instance. I was compelled to upgrade to Ubuntu Pro. According to the upgrade I have five free installations. You can read more about Ubuntu Pro on this web page, and find their pricing schedule on this page.
MongoDB on Ubuntu
This post shows how to install, configure, and use MongoDB with JavaScript programs. You need to complete each section in the order provided (based on Cherry Server post).
Step #1: MongoDB Installation
Install the prerequisite packages with the following command:
sudo apt install -y software-properties-common gnupg apt-transport-https ca-certificates |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done ca-certificates is already the newest version (20230311ubuntu0.22.04.1). ca-certificates set to manually installed. gnupg is already the newest version (2.2.27-3ubuntu2.1). gnupg set to manually installed. software-properties-common is already the newest version (0.99.22.9). apt-transport-https is already the newest version (2.4.11). 0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 22 not upgraded. |
Import the public key for MongoDB on your system using the curl command:
curl -fsSL https://pgp.mongodb.com/server-7.0.asc | sudo gpg -o /usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-7.0.gpg --dearmor |
Add MongoDB 7.0 APT repository to the /etc/apt/sources.list.d directory:
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/mongodb-server-7.0.gpg ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-7.0.list |
Reload the local package index, which refreshes the local repositories and makes Ubuntu aware of the newly added MongoDB repository:
sudo apt update |
Display detailed console log →
Hit:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates InRelease [119 kB] Get:3 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease [110 kB] Hit:4 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease Hit:5 https://download.vscodium.com/debs vscodium InRelease Hit:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease Hit:7 https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/jammy pgadmin4 InRelease Ign:8 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0 InRelease Get:9 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0 Release [2,090 B] Get:10 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0 Release.gpg [866 B] Get:11 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse arm64 Packages [27.6 kB] Get:12 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 Packages [28.6 kB] Fetched 288 kB in 4s (72.8 kB/s) Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done 22 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them. |
Install the mongodb-org meta-package:
sudo apt install -y mongodb-org |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: mongodb-database-tools mongodb-mongosh mongodb-org-database mongodb-org-database-tools-extra mongodb-org-mongos mongodb-org-server mongodb-org-shell mongodb-org-tools The following NEW packages will be installed: mongodb-database-tools mongodb-mongosh mongodb-org mongodb-org-database mongodb-org-database-tools-extra mongodb-org-mongos mongodb-org-server mongodb-org-shell mongodb-org-tools 0 upgraded, 9 newly installed, 0 to remove and 22 not upgraded. Need to get 163 MB of archives. After this operation, 537 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-database-tools amd64 100.9.4 [51.9 MB] Get:2 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-mongosh amd64 2.1.5 [48.7 MB] Get:3 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-org-shell amd64 7.0.6 [2,986 B] Get:4 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-org-server amd64 7.0.6 [36.7 MB] Get:5 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-org-mongos amd64 7.0.6 [25.6 MB] Get:6 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-org-database-tools-extra amd64 7.0.6 [7,786 B] Get:7 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-org-database amd64 7.0.6 [3,422 B] Get:8 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-org-tools amd64 7.0.6 [2,770 B] Get:9 https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu jammy/mongodb-org/7.0/multiverse amd64 mongodb-org amd64 7.0.6 [2,804 B] Fetched 163 MB in 8s (20.2 MB/s) Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-database-tools. (Reading database ... 250115 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../0-mongodb-database-tools_100.9.4_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-database-tools (100.9.4) ... Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-mongosh. Preparing to unpack .../1-mongodb-mongosh_2.1.5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-mongosh (2.1.5) ... Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-org-shell. Preparing to unpack .../2-mongodb-org-shell_7.0.6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-org-shell (7.0.6) ... Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-org-server. Preparing to unpack .../3-mongodb-org-server_7.0.6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-org-server (7.0.6) ... Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-org-mongos. Preparing to unpack .../4-mongodb-org-mongos_7.0.6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-org-mongos (7.0.6) ... Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-org-database-tools-extra. Preparing to unpack .../5-mongodb-org-database-tools-extra_7.0.6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-org-database-tools-extra (7.0.6) ... Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-org-database. Preparing to unpack .../6-mongodb-org-database_7.0.6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-org-database (7.0.6) ... Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-org-tools. Preparing to unpack .../7-mongodb-org-tools_7.0.6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-org-tools (7.0.6) ... Selecting previously unselected package mongodb-org. Preparing to unpack .../8-mongodb-org_7.0.6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking mongodb-org (7.0.6) ... Setting up mongodb-mongosh (2.1.5) ... Setting up mongodb-org-server (7.0.6) ... Adding system user `mongodb' (UID 132) ... Adding new user `mongodb' (UID 132) with group `nogroup' ... Not creating home directory `/home/mongodb'. Adding group `mongodb' (GID 140) ... Done. Adding user `mongodb' to group `mongodb' ... Adding user mongodb to group mongodb Done. Setting up mongodb-org-shell (7.0.6) ... Setting up mongodb-database-tools (100.9.4) ... Setting up mongodb-org-mongos (7.0.6) ... Setting up mongodb-org-database-tools-extra (7.0.6) ... Setting up mongodb-org-database (7.0.6) ... Setting up mongodb-org-tools (7.0.6) ... Setting up mongodb-org (7.0.6) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... |
Verify the installed version of MongoDB with this command:
mongod --version |
It should display:
db version v7.0.6
Build Info: {
"version": "7.0.6",
"gitVersion": "66cdc1f28172cb33ff68263050d73d4ade73b9a4",
"openSSLVersion": "OpenSSL 3.0.2 15 Mar 2022",
"modules": [],
"allocator": "tcmalloc",
"environment": {
"distmod": "ubuntu2204",
"distarch": "x86_64",
"target_arch": "x86_64"
}
} |
Step #2: Start MongoDB Service & Shell
You can verify that the installed mongodb is disabled after initial installation with this command:
sudo systemctl status mongod |
It should display:
○ mongod.service - MongoDB Database Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mongod.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: https://docs.mongodb.org/manual |
Exit the output display from the systemctl utility by typing the escape key, a colon (:) and a q in sequence.
You can start the MongoDB service with this command:
sudo systemctl start mongod |
Then, check the MongoDB service:
sudo systemctl status mongod |
It displays:
● mongod.service - MongoDB Database Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mongod.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2024-03-07 16:38:17 MST; 2s ago
Docs: https://docs.mongodb.org/manual
Main PID: 33795 (mongod)
Memory: 79.2M
CPU: 706ms
CGroup: /system.slice/mongod.service
└─33795 /usr/bin/mongod --config /etc/mongod.conf
Mar 07 16:38:17 student-virtual-machine systemd[1]: Started MongoDB Database Server.
Mar 07 16:38:17 student-virtual-machine mongod[33795]: {"t":{"$date":"2024-03-07T23:38:17.642Z"},"s"> |
You can confirm that the database is up and running by checking if the server is listening on its default port, which is port 27017. Run the ss command to check the port number.
sudo ss -pnltu | grep 27017 |
It will display:
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.1:27017 0.0.0.0:* users:(("mongod",pid=33795,fd=14)) |
You can enable the mongodb service at startup with the following command:
sudo systemctl enable mongod |
It raised the following error:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mongod.service → /lib/systemd/system/mongod.service. |
Now, start the MongoDB Shell (mongosh) by typing either the explicit or implicit MongoDB Shell command. The explicit one uses the port and database path, which are unnecessary when you’ve successfully started the mongosh service. (Please note that at the time of writing this blog post there is erroneous, or obsolete, content on the MongoDB Documentation Enable Access Control web page.
Explicit connection:
mongosh --port 27017 --db /var/lib/mongodb --help |
This version of the command will display most of the options available in MongoDB but it will suppress warning messages.
$ mongosh [options] [db address] [file names (ending in .js or .mongodb)] Options: -h, --help Show this usage information -f, --file [arg] Load the specified mongosh script --host [arg] Server to connect to --port [arg] Port to connect to --build-info Show build information --version Show version information --quiet Silence output from the shell during the connection process --shell Run the shell after executing files --nodb Don't connect to mongod on startup - no 'db address' [arg] expected --norc Will not run the '.mongoshrc.js' file on start up --eval [arg] Evaluate javascript --json[=canonical|relaxed] Print result of --eval as Extended JSON, including errors --retryWrites[=true|false] Automatically retry write operations upon transient network errors (Default: true) Authentication Options: -u, --username [arg] Username for authentication -p, --password [arg] Password for authentication --authenticationDatabase [arg] User source (defaults to dbname) --authenticationMechanism [arg] Authentication mechanism --awsIamSessionToken [arg] AWS IAM Temporary Session Token ID --gssapiServiceName [arg] Service name to use when authenticating using GSSAPI/Kerberos --sspiHostnameCanonicalization [arg] Specify the SSPI hostname canonicalization (none or forward, available on Windows) --sspiRealmOverride [arg] Specify the SSPI server realm (available on Windows) TLS Options: --tls Use TLS for all connections --tlsCertificateKeyFile [arg] PEM certificate/key file for TLS --tlsCertificateKeyFilePassword [arg] Password for key in PEM file for TLS --tlsCAFile [arg] Certificate Authority file for TLS --tlsAllowInvalidHostnames Allow connections to servers with non-matching hostnames --tlsAllowInvalidCertificates Allow connections to servers with invalid certificates --tlsCertificateSelector [arg] TLS Certificate in system store (Windows and macOS only) --tlsCRLFile [arg] Specifies the .pem file that contains the Certificate Revocation List --tlsDisabledProtocols [arg] Comma separated list of TLS protocols to disable [TLS1_0,TLS1_1,TLS1_2] --tlsUseSystemCA Load the operating system trusted certificate list --tlsFIPSMode Enable the system TLS library's FIPS mode API version options: --apiVersion [arg] Specifies the API version to connect with --apiStrict Use strict API version mode --apiDeprecationErrors Fail deprecated commands for the specified API version FLE Options: --awsAccessKeyId [arg] AWS Access Key for FLE Amazon KMS --awsSecretAccessKey [arg] AWS Secret Key for FLE Amazon KMS --awsSessionToken [arg] Optional AWS Session Token ID --keyVaultNamespace [arg] database.collection to store encrypted FLE parameters --kmsURL [arg] Test parameter to override the URL of the KMS endpoint DB Address Examples: foo Foo database on local machine 192.168.0.5/foo Foo database on 192.168.0.5 machine 192.168.0.5:9999/foo Foo database on 192.168.0.5 machine on port 9999 mongodb://192.168.0.5:9999/foo Connection string URI can also be used File Names: A list of files to run. Files must end in .js and will exit after unless --shell is specified. Examples: Start mongosh using 'ships' database on specified connection string: $ mongosh mongodb://192.168.0.5:9999/ships For more information on usage: https://docs.mongodb.com/mongodb-shell. |
Implicit connection:
mongosh |
You should see the following message with any warning messages:
Current Mongosh Log ID: 65ea502a97f4c1e2b7e12af4 Connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/?directConnection=true&serverSelectionTimeoutMS=2000&appName=mongosh+2.1.5 Using MongoDB: 7.0.6 Using Mongosh: 2.1.5 For mongosh info see: https://docs.mongodb.com/mongodb-shell/ To help improve our products, anonymous usage data is collected and sent to MongoDB periodically (https://www.mongodb.com/legal/privacy-policy). You can opt-out by running the disableTelemetry() command. ------ The server generated these startup warnings when booting 2024-03-07T16:38:17.818-07:00: Using the XFS filesystem is strongly recommended with the WiredTiger storage engine. See http://dochub.mongodb.org/core/prodnotes-filesystem 2024-03-07T16:38:18.350-07:00: Access control is not enabled for the database. Read and write access to data and configuration is unrestricted 2024-03-07T16:38:18.350-07:00: vm.max_map_count is too low ------ |
You can run opt out of the data collection by running the disableTelemetry() command from the Linux command line. Use the following command (a broader explanation is in the MongoDB Telemetry documentation):
mongosh --nodb --eval "disableTelemetry()" |
It should return:
Current Mongosh Log ID: 65eab2df3e663bde3711fa2f Using Mongosh: 2.1.5 For mongosh info see: https://docs.mongodb.com/mongodb-shell/ Telemetry is now disabled. |
You still have three warning messages to deal with at this point. You should fix the vm.max_map_count warning first. This is a Linux kernel issue. You can determine the current value of the vm.max_map_count value with this command:
cat /proc/sys/vm/max_map_count |
It should return the system default value:
65530 |
You can change it at runtime with this command:
sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144 |
However, you must restart the mongod service to see the change in the mongosh shell. There won’t be a warning message for the kernel parameter value being too low until you reboot your operating system. You can restart your mongod service with this command:
sudo service mongod restart |
You can make a change to the /etc/sysctl.conf file to ensure the parameter is set to the correct value each time the system reboots. Simply add the following line as the root user or by using the sudo prefacing a text editor or your choice (like vim or nano) to your /etc/sysctl.conf file:
# Adding vm.max_map_count to sysctl.conf defaults. vm.max_map_count=262144 |
At this point, you’ve eliminated two of the warning messages. The next step shows you how to enable Access Control. If you want to check the general server status, run the following command from the Linux Command-Line Interface (CLI):
mongosh --eval "db.serverStatus()" > server_status.log |
You can inspect the log file, which should be slightly less than 2,000 lines of output with MongoDB a 7.0.6 installation. Using the command from the Linux CLI is generally the easiest way to inspect the output from the db.serverStatus() function, which is just too long to scroll from the console output.
Step #3: MongoDB Enabling Access Control
Connect to the mongosh …
Step #4: MongoDB Installing Node.js and React.js
Install Node.js with the following command:
sudo apt install -y nodejs |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: libc-ares2 libjs-highlight.js libnode72 nodejs-doc Suggested packages: npm The following NEW packages will be installed: libc-ares2 libjs-highlight.js libnode72 nodejs nodejs-doc 0 upgraded, 5 newly installed, 0 to remove and 23 not upgraded. Need to get 13.7 MB of archives. After this operation, 53.9 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] y Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libjs-highlight.js all 9.18.5+dfsg1-1 [367 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libc-ares2 amd64 1.18.1-1ubuntu0.22.04.3 [45.1 kB] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libnode72 amd64 12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4 [10.8 MB] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 nodejs-doc all 12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4 [2,410 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 nodejs amd64 12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4 [122 kB] Fetched 13.7 MB in 3s (4,006 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package libjs-highlight.js. (Reading database ... 250172 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libjs-highlight.js_9.18.5+dfsg1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-highlight.js (9.18.5+dfsg1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libc-ares2:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../libc-ares2_1.18.1-1ubuntu0.22.04.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libc-ares2:amd64 (1.18.1-1ubuntu0.22.04.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libnode72:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../libnode72_12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libnode72:amd64 (12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4) ... Selecting previously unselected package nodejs-doc. Preparing to unpack .../nodejs-doc_12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4_all.deb ... Unpacking nodejs-doc (12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4) ... Selecting previously unselected package nodejs. Preparing to unpack .../nodejs_12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4_amd64.deb ... Unpacking nodejs (12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4) ... Setting up libc-ares2:amd64 (1.18.1-1ubuntu0.22.04.3) ... Setting up libnode72:amd64 (12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4) ... Setting up libjs-highlight.js (9.18.5+dfsg1-1) ... Setting up nodejs (12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/nodejs to provide /usr/bin/js (js) in auto m ode Setting up nodejs-doc (12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.6) ... |
You can check the Node.js version with this command:
node -v |
v12.22.9 |
Install the Node.js package manager npm with the following command:
sudo apt install -y npm |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: gyp libjs-events libjs-inherits libjs-is-typedarray libjs-psl libjs-source-map libjs-sprintf-js libjs-typedarray-to-buffer libnode-dev libuv1-dev node-abab node-abbrev node-agent-base node-ansi-regex node-ansi-styles node-ansistyles node-aproba node-archy node-are-we-there-yet node-argparse node-arrify node-asap node-asynckit node-balanced-match node-brace-expansion node-builtins node-cacache node-chalk node-chownr node-clean-yaml-object node-cli-table node-clone node-color-convert node-color-name node-colors node-columnify node-combined-stream node-commander node-console-control-strings node-copy-concurrently node-core-util-is node-coveralls node-cssom node-cssstyle node-debug node-decompress-response node-defaults node-delayed-stream node-delegates node-depd node-diff node-encoding node-end-of-stream node-err-code node-escape-string-regexp node-esprima node-events node-fancy-log node-fetch node-foreground-child node-form-data node-fs-write-stream-atomic node-fs.realpath node-function-bind node-gauge node-get-stream node-glob node-got node-graceful-fs node-growl node-gyp node-has-flag node-has-unicode node-hosted-git-info node-https-proxy-agent node-iconv-lite node-iferr node-imurmurhash node-indent-string node-inflight node-inherits node-ini node-ip node-ip-regex node-is-buffer node-is-plain-obj node-is-typedarray node-isarray node-isexe node-js-yaml node-jsdom node-json-buffer node-json-parse-better-errors node-jsonparse node-kind-of node-lcov-parse node-lodash-packages node-log-driver node-lowercase-keys node-lru-cache node-mime node-mime-types node-mimic-response node-minimatch node-minimist node-minipass node-mkdirp node-move-concurrently node-ms node-mute-stream node-negotiator node-nopt node-normalize-package-data node-npm-bundled node-npm-package-arg node-npmlog node-object-assign node-once node-opener node-osenv node-p-cancelable node-p-map node-path-is-absolute node-process-nextick-args node-promise-inflight node-promise-retry node-promzard node-psl node-pump node-punycode node-quick-lru node-read node-read-package-json node-readable-stream node-resolve node-retry node-rimraf node-run-queue node-safe-buffer node-semver node-set-blocking node-signal-exit node-slash node-slice-ansi node-source-map node-source-map-support node-spdx-correct node-spdx-exceptions node-spdx-expression-parse node-spdx-license-ids node-sprintf-js node-ssri node-stack-utils node-stealthy-require node-string-decoder node-string-width node-strip-ansi node-supports-color node-tap node-tap-mocha-reporter node-tap-parser node-tar node-text-table node-time-stamp node-tmatch node-tough-cookie node-typedarray-to-buffer node-unique-filename node-universalify node-util-deprecate node-validate-npm-package-license node-validate-npm-package-name node-wcwidth.js node-webidl-conversions node-whatwg-fetch node-which node-wide-align node-wrappy node-write-file-atomic node-ws node-yallist Suggested packages: libjs-angularjs node-nyc The following NEW packages will be installed: gyp libjs-events libjs-inherits libjs-is-typedarray libjs-psl libjs-source-map libjs-sprintf-js libjs-typedarray-to-buffer libnode-dev libuv1-dev node-abab node-abbrev node-agent-base node-ansi-regex node-ansi-styles node-ansistyles node-aproba node-archy node-are-we-there-yet node-argparse node-arrify node-asap node-asynckit node-balanced-match node-brace-expansion node-builtins node-cacache node-chalk node-chownr node-clean-yaml-object node-cli-table node-clone node-color-convert node-color-name node-colors node-columnify node-combined-stream node-commander node-console-control-strings node-copy-concurrently node-core-util-is node-coveralls node-cssom node-cssstyle node-debug node-decompress-response node-defaults node-delayed-stream node-delegates node-depd node-diff node-encoding node-end-of-stream node-err-code node-escape-string-regexp node-esprima node-events node-fancy-log node-fetch node-foreground-child node-form-data node-fs-write-stream-atomic node-fs.realpath node-function-bind node-gauge node-get-stream node-glob node-got node-graceful-fs node-growl node-gyp node-has-flag node-has-unicode node-hosted-git-info node-https-proxy-agent node-iconv-lite node-iferr node-imurmurhash node-indent-string node-inflight node-inherits node-ini node-ip node-ip-regex node-is-buffer node-is-plain-obj node-is-typedarray node-isarray node-isexe node-js-yaml node-jsdom node-json-buffer node-json-parse-better-errors node-jsonparse node-kind-of node-lcov-parse node-lodash-packages node-log-driver node-lowercase-keys node-lru-cache node-mime node-mime-types node-mimic-response node-minimatch node-minimist node-minipass node-mkdirp node-move-concurrently node-ms node-mute-stream node-negotiator node-nopt node-normalize-package-data node-npm-bundled node-npm-package-arg node-npmlog node-object-assign node-once node-opener node-osenv node-p-cancelable node-p-map node-path-is-absolute node-process-nextick-args node-promise-inflight node-promise-retry node-promzard node-psl node-pump node-punycode node-quick-lru node-read node-read-package-json node-readable-stream node-resolve node-retry node-rimraf node-run-queue node-safe-buffer node-semver node-set-blocking node-signal-exit node-slash node-slice-ansi node-source-map node-source-map-support node-spdx-correct node-spdx-exceptions node-spdx-expression-parse node-spdx-license-ids node-sprintf-js node-ssri node-stack-utils node-stealthy-require node-string-decoder node-string-width node-strip-ansi node-supports-color node-tap node-tap-mocha-reporter node-tap-parser node-tar node-text-table node-time-stamp node-tmatch node-tough-cookie node-typedarray-to-buffer node-unique-filename node-universalify node-util-deprecate node-validate-npm-package-license node-validate-npm-package-name node-wcwidth.js node-webidl-conversions node-whatwg-fetch node-which node-wide-align node-wrappy node-write-file-atomic node-ws node-yallist npm 0 upgraded, 182 newly installed, 0 to remove and 23 not upgraded. Need to get 5,075 kB of archives. After this operation, 36.3 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 gyp all 0.1+20210831gitd6c5dd5-5 [238 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libjs-events all 3.3.0+~3.0.0-2 [9,734 B] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libjs-is-typedarray all 1.0.0-4 [3,804 B] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libjs-psl all 1.8.0+ds-6 [76.3 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libjs-sprintf-js all 1.1.2+ds1+~1.1.2-1 [12.8 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libjs-typedarray-to-buffer all 4.0.0-2 [4,658 B] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libuv1-dev amd64 1.43.0-1ubuntu0.1 [130 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libnode-dev amd64 12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4 [609 kB] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-abab all 2.0.5-2 [6,578 B] Get:10 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ms all 2.1.3+~cs0.7.31-2 [5,782 B] Get:11 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-debug all 4.3.2+~cs4.1.7-1 [17.6 kB] Get:12 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-yallist all 4.0.0+~4.0.1-1 [8,322 B] Get:13 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-lru-cache all 6.0.0+~5.1.1-1 [11.3 kB] Get:14 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-semver all 7.3.5+~7.3.8-1 [41.5 kB] Get:15 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-agent-base all 6.0.2+~cs5.4.2-1 [17.9 kB] Get:16 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ansi-regex all 5.0.1-1 [4,984 B] Get:17 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ansistyles all 0.1.3-5 [4,546 B] Get:18 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-aproba all 2.0.0-2 [5,620 B] Get:19 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-delegates all 1.0.0-3 [4,280 B] Get:20 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libjs-inherits all 2.0.4-4 [3,468 B] Get:21 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-inherits all 2.0.4-4 [3,010 B] Get:22 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-core-util-is all 1.0.3-1 [4,066 B] Get:23 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-safe-buffer all 5.2.1+~cs2.1.2-2 [15.7 kB] Get:24 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-string-decoder all 1.3.0-5 [7,046 B] Get:25 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-process-nextick-args all 2.0.1-2 [3,730 B] Get:26 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-util-deprecate all 1.0.2-3 [4,202 B] Get:27 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-isarray all 2.0.5-3 [3,934 B] Get:28 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-readable-stream all 3.6.0+~cs3.0.0-1 [32.6 kB] Get:29 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-are-we-there-yet all 3.0.0+~1.1.0-1 [8,920 B] Get:30 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-arrify all 2.0.1-2 [3,610 B] Get:31 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-asap all 2.0.6+~2.0.0-1 [14.4 kB] Get:32 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-asynckit all 0.4.0-4 [10.6 kB] Get:33 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-builtins all 4.0.0-1 [3,860 B] Get:34 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-chownr all 2.0.0-1 [4,404 B] Get:35 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-fs.realpath all 1.0.0-2 [6,106 B] Get:36 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-wrappy all 1.0.2-2 [3,658 B] Get:37 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-once all 1.4.0-4 [4,708 B] Get:38 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-inflight all 1.0.6-2 [3,940 B] Get:39 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-balanced-match all 2.0.0-1 [4,910 B] Get:40 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-brace-expansion all 2.0.1-1 [7,458 B] Get:41 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-minimatch all 3.1.1+~3.0.5-1 [16.9 kB] Get:42 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-path-is-absolute all 2.0.0-2 [4,062 B] Get:43 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-glob all 7.2.1+~cs7.6.15-1 [131 kB] Get:44 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-graceful-fs all 4.2.4+repack-1 [12.5 kB] Get:45 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-mkdirp all 1.0.4+~1.0.2-1 [11.4 kB] Get:46 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-iferr all 1.0.2+~1.0.2-1 [4,610 B] Get:47 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-imurmurhash all 0.1.4+dfsg+~0.1.1-1 [8,510 B] Get:48 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-fs-write-stream-atomic all 1.0.10-5 [5,256 B] Get:49 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-rimraf all 3.0.2-1 [10.1 kB] Get:50 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-run-queue all 2.0.0-2 [5,092 B] Get:51 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-copy-concurrently all 1.0.5-8 [7,118 B] Get:52 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-move-concurrently all 1.0.1-4 [5,120 B] Get:53 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-escape-string-regexp all 4.0.0-2 [4,328 B] Get:54 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-indent-string all 4.0.0-2 [4,122 B] Get:55 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-p-map all 4.0.0+~3.1.0+~3.0.1-1 [8,058 B] Get:56 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-promise-inflight all 1.0.1+~1.0.0-1 [4,896 B] Get:57 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ssri all 8.0.1-2 [19.6 kB] Get:58 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-unique-filename all 1.1.1+ds-1 [3,832 B] Get:59 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-cacache all 15.0.5+~cs13.9.21-3 [34.9 kB] Get:60 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-clean-yaml-object all 0.1.0-5 [4,718 B] Get:61 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-clone all 2.1.2-3 [8,344 B] Get:62 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-color-name all 1.1.4+~1.1.1-2 [6,076 B] Get:63 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-color-convert all 2.0.1-1 [10.2 kB] Get:64 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-colors all 1.4.0-3 [12.3 kB] Get:65 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-strip-ansi all 6.0.1-1 [4,184 B] Get:66 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-defaults all 1.0.3+~1.0.3-1 [4,288 B] Get:67 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-wcwidth.js all 1.0.2-1 [7,278 B] Get:68 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-columnify all 1.5.4+~1.5.1-1 [12.6 kB] Get:69 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-console-control-strings all 1.1.0-2 [5,428 B] Get:70 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-growl all 1.10.5-4 [7,064 B] Get:71 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-sprintf-js all 1.1.2+ds1+~1.1.2-1 [3,916 B] Get:72 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-argparse all 2.0.1-2 [33.2 kB] Get:73 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-esprima all 4.0.1+ds+~4.0.3-2 [69.3 kB] Get:74 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-js-yaml all 4.1.0+dfsg+~4.0.5-6 [62.7 kB] Get:75 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-lcov-parse all 1.0.0+20170612git80d039574ed9-5 [5,084 B] Get:76 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-log-driver all 1.2.7+git+20180219+bba1761737-7 [5,436 B] Get:77 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-is-plain-obj all 3.0.0-2 [3,994 B] Get:78 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-is-buffer all 2.0.5-2 [4,128 B] Get:79 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-kind-of all 6.0.3+dfsg-2 [8,628 B] Get:80 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-minimist all 1.2.5+~cs5.3.2-1 [9,434 B] Get:81 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-cssom all 0.4.4-3 [14.1 kB] Get:82 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-cssstyle all 2.3.0-2 [30.3 kB] Get:83 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-delayed-stream all 1.0.0-5 [5,464 B] Get:84 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-combined-stream all 1.0.8+~1.0.3-1 [7,432 B] Get:85 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-mime all 3.0.0+dfsg+~cs3.96.1-1 [38.1 kB] Get:86 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-mime-types all 2.1.33-1 [6,944 B] Get:87 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-form-data all 3.0.1-1 [13.4 kB] Get:88 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-events all 3.3.0+~3.0.0-2 [3,090 B] Get:89 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-https-proxy-agent all 5.0.0+~cs8.0.0-3 [16.4 kB] Get:90 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-iconv-lite all 0.6.3-2 [167 kB] Get:91 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-lodash-packages all 4.17.21+dfsg+~cs8.31.198.20210220-5 [166 kB] Get:92 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-stealthy-require all 1.1.1-5 [7,176 B] Get:93 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-punycode all 2.1.1-5 [9,902 B] Get:94 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-psl all 1.8.0+ds-6 [39.6 kB] Get:95 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-universalify all 2.0.0-3 [4,266 B] Get:96 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-tough-cookie all 4.0.0-2 [31.7 kB] Get:97 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-webidl-conversions all 7.0.0~1.1.0+~cs15.1.20180823-2 [27.5 kB] Get:98 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-commander all 9.0.0-2 [48.0 kB] Get:99 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-mute-stream all 0.0.8+~0.0.1-1 [6,448 B] Get:100 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-read all 1.0.7-3 [5,478 B] Get:101 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ws all 8.5.0+~cs13.3.3-2 [49.5 kB] Get:102 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-jsdom all 19.0.0+~cs90.11.27-1 [446 kB] Get:103 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-fetch all 2.6.7+~2.5.12-1 [27.1 kB] Get:104 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-coveralls all 3.1.1-1 [14.2 kB] Get:105 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-mimic-response all 3.1.0-7 [5,430 B] Get:106 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-decompress-response all 6.0.0-2 [4,656 B] Get:107 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-diff all 5.0.0~dfsg+~5.0.1-3 [77.4 kB] Get:108 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-err-code all 2.0.3+dfsg-3 [4,918 B] Get:109 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-time-stamp all 2.2.0-1 [5,984 B] Get:110 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-fancy-log all 1.3.3+~cs1.3.1-2 [8,102 B] Get:111 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-signal-exit all 3.0.6+~3.0.1-1 [7,000 B] Get:112 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-foreground-child all 2.0.0-3 [5,542 B] Get:113 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-function-bind all 1.1.1+repacked+~1.0.3-1 [5,244 B] Get:114 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-has-unicode all 2.0.1-4 [3,948 B] Get:115 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ansi-styles all 4.3.0+~4.2.0-1 [8,968 B] Get:116 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-slice-ansi all 5.0.0+~cs9.0.0-4 [8,044 B] Get:117 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-string-width all 4.2.3+~cs13.2.3-1 [11.4 kB] Get:118 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-wide-align all 1.1.3-4 [4,228 B] Get:119 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-gauge all 4.0.2-1 [16.3 kB] Get:120 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-end-of-stream all 1.4.4+~1.4.1-1 [5,340 B] Get:121 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-pump all 3.0.0-5 [5,160 B] Get:122 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-get-stream all 6.0.1-1 [7,324 B] Get:123 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-lowercase-keys all 2.0.0-2 [3,754 B] Get:124 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-json-buffer all 3.0.1-1 [3,812 B] Get:125 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-p-cancelable all 2.1.1-1 [7,358 B] Get:126 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-quick-lru all 5.1.1-1 [5,532 B] Get:127 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-got all 11.8.3+~cs58.7.37-1 [122 kB] Get:128 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-has-flag all 4.0.0-2 [4,228 B] Get:129 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-hosted-git-info all 4.0.2-1 [9,006 B] Get:130 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ip all 1.1.5+~1.1.0-1 [8,140 B] Get:131 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ip-regex all 4.3.0+~4.1.1-1 [5,254 B] Get:132 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-is-typedarray all 1.0.0-4 [2,072 B] Get:133 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-isexe all 2.0.0+~2.0.1-4 [6,102 B] Get:134 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-json-parse-better-errors all 1.0.2+~cs3.3.1-1 [7,328 B] Get:135 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-encoding all 0.1.13-2 [4,366 B] Get:136 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-jsonparse all 1.3.1-10 [8,060 B] Get:137 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-minipass all 3.1.6+~cs8.7.18-1 [32.9 kB] Get:138 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-npm-bundled all 1.1.2-1 [6,228 B] Get:139 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-osenv all 0.1.5+~0.1.0-1 [5,896 B] Get:140 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-validate-npm-package-name all 3.0.0-4 [5,058 B] Get:141 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-npm-package-arg all 8.1.5-1 [8,132 B] Get:142 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-object-assign all 4.1.1-6 [4,754 B] Get:143 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-opener all 1.5.2+~1.4.0-1 [6,000 B] Get:144 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-retry all 0.13.1+~0.12.1-1 [11.5 kB] Get:145 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-promise-retry all 2.0.1-2 [5,010 B] Get:146 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-promzard all 0.3.0-2 [6,888 B] Get:147 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-set-blocking all 2.0.0-2 [3,766 B] Get:148 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-slash all 3.0.0-2 [3,922 B] Get:149 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libjs-source-map all 0.7.0++dfsg2+really.0.6.1-9 [93.9 kB] Get:150 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-source-map all 0.7.0++dfsg2+really.0.6.1-9 [33.6 kB] Get:151 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-source-map-support all 0.5.21+ds+~0.5.4-1 [14.2 kB] Get:152 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-spdx-license-ids all 3.0.11-1 [7,306 B] Get:153 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-spdx-exceptions all 2.3.0-2 [3,978 B] Get:154 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-spdx-expression-parse all 3.0.1+~3.0.1-1 [7,658 B] Get:155 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-spdx-correct all 3.1.1-2 [5,476 B] Get:156 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-stack-utils all 2.0.5+~2.0.1-1 [9,368 B] Get:157 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-supports-color all 8.1.1+~8.1.1-1 [7,048 B] Get:158 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-tap-parser all 7.0.0+ds1-6 [19.4 kB] Get:159 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-tap-mocha-reporter all 3.0.7+ds-2 [39.2 kB] Get:160 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-text-table all 0.2.0-4 [4,762 B] Get:161 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-tmatch all 5.0.0-4 [6,002 B] Get:162 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-typedarray-to-buffer all 4.0.0-2 [2,242 B] Get:163 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-validate-npm-package-license all 3.0.4-2 [4,252 B] Get:164 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-whatwg-fetch all 3.6.2-5 [15.0 kB] Get:165 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-write-file-atomic all 3.0.3+~3.0.2-1 [7,690 B] Get:166 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-abbrev all 1.1.1+~1.1.2-1 [5,784 B] Get:167 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-archy all 1.0.0-4 [4,728 B] Get:168 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-chalk all 4.1.2-1 [15.9 kB] Get:169 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-cli-table all 0.3.11+~cs0.13.3-1 [23.2 kB] Get:170 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-depd all 2.0.0-2 [10.5 kB] Get:171 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-nopt all 5.0.0-2 [11.3 kB] Get:172 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-npmlog all 6.0.1+~4.1.4-1 [9,968 B] Get:173 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-tar all 6.1.11+ds1+~cs6.0.6-1 [38.8 kB] Get:174 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-which all 2.0.2+~cs1.3.2-2 [7,374 B] Get:175 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-gyp all 8.4.1-1 [34.7 kB] Get:176 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-ini all 2.0.1-1 [6,528 B] Get:177 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-negotiator all 0.6.2+~0.6.1-1 [10.3 kB] Get:178 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-resolve all 1.20.0+~cs5.27.9-1 [20.7 kB] Get:179 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-normalize-package-data all 3.0.3+~2.4.1-1 [12.8 kB] Get:180 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-read-package-json all 4.1.1-1 [10.4 kB] Get:181 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 node-tap all 12.0.1+ds-4 [43.6 kB] Get:182 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 npm all 8.5.1~ds-1 [894 kB] Fetched 5,075 kB in 19s (272 kB/s) Extracting templates from packages: 100% Selecting previously unselected package gyp. (Reading database ... 250530 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../000-gyp_0.1+20210831gitd6c5dd5-5_all.deb ... Unpacking gyp (0.1+20210831gitd6c5dd5-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-events. Preparing to unpack .../001-libjs-events_3.3.0+~3.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-events (3.3.0+~3.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-is-typedarray. Preparing to unpack .../002-libjs-is-typedarray_1.0.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-is-typedarray (1.0.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-psl. Preparing to unpack .../003-libjs-psl_1.8.0+ds-6_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-psl (1.8.0+ds-6) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-sprintf-js. Preparing to unpack .../004-libjs-sprintf-js_1.1.2+ds1+~1.1.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-sprintf-js (1.1.2+ds1+~1.1.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-typedarray-to-buffer. Preparing to unpack .../005-libjs-typedarray-to-buffer_4.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-typedarray-to-buffer (4.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libuv1-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../006-libuv1-dev_1.43.0-1ubuntu0.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libuv1-dev:amd64 (1.43.0-1ubuntu0.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libnode-dev. Preparing to unpack .../007-libnode-dev_12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libnode-dev (12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-abab. Preparing to unpack .../008-node-abab_2.0.5-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-abab (2.0.5-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ms. Preparing to unpack .../009-node-ms_2.1.3+~cs0.7.31-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ms (2.1.3+~cs0.7.31-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-debug. Preparing to unpack .../010-node-debug_4.3.2+~cs4.1.7-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-debug (4.3.2+~cs4.1.7-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-yallist. Preparing to unpack .../011-node-yallist_4.0.0+~4.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-yallist (4.0.0+~4.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-lru-cache. Preparing to unpack .../012-node-lru-cache_6.0.0+~5.1.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-lru-cache (6.0.0+~5.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-semver. Preparing to unpack .../013-node-semver_7.3.5+~7.3.8-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-semver (7.3.5+~7.3.8-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-agent-base. Preparing to unpack .../014-node-agent-base_6.0.2+~cs5.4.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-agent-base (6.0.2+~cs5.4.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ansi-regex. Preparing to unpack .../015-node-ansi-regex_5.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ansi-regex (5.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ansistyles. Preparing to unpack .../016-node-ansistyles_0.1.3-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ansistyles (0.1.3-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-aproba. Preparing to unpack .../017-node-aproba_2.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-aproba (2.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-delegates. Preparing to unpack .../018-node-delegates_1.0.0-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-delegates (1.0.0-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-inherits. Preparing to unpack .../019-libjs-inherits_2.0.4-4_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-inherits (2.0.4-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-inherits. Preparing to unpack .../020-node-inherits_2.0.4-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-inherits (2.0.4-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-core-util-is. Preparing to unpack .../021-node-core-util-is_1.0.3-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-core-util-is (1.0.3-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-safe-buffer. Preparing to unpack .../022-node-safe-buffer_5.2.1+~cs2.1.2-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-safe-buffer (5.2.1+~cs2.1.2-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-string-decoder. Preparing to unpack .../023-node-string-decoder_1.3.0-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-string-decoder (1.3.0-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-process-nextick-args. Preparing to unpack .../024-node-process-nextick-args_2.0.1-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-process-nextick-args (2.0.1-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-util-deprecate. Preparing to unpack .../025-node-util-deprecate_1.0.2-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-util-deprecate (1.0.2-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-isarray. Preparing to unpack .../026-node-isarray_2.0.5-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-isarray (2.0.5-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-readable-stream. Preparing to unpack .../027-node-readable-stream_3.6.0+~cs3.0.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-readable-stream (3.6.0+~cs3.0.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-are-we-there-yet. Preparing to unpack .../028-node-are-we-there-yet_3.0.0+~1.1.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-are-we-there-yet (3.0.0+~1.1.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-arrify. Preparing to unpack .../029-node-arrify_2.0.1-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-arrify (2.0.1-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-asap. Preparing to unpack .../030-node-asap_2.0.6+~2.0.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-asap (2.0.6+~2.0.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-asynckit. Preparing to unpack .../031-node-asynckit_0.4.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-asynckit (0.4.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-builtins. Preparing to unpack .../032-node-builtins_4.0.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-builtins (4.0.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-chownr. Preparing to unpack .../033-node-chownr_2.0.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-chownr (2.0.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-fs.realpath. Preparing to unpack .../034-node-fs.realpath_1.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-fs.realpath (1.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-wrappy. Preparing to unpack .../035-node-wrappy_1.0.2-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-wrappy (1.0.2-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-once. Preparing to unpack .../036-node-once_1.4.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-once (1.4.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-inflight. Preparing to unpack .../037-node-inflight_1.0.6-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-inflight (1.0.6-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-balanced-match. Preparing to unpack .../038-node-balanced-match_2.0.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-balanced-match (2.0.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-brace-expansion. Preparing to unpack .../039-node-brace-expansion_2.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-brace-expansion (2.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-minimatch. Preparing to unpack .../040-node-minimatch_3.1.1+~3.0.5-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-minimatch (3.1.1+~3.0.5-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-path-is-absolute. Preparing to unpack .../041-node-path-is-absolute_2.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-path-is-absolute (2.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-glob. Preparing to unpack .../042-node-glob_7.2.1+~cs7.6.15-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-glob (7.2.1+~cs7.6.15-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-graceful-fs. Preparing to unpack .../043-node-graceful-fs_4.2.4+repack-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-graceful-fs (4.2.4+repack-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-mkdirp. Preparing to unpack .../044-node-mkdirp_1.0.4+~1.0.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-mkdirp (1.0.4+~1.0.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-iferr. Preparing to unpack .../045-node-iferr_1.0.2+~1.0.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-iferr (1.0.2+~1.0.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-imurmurhash. Preparing to unpack .../046-node-imurmurhash_0.1.4+dfsg+~0.1.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-imurmurhash (0.1.4+dfsg+~0.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-fs-write-stream-atomic. Preparing to unpack .../047-node-fs-write-stream-atomic_1.0.10-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-fs-write-stream-atomic (1.0.10-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-rimraf. Preparing to unpack .../048-node-rimraf_3.0.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-rimraf (3.0.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-run-queue. Preparing to unpack .../049-node-run-queue_2.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-run-queue (2.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-copy-concurrently. Preparing to unpack .../050-node-copy-concurrently_1.0.5-8_all.deb ... Unpacking node-copy-concurrently (1.0.5-8) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-move-concurrently. Preparing to unpack .../051-node-move-concurrently_1.0.1-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-move-concurrently (1.0.1-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-escape-string-regexp. Preparing to unpack .../052-node-escape-string-regexp_4.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-escape-string-regexp (4.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-indent-string. Preparing to unpack .../053-node-indent-string_4.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-indent-string (4.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-p-map. Preparing to unpack .../054-node-p-map_4.0.0+~3.1.0+~3.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-p-map (4.0.0+~3.1.0+~3.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-promise-inflight. Preparing to unpack .../055-node-promise-inflight_1.0.1+~1.0.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-promise-inflight (1.0.1+~1.0.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ssri. Preparing to unpack .../056-node-ssri_8.0.1-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ssri (8.0.1-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-unique-filename. Preparing to unpack .../057-node-unique-filename_1.1.1+ds-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-unique-filename (1.1.1+ds-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-cacache. Preparing to unpack .../058-node-cacache_15.0.5+~cs13.9.21-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-cacache (15.0.5+~cs13.9.21-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-clean-yaml-object. Preparing to unpack .../059-node-clean-yaml-object_0.1.0-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-clean-yaml-object (0.1.0-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-clone. Preparing to unpack .../060-node-clone_2.1.2-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-clone (2.1.2-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-color-name. Preparing to unpack .../061-node-color-name_1.1.4+~1.1.1-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-color-name (1.1.4+~1.1.1-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-color-convert. Preparing to unpack .../062-node-color-convert_2.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-color-convert (2.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-colors. Preparing to unpack .../063-node-colors_1.4.0-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-colors (1.4.0-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-strip-ansi. Preparing to unpack .../064-node-strip-ansi_6.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-strip-ansi (6.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-defaults. Preparing to unpack .../065-node-defaults_1.0.3+~1.0.3-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-defaults (1.0.3+~1.0.3-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-wcwidth.js. Preparing to unpack .../066-node-wcwidth.js_1.0.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-wcwidth.js (1.0.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-columnify. Preparing to unpack .../067-node-columnify_1.5.4+~1.5.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-columnify (1.5.4+~1.5.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-console-control-strings. Preparing to unpack .../068-node-console-control-strings_1.1.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-console-control-strings (1.1.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-growl. Preparing to unpack .../069-node-growl_1.10.5-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-growl (1.10.5-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-sprintf-js. Preparing to unpack .../070-node-sprintf-js_1.1.2+ds1+~1.1.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-sprintf-js (1.1.2+ds1+~1.1.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-argparse. Preparing to unpack .../071-node-argparse_2.0.1-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-argparse (2.0.1-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-esprima. Preparing to unpack .../072-node-esprima_4.0.1+ds+~4.0.3-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-esprima (4.0.1+ds+~4.0.3-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-js-yaml. Preparing to unpack .../073-node-js-yaml_4.1.0+dfsg+~4.0.5-6_all.deb ... Unpacking node-js-yaml (4.1.0+dfsg+~4.0.5-6) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-lcov-parse. Preparing to unpack .../074-node-lcov-parse_1.0.0+20170612git80d039574ed9-5_all. deb ... Unpacking node-lcov-parse (1.0.0+20170612git80d039574ed9-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-log-driver. Preparing to unpack .../075-node-log-driver_1.2.7+git+20180219+bba1761737-7_all. deb ... Unpacking node-log-driver (1.2.7+git+20180219+bba1761737-7) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-is-plain-obj. Preparing to unpack .../076-node-is-plain-obj_3.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-is-plain-obj (3.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-is-buffer. Preparing to unpack .../077-node-is-buffer_2.0.5-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-is-buffer (2.0.5-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-kind-of. Preparing to unpack .../078-node-kind-of_6.0.3+dfsg-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-kind-of (6.0.3+dfsg-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-minimist. Preparing to unpack .../079-node-minimist_1.2.5+~cs5.3.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-minimist (1.2.5+~cs5.3.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-cssom. Preparing to unpack .../080-node-cssom_0.4.4-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-cssom (0.4.4-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-cssstyle. Preparing to unpack .../081-node-cssstyle_2.3.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-cssstyle (2.3.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-delayed-stream. Preparing to unpack .../082-node-delayed-stream_1.0.0-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-delayed-stream (1.0.0-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-combined-stream. Preparing to unpack .../083-node-combined-stream_1.0.8+~1.0.3-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-combined-stream (1.0.8+~1.0.3-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-mime. Preparing to unpack .../084-node-mime_3.0.0+dfsg+~cs3.96.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-mime (3.0.0+dfsg+~cs3.96.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-mime-types. Preparing to unpack .../085-node-mime-types_2.1.33-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-mime-types (2.1.33-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-form-data. Preparing to unpack .../086-node-form-data_3.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-form-data (3.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-events. Preparing to unpack .../087-node-events_3.3.0+~3.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-events (3.3.0+~3.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-https-proxy-agent. Preparing to unpack .../088-node-https-proxy-agent_5.0.0+~cs8.0.0-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-https-proxy-agent (5.0.0+~cs8.0.0-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-iconv-lite. Preparing to unpack .../089-node-iconv-lite_0.6.3-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-iconv-lite (0.6.3-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-lodash-packages. Preparing to unpack .../090-node-lodash-packages_4.17.21+dfsg+~cs8.31.198.202102 20-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-lodash-packages (4.17.21+dfsg+~cs8.31.198.20210220-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-stealthy-require. Preparing to unpack .../091-node-stealthy-require_1.1.1-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-stealthy-require (1.1.1-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-punycode. Preparing to unpack .../092-node-punycode_2.1.1-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-punycode (2.1.1-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-psl. Preparing to unpack .../093-node-psl_1.8.0+ds-6_all.deb ... Unpacking node-psl (1.8.0+ds-6) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-universalify. Preparing to unpack .../094-node-universalify_2.0.0-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-universalify (2.0.0-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-tough-cookie. Preparing to unpack .../095-node-tough-cookie_4.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-tough-cookie (4.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-webidl-conversions. Preparing to unpack .../096-node-webidl-conversions_7.0.0~1.1.0+~cs15.1.20180823 -2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-webidl-conversions (7.0.0~1.1.0+~cs15.1.20180823-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-commander. Preparing to unpack .../097-node-commander_9.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-commander (9.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-mute-stream. Preparing to unpack .../098-node-mute-stream_0.0.8+~0.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-mute-stream (0.0.8+~0.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-read. Preparing to unpack .../099-node-read_1.0.7-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-read (1.0.7-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ws. Preparing to unpack .../100-node-ws_8.5.0+~cs13.3.3-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ws (8.5.0+~cs13.3.3-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-jsdom. Preparing to unpack .../101-node-jsdom_19.0.0+~cs90.11.27-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-jsdom (19.0.0+~cs90.11.27-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-fetch. Preparing to unpack .../102-node-fetch_2.6.7+~2.5.12-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-fetch (2.6.7+~2.5.12-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-coveralls. Preparing to unpack .../103-node-coveralls_3.1.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-coveralls (3.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-mimic-response. Preparing to unpack .../104-node-mimic-response_3.1.0-7_all.deb ... Unpacking node-mimic-response (3.1.0-7) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-decompress-response. Preparing to unpack .../105-node-decompress-response_6.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-decompress-response (6.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-diff. Preparing to unpack .../106-node-diff_5.0.0~dfsg+~5.0.1-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-diff (5.0.0~dfsg+~5.0.1-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-err-code. Preparing to unpack .../107-node-err-code_2.0.3+dfsg-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-err-code (2.0.3+dfsg-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-time-stamp. Preparing to unpack .../108-node-time-stamp_2.2.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-time-stamp (2.2.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-fancy-log. Preparing to unpack .../109-node-fancy-log_1.3.3+~cs1.3.1-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-fancy-log (1.3.3+~cs1.3.1-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-signal-exit. Preparing to unpack .../110-node-signal-exit_3.0.6+~3.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-signal-exit (3.0.6+~3.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-foreground-child. Preparing to unpack .../111-node-foreground-child_2.0.0-3_all.deb ... Unpacking node-foreground-child (2.0.0-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-function-bind. Preparing to unpack .../112-node-function-bind_1.1.1+repacked+~1.0.3-1_all.deb . .. Unpacking node-function-bind (1.1.1+repacked+~1.0.3-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-has-unicode. Preparing to unpack .../113-node-has-unicode_2.0.1-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-has-unicode (2.0.1-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ansi-styles. Preparing to unpack .../114-node-ansi-styles_4.3.0+~4.2.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ansi-styles (4.3.0+~4.2.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-slice-ansi. Preparing to unpack .../115-node-slice-ansi_5.0.0+~cs9.0.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-slice-ansi (5.0.0+~cs9.0.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-string-width. Preparing to unpack .../116-node-string-width_4.2.3+~cs13.2.3-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-string-width (4.2.3+~cs13.2.3-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-wide-align. Preparing to unpack .../117-node-wide-align_1.1.3-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-wide-align (1.1.3-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-gauge. Preparing to unpack .../118-node-gauge_4.0.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-gauge (4.0.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-end-of-stream. Preparing to unpack .../119-node-end-of-stream_1.4.4+~1.4.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-end-of-stream (1.4.4+~1.4.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-pump. Preparing to unpack .../120-node-pump_3.0.0-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-pump (3.0.0-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-get-stream. Preparing to unpack .../121-node-get-stream_6.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-get-stream (6.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-lowercase-keys. Preparing to unpack .../122-node-lowercase-keys_2.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-lowercase-keys (2.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-json-buffer. Preparing to unpack .../123-node-json-buffer_3.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-json-buffer (3.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-p-cancelable. Preparing to unpack .../124-node-p-cancelable_2.1.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-p-cancelable (2.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-quick-lru. Preparing to unpack .../125-node-quick-lru_5.1.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-quick-lru (5.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-got. Preparing to unpack .../126-node-got_11.8.3+~cs58.7.37-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-got (11.8.3+~cs58.7.37-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-has-flag. Preparing to unpack .../127-node-has-flag_4.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-has-flag (4.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-hosted-git-info. Preparing to unpack .../128-node-hosted-git-info_4.0.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-hosted-git-info (4.0.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ip. Preparing to unpack .../129-node-ip_1.1.5+~1.1.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ip (1.1.5+~1.1.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ip-regex. Preparing to unpack .../130-node-ip-regex_4.3.0+~4.1.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ip-regex (4.3.0+~4.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-is-typedarray. Preparing to unpack .../131-node-is-typedarray_1.0.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-is-typedarray (1.0.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-isexe. Preparing to unpack .../132-node-isexe_2.0.0+~2.0.1-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-isexe (2.0.0+~2.0.1-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-json-parse-better-errors. Preparing to unpack .../133-node-json-parse-better-errors_1.0.2+~cs3.3.1-1_all.d eb ... Unpacking node-json-parse-better-errors (1.0.2+~cs3.3.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-encoding. Preparing to unpack .../134-node-encoding_0.1.13-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-encoding (0.1.13-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-jsonparse. Preparing to unpack .../135-node-jsonparse_1.3.1-10_all.deb ... Unpacking node-jsonparse (1.3.1-10) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-minipass. Preparing to unpack .../136-node-minipass_3.1.6+~cs8.7.18-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-minipass (3.1.6+~cs8.7.18-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-npm-bundled. Preparing to unpack .../137-node-npm-bundled_1.1.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-npm-bundled (1.1.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-osenv. Preparing to unpack .../138-node-osenv_0.1.5+~0.1.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-osenv (0.1.5+~0.1.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-validate-npm-package-name. Preparing to unpack .../139-node-validate-npm-package-name_3.0.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-validate-npm-package-name (3.0.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-npm-package-arg. Preparing to unpack .../140-node-npm-package-arg_8.1.5-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-npm-package-arg (8.1.5-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-object-assign. Preparing to unpack .../141-node-object-assign_4.1.1-6_all.deb ... Unpacking node-object-assign (4.1.1-6) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-opener. Preparing to unpack .../142-node-opener_1.5.2+~1.4.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-opener (1.5.2+~1.4.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-retry. Preparing to unpack .../143-node-retry_0.13.1+~0.12.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-retry (0.13.1+~0.12.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-promise-retry. Preparing to unpack .../144-node-promise-retry_2.0.1-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-promise-retry (2.0.1-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-promzard. Preparing to unpack .../145-node-promzard_0.3.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-promzard (0.3.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-set-blocking. Preparing to unpack .../146-node-set-blocking_2.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-set-blocking (2.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-slash. Preparing to unpack .../147-node-slash_3.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-slash (3.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-source-map. Preparing to unpack .../148-libjs-source-map_0.7.0++dfsg2+really.0.6.1-9_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-source-map (0.7.0++dfsg2+really.0.6.1-9) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-source-map. Preparing to unpack .../149-node-source-map_0.7.0++dfsg2+really.0.6.1-9_all.deb ... Unpacking node-source-map (0.7.0++dfsg2+really.0.6.1-9) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-source-map-support. Preparing to unpack .../150-node-source-map-support_0.5.21+ds+~0.5.4-1_all.deb . .. Unpacking node-source-map-support (0.5.21+ds+~0.5.4-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-spdx-license-ids. Preparing to unpack .../151-node-spdx-license-ids_3.0.11-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-spdx-license-ids (3.0.11-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-spdx-exceptions. Preparing to unpack .../152-node-spdx-exceptions_2.3.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-spdx-exceptions (2.3.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-spdx-expression-parse. Preparing to unpack .../153-node-spdx-expression-parse_3.0.1+~3.0.1-1_all.deb .. . Unpacking node-spdx-expression-parse (3.0.1+~3.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-spdx-correct. Preparing to unpack .../154-node-spdx-correct_3.1.1-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-spdx-correct (3.1.1-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-stack-utils. Preparing to unpack .../155-node-stack-utils_2.0.5+~2.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-stack-utils (2.0.5+~2.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-supports-color. Preparing to unpack .../156-node-supports-color_8.1.1+~8.1.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-supports-color (8.1.1+~8.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-tap-parser. Preparing to unpack .../157-node-tap-parser_7.0.0+ds1-6_all.deb ... Unpacking node-tap-parser (7.0.0+ds1-6) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-tap-mocha-reporter. Preparing to unpack .../158-node-tap-mocha-reporter_3.0.7+ds-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-tap-mocha-reporter (3.0.7+ds-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-text-table. Preparing to unpack .../159-node-text-table_0.2.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-text-table (0.2.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-tmatch. Preparing to unpack .../160-node-tmatch_5.0.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-tmatch (5.0.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-typedarray-to-buffer. Preparing to unpack .../161-node-typedarray-to-buffer_4.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-typedarray-to-buffer (4.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-validate-npm-package-license. Preparing to unpack .../162-node-validate-npm-package-license_3.0.4-2_all.deb .. . Unpacking node-validate-npm-package-license (3.0.4-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-whatwg-fetch. Preparing to unpack .../163-node-whatwg-fetch_3.6.2-5_all.deb ... Unpacking node-whatwg-fetch (3.6.2-5) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-write-file-atomic. Preparing to unpack .../164-node-write-file-atomic_3.0.3+~3.0.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-write-file-atomic (3.0.3+~3.0.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-abbrev. Preparing to unpack .../165-node-abbrev_1.1.1+~1.1.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-abbrev (1.1.1+~1.1.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-archy. Preparing to unpack .../166-node-archy_1.0.0-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-archy (1.0.0-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-chalk. Preparing to unpack .../167-node-chalk_4.1.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-chalk (4.1.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-cli-table. Preparing to unpack .../168-node-cli-table_0.3.11+~cs0.13.3-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-cli-table (0.3.11+~cs0.13.3-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-depd. Preparing to unpack .../169-node-depd_2.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-depd (2.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-nopt. Preparing to unpack .../170-node-nopt_5.0.0-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-nopt (5.0.0-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-npmlog. Preparing to unpack .../171-node-npmlog_6.0.1+~4.1.4-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-npmlog (6.0.1+~4.1.4-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-tar. Preparing to unpack .../172-node-tar_6.1.11+ds1+~cs6.0.6-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-tar (6.1.11+ds1+~cs6.0.6-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-which. Preparing to unpack .../173-node-which_2.0.2+~cs1.3.2-2_all.deb ... Unpacking node-which (2.0.2+~cs1.3.2-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-gyp. Preparing to unpack .../174-node-gyp_8.4.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-gyp (8.4.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-ini. Preparing to unpack .../175-node-ini_2.0.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-ini (2.0.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-negotiator. Preparing to unpack .../176-node-negotiator_0.6.2+~0.6.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-negotiator (0.6.2+~0.6.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-resolve. Preparing to unpack .../177-node-resolve_1.20.0+~cs5.27.9-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-resolve (1.20.0+~cs5.27.9-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-normalize-package-data. Preparing to unpack .../178-node-normalize-package-data_3.0.3+~2.4.1-1_all.deb . .. Unpacking node-normalize-package-data (3.0.3+~2.4.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-read-package-json. Preparing to unpack .../179-node-read-package-json_4.1.1-1_all.deb ... Unpacking node-read-package-json (4.1.1-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package node-tap. Preparing to unpack .../180-node-tap_12.0.1+ds-4_all.deb ... Unpacking node-tap (12.0.1+ds-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package npm. Preparing to unpack .../181-npm_8.5.1~ds-1_all.deb ... Unpacking npm (8.5.1~ds-1) ... Setting up node-delayed-stream (1.0.0-5) ... Setting up libuv1-dev:amd64 (1.43.0-1ubuntu0.1) ... Setting up node-colors (1.4.0-3) ... Setting up node-log-driver (1.2.7+git+20180219+bba1761737-7) ... Setting up node-fs.realpath (1.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-diff (5.0.0~dfsg+~5.0.1-3) ... Setting up node-object-assign (4.1.1-6) ... Setting up node-abbrev (1.1.1+~1.1.2-1) ... Setting up libjs-sprintf-js (1.1.2+ds1+~1.1.2-1) ... Setting up node-yallist (4.0.0+~4.0.1-1) ... Setting up libjs-inherits (2.0.4-4) ... Setting up node-p-cancelable (2.1.1-1) ... Setting up node-ansi-regex (5.0.1-1) ... Setting up libnode-dev (12.22.9~dfsg-1ubuntu3.4) ... Setting up node-slash (3.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-util-deprecate (1.0.2-3) ... Setting up node-retry (0.13.1+~0.12.1-1) ... Setting up node-arrify (2.0.1-2) ... Setting up node-ansistyles (0.1.3-5) ... Setting up node-delegates (1.0.0-3) ... Setting up node-depd (2.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-isexe (2.0.0+~2.0.1-4) ... Setting up node-jsonparse (1.3.1-10) ... Setting up node-escape-string-regexp (4.0.0-2) ... Setting up libjs-source-map (0.7.0++dfsg2+really.0.6.1-9) ... Setting up node-negotiator (0.6.2+~0.6.1-1) ... Setting up node-stack-utils (2.0.5+~2.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-color-name (1.1.4+~1.1.1-2) ... Setting up node-growl (1.10.5-4) ... Setting up node-json-buffer (3.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-console-control-strings (1.1.0-2) ... Setting up node-abab (2.0.5-2) ... Setting up node-indent-string (4.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-function-bind (1.1.1+repacked+~1.0.3-1) ... Setting up node-clone (2.1.2-3) ... Setting up node-p-map (4.0.0+~3.1.0+~3.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-iferr (1.0.2+~1.0.2-1) ... Setting up node-chownr (2.0.0-1) ... Setting up node-has-flag (4.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-lodash-packages (4.17.21+dfsg+~cs8.31.198.20210220-5) ... Setting up libjs-psl (1.8.0+ds-6) ... Setting up node-asap (2.0.6+~2.0.0-1) ... Setting up node-mime (3.0.0+dfsg+~cs3.96.1-1) ... Setting up node-inherits (2.0.4-4) ... Setting up node-path-is-absolute (2.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-universalify (2.0.0-3) ... Setting up node-ini (2.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-safe-buffer (5.2.1+~cs2.1.2-2) ... Setting up node-promise-inflight (1.0.1+~1.0.0-1) ... Setting up node-combined-stream (1.0.8+~1.0.3-1) ... Setting up node-json-parse-better-errors (1.0.2+~cs3.3.1-1) ... Setting up node-sprintf-js (1.1.2+ds1+~1.1.2-1) ... Setting up node-tmatch (5.0.0-4) ... Setting up node-mime-types (2.1.33-1) ... Setting up node-err-code (2.0.3+dfsg-3) ... Setting up node-balanced-match (2.0.0-1) ... Setting up node-brace-expansion (2.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-spdx-exceptions (2.3.0-2) ... Setting up node-lcov-parse (1.0.0+20170612git80d039574ed9-5) ... Setting up node-cssom (0.4.4-3) ... Setting up node-strip-ansi (6.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-set-blocking (2.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-npm-bundled (1.1.2-1) ... Setting up node-signal-exit (3.0.6+~3.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-which (2.0.2+~cs1.3.2-2) ... Setting up node-source-map (0.7.0++dfsg2+really.0.6.1-9) ... Setting up node-wrappy (1.0.2-2) ... Setting up node-text-table (0.2.0-4) ... Setting up node-asynckit (0.4.0-4) ... Setting up node-ip (1.1.5+~1.1.0-1) ... Setting up node-quick-lru (5.1.1-1) ... Setting up node-punycode (2.1.1-5) ... Setting up node-defaults (1.0.3+~1.0.3-1) ... Setting up node-mute-stream (0.0.8+~0.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-mimic-response (3.1.0-7) ... Setting up node-commander (9.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-whatwg-fetch (3.6.2-5) ... Setting up libjs-typedarray-to-buffer (4.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-graceful-fs (4.2.4+repack-1) ... Setting up node-clean-yaml-object (0.1.0-5) ... Setting up node-aproba (2.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-esprima (4.0.1+ds+~4.0.3-2) ... Setting up node-ip-regex (4.3.0+~4.1.1-1) ... Setting up node-stealthy-require (1.1.1-5) ... Setting up node-spdx-license-ids (3.0.11-1) ... Setting up node-string-decoder (1.3.0-5) ... Setting up node-time-stamp (2.2.0-1) ... Setting up libjs-events (3.3.0+~3.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-mkdirp (1.0.4+~1.0.2-1) ... Setting up node-run-queue (2.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-core-util-is (1.0.3-1) ... Setting up node-minimatch (3.1.1+~3.0.5-1) ... Setting up node-opener (1.5.2+~1.4.0-1) ... Setting up node-archy (1.0.0-4) ... Setting up node-imurmurhash (0.1.4+dfsg+~0.1.1-1) ... Setting up node-foreground-child (2.0.0-3) ... Setting up node-read (1.0.7-3) ... Setting up node-nopt (5.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-is-buffer (2.0.5-2) ... Setting up node-color-convert (2.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-webidl-conversions (7.0.0~1.1.0+~cs15.1.20180823-2) ... Setting up node-isarray (2.0.5-3) ... Setting up node-osenv (0.1.5+~0.1.0-1) ... Setting up node-is-plain-obj (3.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-ms (2.1.3+~cs0.7.31-2) ... Setting up libjs-is-typedarray (1.0.0-4) ... Setting up node-lowercase-keys (2.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-decompress-response (6.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-process-nextick-args (2.0.1-2) ... Setting up node-has-unicode (2.0.1-4) ... Setting up node-fs-write-stream-atomic (1.0.10-5) ... Setting up gyp (0.1+20210831gitd6c5dd5-5) ... Setting up node-readable-stream (3.6.0+~cs3.0.0-1) ... Setting up node-ssri (8.0.1-2) ... Setting up node-lru-cache (6.0.0+~5.1.1-1) ... Setting up node-promise-retry (2.0.1-2) ... Setting up node-supports-color (8.1.1+~8.1.1-1) ... Setting up node-once (1.4.0-4) ... Setting up node-psl (1.8.0+ds-6) ... Setting up node-resolve (1.20.0+~cs5.27.9-1) ... Setting up node-are-we-there-yet (3.0.0+~1.1.0-1) ... Setting up node-kind-of (6.0.3+dfsg-2) ... Setting up node-debug (4.3.2+~cs4.1.7-1) ... Setting up node-events (3.3.0+~3.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-minimist (1.2.5+~cs5.3.2-1) ... Setting up node-argparse (2.0.1-2) ... Setting up node-fancy-log (1.3.3+~cs1.3.1-2) ... Setting up node-promzard (0.3.0-2) ... Setting up node-wcwidth.js (1.0.2-1) ... Setting up node-cssstyle (2.3.0-2) ... Setting up node-source-map-support (0.5.21+ds+~0.5.4-1) ... Setting up node-iconv-lite (0.6.3-2) ... Setting up node-unique-filename (1.1.1+ds-1) ... Setting up node-ansi-styles (4.3.0+~4.2.0-1) ... Setting up node-form-data (3.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-chalk (4.1.2-1) ... Setting up node-spdx-expression-parse (3.0.1+~3.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-is-typedarray (1.0.0-4) ... Setting up node-inflight (1.0.6-2) ... Setting up node-hosted-git-info (4.0.2-1) ... Setting up node-tough-cookie (4.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-encoding (0.1.13-2) ... Setting up node-js-yaml (4.1.0+dfsg+~4.0.5-6) ... Setting up node-slice-ansi (5.0.0+~cs9.0.0-4) ... Setting up node-string-width (4.2.3+~cs13.2.3-1) ... Setting up node-semver (7.3.5+~7.3.8-1) ... Setting up node-builtins (4.0.0-1) ... Setting up node-end-of-stream (1.4.4+~1.4.1-1) ... Setting up node-pump (3.0.0-5) ... Setting up node-columnify (1.5.4+~1.5.1-1) ... Setting up node-agent-base (6.0.2+~cs5.4.2-1) ... Setting up node-validate-npm-package-name (3.0.0-4) ... Setting up node-spdx-correct (3.1.1-2) ... Setting up node-glob (7.2.1+~cs7.6.15-1) ... Setting up node-get-stream (6.0.1-1) ... Setting up node-got (11.8.3+~cs58.7.37-1) ... Setting up node-typedarray-to-buffer (4.0.0-2) ... Setting up node-cli-table (0.3.11+~cs0.13.3-1) ... Setting up node-tap-parser (7.0.0+ds1-6) ... Setting up node-minipass (3.1.6+~cs8.7.18-1) ... Setting up node-wide-align (1.1.3-4) ... Setting up node-npm-package-arg (8.1.5-1) ... Setting up node-https-proxy-agent (5.0.0+~cs8.0.0-3) ... Setting up node-rimraf (3.0.2-1) ... Setting up node-validate-npm-package-license (3.0.4-2) ... Setting up node-write-file-atomic (3.0.3+~3.0.2-1) ... Setting up node-copy-concurrently (1.0.5-8) ... Setting up node-move-concurrently (1.0.1-4) ... Setting up node-gauge (4.0.2-1) ... Setting up node-tap-mocha-reporter (3.0.7+ds-2) ... Setting up node-normalize-package-data (3.0.3+~2.4.1-1) ... Setting up node-ws (8.5.0+~cs13.3.3-2) ... Setting up node-jsdom (19.0.0+~cs90.11.27-1) ... Setting up node-tar (6.1.11+ds1+~cs6.0.6-1) ... Setting up node-tap (12.0.1+ds-4) ... Setting up node-npmlog (6.0.1+~4.1.4-1) ... Setting up node-cacache (15.0.5+~cs13.9.21-3) ... Setting up node-read-package-json (4.1.1-1) ... Setting up node-fetch (2.6.7+~2.5.12-1) ... Setting up node-gyp (8.4.1-1) ... Setting up npm (8.5.1~ds-1) ... Setting up node-coveralls (3.1.1-1) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... |
You can check the Node.js version with this command:
npm -v |
8.5.1 |
As always, I hope this helps those looking for concise and complete free answer.
Parametric Queries
In 2021, I wrote a MySQL example for my class on the usefulness of Common Table Expressions (CTEs). When discussing the original post, I would comment on how you could extend the last example to build a parametric reporting table.
Somebody finally asked for a concrete example. So, this explains how to build a sample MySQL parametric query by leveraging a filter cross join and tests the parameter use with a Python script.
You can build this in any database you prefer but I used a studentdb database with the sakila sample database installed. I’ve granted privileges to both databases to the student user. The following SQL is required for the example:
-- Conditionally drop the levels table. DROP TABLE IF EXISTS levels; -- Create the levels list. CREATE TABLE levels ( level_id int unsigned primary key auto_increment , parameter_set enum('Three','Five') , description varchar(20) , min_roles int , max_roles int ); -- Insert values into the list table. INSERT INTO levels ( parameter_set , description , min_roles , max_roles ) VALUES ('Three','Hollywood Star', 30, 99999) ,('Three','Prolific Actor', 20, 29) ,('Three','Newcommer',1,19) ,('Five','Newcommer',1,9) ,('Five','Junior Actor',10,19) ,('Five','Professional Actor',20,29) ,('Five','Major Actor',30,39) ,('Five','Hollywood Star',40,99999); |
The sample lets you use the three or five value labels while filtering on any partial full_name value as the result of the query below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | -- Query the data. WITH actors AS (SELECT a.actor_id , a.first_name , a.last_name , COUNT(*) AS num_roles FROM sakila.actor a INNER JOIN sakila.film_actor fa ON a.actor_id = fa.actor_id GROUP BY actor_id) SELECT CONCAT(a.last_name,', ',a.first_name) full_name , l.description , a.num_roles FROM actors a CROSS JOIN levels l WHERE a.num_roles BETWEEN l.min_roles AND l.max_roles AND l.parameter_set = 'Five' AND a.last_name LIKE CONCAT('H','%') ORDER BY a.last_name , a.first_name; |
They extends a concept exercise found in Chapter 9 on subqueries in Alan Beaulieu’s Learning SQL book.
This is the parametric Python program, which embeds the function locally (to make it easier for those who don’t write a lot of Python). You could set the PYTHONPATH to a relative src directory and import your function if you prefer.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 | #!/usr/bin/python # Import the libraries. import sys import mysql.connector from mysql.connector import errorcode # ============================================================ # Define function to check and replace arguments. def check_replace(argv): # Set defaults for incorrect parameter values. defaults = ("Three","_") # Declare empty list variables. inputs = [] args = () # Check whether or not parameters exist after file name. if isinstance(argv,list) and len(argv) != 0: # Check whether there are at least two parameters. if len(argv) >= 2: # Loop through available command-line arguments. for element in argv: # Check first of two parameter values and substitute # default value if input value is an invalid option. if len(inputs) == 0 and (element in ('Three','Five')) or \ len(inputs) == 1 and (isinstance(element,str)): inputs.append(element) elif len(inputs) == 0: inputs.append(defaults[0]) elif len(inputs) == 1: inputs.append(defaults[1]) # Assign arguments to parameters. args = (inputs) # Check whether only one parameter value exists. elif len(argv) == 1 and (argv[0] in ('Three','Five')): args = (argv[0],"_") # Assume only one parameter is valid and substitute an # empty string as the second parameter. else: args = (defaults[0],"_") # Substitute defaults when missing parameters. else: args = defaults # Return parameters as a tuple. return args # ============================================================ # Assign command-line argument list to variable by removing # the program file name. # ============================================================ params = check_replace(sys.argv[1:]) # ============================================================ # Attempt the query. # ============================================================ # Use a try-catch block to manage the connection. # ============================================================ try: # Open connection. cnx = mysql.connector.connect(user='student', password='student', host='127.0.0.1', database='studentdb') # Create cursor. cursor = cnx.cursor() # Set the query statement. query = ("WITH actors AS " "(SELECT a.first_name " " , a.last_name " " , COUNT(*) AS num_roles " " FROM sakila.actor a INNER JOIN sakila.film_actor fa " " ON a.actor_id = fa.actor_id " " GROUP BY a.first_name " " , a.last_name ) " " SELECT CONCAT(a.last_name,', ',a.first_name) AS full_name " " , l.description " " , a.num_roles " " FROM actors a CROSS JOIN levels l " " WHERE a.num_roles BETWEEN l.min_roles AND l.max_roles " " AND l.parameter_set = %s " " AND a.last_name LIKE CONCAT(%s,'%') " " ORDER BY a.last_name " " , a.first_name") # Execute cursor. cursor.execute(query, params) # Display the rows returned by the query. for (full_name, description, num_roles) in cursor: print('{0} is a {1} with {2} films.'.format( full_name.title() , description.title() , num_roles)) # Close cursor. cursor.close() # ------------------------------------------------------------ # Handle exception and close connection. except mysql.connector.Error as e: if e.errno == errorcode.ER_ACCESS_DENIED_ERROR: print("Something is wrong with your user name or password") elif e.errno == errorcode.ER_BAD_DB_ERROR: print("Database does not exist") else: print("Error code:", e.errno) # error number print("SQLSTATE value:", e.sqlstate) # SQLSTATE value print("Error message:", e.msg) # error message # Close the connection when the try block completes. else: cnx.close() |
As always, I hope this helps those trying to understand how CTEs can solve problems that would otherwise be coded in external imperative languages like Python.