Archive for the ‘Linux DBA’ tag
Bash Arrays & MySQL
Student questions are always interesting! They get me to think and to write. The question this time is: “How do I write a Bash Shell script to process multiple MySQL script files?” This post builds the following model (courtesy of MySQL Workbench) by using a bash shell script and MySQL script files, but there’s a disclaimer on this post. It shows both insecure and secure approaches and you should avoid the insecure ones.
It seems a quick refresher on how to use arrays in bash shell may be helpful. While it’s essential in a Linux environment, it’s seems not everyone masters the bash shell.
Especially, since I checked my Learning the Bash Shell (2nd Edition) and found a typo on how you handle arrays in the bash shell, and it’s a mistake that could hang newbies up (on page 161). Perhaps I should update my copy because I bought it in 1998. 😉 It was good then, and the new edition is probably better. The error is probably corrected in the current Learning the Bash Shell, but if not, the following examples show you how to use arrays in loops.
Naturally, these do presume some knowledge of working with bash shell, like the first line always is the same in any bash shell script. That you open an if-statement with an if and close it with a fi, and that you else-if is elif; and that a semicolon between a for-statement and the do statement is required when they’re on the same line because they’re two statements.
If you’re new to bash shell arrays, click on the link below to expand a brief tutorial. It takes you through three progressive examples of working with bash arrays.
Working with bash Arrays ↓
A basic example of working with an array in bash shell is the following list1.sh script:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | #!/usr/bin/bash # Print script name. echo $0 #!/usr/bin/bash # Define an array. declare -a cmd=("one" "two" "three") # Call the array elements. for i in ${cmd[*]}; do echo ${i} done |
Line 8 declares the cmd array by assigning three strings. Line 12 returns the elements of the array to the ${i} variable, which lets you manage them one at a time. You use the chmod command to make the list1.sh executable, like this:
chmod 755 list1.sh |
Then, you can run it like this from the present working directory (pwd):
./list1.sh |
It should print:
one two three |
The list2.sh example changes the cmd array declaration from list1.sh. It declares the cmd array as an empty array, and then it assigns elements by index numbers (using a zero-based index), as shown below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | #!/usr/bin/bash # Define an array. declare -a cmd # Assign elements to an array. cmd[0]="one" cmd[1]="two" cmd[2]="three" # Call the array elements. for i in ${cmd[*]}; do echo ${i} done |
Lines 7 through 9 assign values to the elements of the cmd array. You would chmod the file, and run the file as qualified above for the list1.sh script.
The last pre-implementation example requires that you create three demonstration scripts, the one.sh, two.sh, and three.sh scripts. You should put them in the same directory as the list3.sh script.
The demonstration scripts should all have the same code, like this:
1 2 3 4 | #!/usr/bin/bash # Print script name. echo $0 |
Line 4 returns command line parameter $0 or ${0}, which is always the command line program’s file name. The file name may be provided as a relative or absolute file name, and if that’s new to you please check out The Linux Command Line: A Complete Introduction (also downloadable as a PDF for free).
The list3.sh script should contain the following:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | #!/usr/bin/bash <code> # Define an array. declare -a cmd # Assign elements to an array. cmd[0]="one.sh" cmd[1]="two.sh" cmd[2]="three.sh" # Call the array elements. for i in ${cmd[*]}; do `pwd`/${i} done |
When you run the list3.sh script from the /home/student/Code/bash directory with a local syntax, the script should return the fully qualified file names of the subshell programs. The output should look like this:
/home/student/Code/bash/one.sh /home/student/Code/bash/two.sh /home/student/Code/bash/three.sh |
The list3.sh script provides the present working directory (pwd) and the one.sh, two.sh, and three.sh scripts return only their executable name. For example, if you ran one.sh with the following syntax:
./one.sh |
It returns
./one.sh |
Only one more trick needs to be qualified before our main MySQL examples. That trick is how you pass parameters to a bash shell script. For reference, this is the part that’s insecure because user command histories are available inside the Linux OS.
Here’s a hello_whom.sh script to demonstrates the concept of parameter passing:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | #!/usr/bin/bash # This says hello to the argument while managing no argument. if [[ ${#} = 1 ]]; then echo 'The '${0}' program says: "Hello '${1}'!"' elif [[ ${#} > 1 ]]; then echo 'The '${0}' program wants to know if you have more than one name?' else echo 'The '${0}' program wants to know if you have a name?' fi |
If you need more on how parameters are passed and managed, you can check a prior blob post on Handling bash Parameters, or check the bash help pages. The following leverages bash arrays to run scripts and query the MySQL database from the command line.
You will need the three batch SQL files first, so here they are:
Setup SQL Files ↓
The actor.sql file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | -- Use the sampledb database. USE sampledb; -- Disable foreign key checking. SET foreign_key_checks = 0; -- Drop an actor table. DROP TABLE IF EXISTS actor; -- Create an actor table. CREATE TABLE actor ( actor_id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT , actor_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL ); -- Insert two rows. INSERT INTO actor (actor_name) VALUES ('Chris Hemsworth'); INSERT INTO actor (actor_name) VALUES ('Chris Pine'); INSERT INTO actor (actor_name) VALUES ('Chris Pratt'); |
The film.sql file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | -- Use the sampledb database. USE sampledb; -- Disable foreign key checking. SET foreign_key_checks = 0; -- Drop a film table. DROP TABLE IF EXISTS film; -- Create a film table. CREATE TABLE film ( film_id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT , film_name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL ); -- Insert rows. INSERT INTO film (film_name) VALUES ('Thor'); INSERT INTO film (film_name) VALUES ('Thor: The Dark World'); INSERT INTO film (film_name) VALUES ('Star Trek'); INSERT INTO film (film_name) VALUES ('Star Trek into Darkness'); INSERT INTO film (film_name) VALUES ('Guardians of the Galaxy'); |
The movie.sql file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 | -- Use the sampledb database. USE sampledb; -- Disable foreign key checking. SET foreign_key_checks = 0; -- Drop an movie table. DROP TABLE IF EXISTS movie; -- Create an movie table. CREATE TABLE movie ( movie_id int unsigned PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT , actor_id int unsigned NOT NULL , film_id int unsigned NOT NULL , CONSTRAINT actor_fk FOREIGN KEY (actor_id) REFERENCES actor (actor_id) , CONSTRAINT film_fk FOREIGN KEY (film_id) REFERENCES film(film_id)); -- Use scalar subqueries to discover surrogate keys by using the faux natural key. INSERT INTO movie ( actor_id , film_id ) VALUES ((SELECT actor_id FROM actor WHERE actor_name = 'Chris Hemsworth') ,(SELECT film_id FROM film WHERE film_name = 'Thor')); -- Use scalar subqueries to discover surrogate keys by using the faux natural key. INSERT INTO movie ( actor_id , film_id ) VALUES ((SELECT actor_id FROM actor WHERE actor_name = 'Chris Hemsworth') ,(SELECT film_id FROM film WHERE film_name = 'Thor: The Dark World')); -- Use scalar subqueries to discover surrogate keys by using the faux natural key. INSERT INTO movie ( actor_id , film_id ) VALUES ((SELECT actor_id FROM actor WHERE actor_name = 'Chris Pine') ,(SELECT film_id FROM film WHERE film_name = 'Star Trek')); -- Use scalar subqueries to discover surrogate keys by using the faux natural key. INSERT INTO movie ( actor_id , film_id ) VALUES ((SELECT actor_id FROM actor WHERE actor_name = 'Chris Pine') ,(SELECT film_id FROM film WHERE film_name = 'Star Trek into Darkness')); -- Use scalar subqueries to discover surrogate keys by using the faux natural key. INSERT INTO movie ( actor_id , film_id ) VALUES ((SELECT actor_id FROM actor WHERE actor_name = 'Chris Pratt') ,(SELECT film_id FROM film WHERE film_name = 'Guardians of the Galaxy')); |
The following list_mysql.sh shell script expects to receive the username, password, database and fully qualified path in that specific order. The script names are entered manually because this should be a unit test script. Naturally, you can extend the script to manage those parameters but as mentioned I see this type of solution as a developer machine only script to simplify unit testing. Anything beyond that is risky!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 | #!/usr/bin/bash # Assign user and password username="${1}" password="${2}" database="${3}" directory="${4}" # List the parameter values passed. echo "Username: " ${username} echo "Password: " ${password} echo "Database: " ${database} echo "Directory: " ${directory} echo "" # Define an array. declare -a cmd # Assign elements to an array. cmd[0]="actor.sql" cmd[1]="film.sql" cmd[2]="movie.sql" # Call the array elements. for i in ${cmd[*]}; do mysql -s -u${username} -p${password} -D${database} < ${directory}/${i} > /dev/null 2>/dev/null done # Connect and pipe the query result minus errors and warnings to the while loop. mysql -u${username} -p${password} -D${database} <<<'show tables' 2>/dev/null | # Read through the piped result until it's empty but format the title. while IFS='\n' read list; do if [[ ${list} = "Tables_in_sampledb" ]]; then echo $list echo "----------------------------------------" else echo $list fi done echo "" # Connect and pipe the query result minus errors and warnings to the while loop. mysql -u${username} -p${password} -D${database} <<<'SELECT CONCAT(a.actor_name," in ",f.film_name) AS "Actors in Films" FROM actor a INNER JOIN movie m ON a.actor_id = m.actor_id INNER JOIN film f ON m.film_id = f.film_id' 2>/dev/null | # Read through the piped result until it's empty but format the title. while IFS='\n' read actor_name; do if [[ ${actor_name} = "Actors in Films" ]]; then echo $actor_name echo "----------------------------------------" else echo $actor_name fi done |
The IFS (Internal Field Separator) works with whitespace by default. The IFS on lines 33 and 47 sets the IFS to a line return ('\n'). That’s the trick to display the data, and you can read more about the IFS in this question and answer post.
You can run this script with the following input parameters from the local directory where you deploy it. The a parameters are: (1) username, (2) password, (3) database, and (4) a fully qualified path to the SQL setup files.
./list_mysql.sh student student sampledb "/home/student/Code/bash/mysql" |
With valid input values, the list_mysql.sh bash script generates the following output, which confirms inputs and verifies actions taken by the scripts with queries:
Username: student Password: student Database: sampledb Directory: /home/student/Code/bash/mysql Tables_in_sampledb ---------------------------------------- actor film movie Actors in Films ---------------------------------------- Chris Hemsworth in Thor Chris Hemsworth in Thor: The Dark World Chris Pine in Star Trek Chris Pine in Star Trek into Darkness Chris Pine in Guardians of the Galaxy |
If you forgot to provide the required inputs to the list_mysql.sh bash script, it alternatively returns the following output:
Username: Password: Database: Directory: ./list_mysql.sh: line 25: /actor.sql: No such file or directory ./list_mysql.sh: line 25: /film.sql: No such file or directory ./list_mysql.sh: line 25: /movie.sql: No such file or directory |
The secure way removes the password at a minimum! The refactored program will require you to manually enter the password for all elements of the array (three in this sample), and twice for the two queries. Here’s the refactored code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | #!/usr/bin/bash # Assign user and password username="${1}" database="${2}" directory="${3}" # List the parameter values passed. echo "Username: " ${username} echo "Database: " ${database} echo "Directory: " ${directory} echo "" # Define an array. declare -a cmd # Assign elements to an array. cmd[0]="actor.sql" cmd[1]="film.sql" cmd[2]="movie.sql" # Call the array elements. for i in ${cmd[*]}; do mysql -s -u${username} -p -D${database} < ${directory}/${i} > /dev/null 2>/dev/null done # Connect and pipe the query result minus errors and warnings to the while loop. mysql -u${username} -p -D${database} <<<'show tables' 2>/dev/null | # Read through the piped result until it's empty. while IFS='\n' read list; do if [[ ${list} = "Tables_in_sampledb" ]]; then echo $list echo "----------------------------------------" else echo $list fi done echo "" # Connect and pipe the query result minus errors and warnings to the while loop. mysql -u${username} -p -D${database} <<<'SELECT CONCAT(a.actor_name," in ",f.film_name) AS "Actors in Films" FROM actor a INNER JOIN movie m ON a.actor_id = m.actor_id INNER JOIN film f ON m.film_id = f.film_id' 2>/dev/null | # Read through the piped result until it's empty. while IFS='\n' read actor_name; do if [[ ${actor_name} = "Actors in Films" ]]; then echo $actor_name echo "----------------------------------------" else echo $actor_name fi done |
Please let me know if you think there should be any more scaffolding for newbies in this post. As always, I hope this helps those looking for this type of solution.
Add Gedit Plugins
Fedora comes with vim and gedit installed but the gedit installation is bare bones. You can update gedit to include supplemental Plug-ins with the following yum command as the root user:
yum install -y gedit-plugins |
It generates the following log file:
Loaded plugins: langpacks, refresh-packagekit mysql-connectors-community | 2.5 kB 00:00 mysql-tools-community | 2.5 kB 00:00 mysql56-community | 2.5 kB 00:00 pgdg93 | 3.6 kB 00:00 updates/20/x86_64/metalink | 14 kB 00:00 updates | 4.9 kB 00:00 (1/2): pgdg93/20/x86_64/primary_db | 86 kB 00:00 (2/2): updates/20/x86_64/primary_db | 11 MB 00:03 (1/2): updates/20/x86_64/pkgtags | 1.5 MB 00:00 (2/2): updates/20/x86_64/updateinfo | 2.0 MB 00:01 Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package gedit-plugins.x86_64 0:3.10.1-1.fc20 will be installed --> Processing Dependency: libgit2-glib for package: gedit-plugins-3.10.1-1.fc20.x86_64 --> Running transaction check ---> Package libgit2-glib.x86_64 0:0.0.6-2.fc20 will be installed --> Processing Dependency: libgit2.so.0()(64bit) for package: libgit2-glib-0.0.6-2.fc20.x86_64 --> Running transaction check ---> Package libgit2.x86_64 0:0.19.0-2.fc20 will be installed --> Processing Dependency: libxdiff.so.1()(64bit) for package: libgit2-0.19.0-2.fc20.x86_64 --> Processing Dependency: libhttp_parser.so.2()(64bit) for package: libgit2-0.19.0-2.fc20.x86_64 --> Running transaction check ---> Package http-parser.x86_64 0:2.0-5.20121128gitcd01361.fc20 will be installed ---> Package libxdiff.x86_64 0:1.0-3.fc20 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: gedit-plugins x86_64 3.10.1-1.fc20 updates 830 k Installing for dependencies: http-parser x86_64 2.0-5.20121128gitcd01361.fc20 fedora 23 k libgit2 x86_64 0.19.0-2.fc20 fedora 281 k libgit2-glib x86_64 0.0.6-2.fc20 fedora 82 k libxdiff x86_64 1.0-3.fc20 fedora 33 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package (+4 Dependent packages) Total download size: 1.2 M Installed size: 5.2 M Downloading packages: (1/5): http-parser-2.0-5.20121128gitcd01361.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 23 kB 00:00 (2/5): libgit2-0.19.0-2.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 281 kB 00:00 (3/5): libgit2-glib-0.0.6-2.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 82 kB 00:00 (4/5): libxdiff-1.0-3.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 33 kB 00:00 (5/5): gedit-plugins-3.10.1-1.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 830 kB 00:01 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 899 kB/s | 1.2 MB 00:01 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction (shutdown inhibited) Installing : libxdiff-1.0-3.fc20.x86_64 1/5 Installing : http-parser-2.0-5.20121128gitcd01361.fc20.x86_64 2/5 Installing : libgit2-0.19.0-2.fc20.x86_64 3/5 Installing : libgit2-glib-0.0.6-2.fc20.x86_64 4/5 Installing : gedit-plugins-3.10.1-1.fc20.x86_64 5/5 Verifying : libgit2-0.19.0-2.fc20.x86_64 1/5 Verifying : libgit2-glib-0.0.6-2.fc20.x86_64 2/5 Verifying : gedit-plugins-3.10.1-1.fc20.x86_64 3/5 Verifying : http-parser-2.0-5.20121128gitcd01361.fc20.x86_64 4/5 Verifying : libxdiff-1.0-3.fc20.x86_64 5/5 Installed: gedit-plugins.x86_64 0:3.10.1-1.fc20 Dependency Installed: http-parser.x86_64 0:2.0-5.20121128gitcd01361.fc20 libgit2.x86_64 0:0.19.0-2.fc20 libgit2-glib.x86_64 0:0.0.6-2.fc20 libxdiff.x86_64 0:1.0-3.fc20 Complete! |
When you launch the gedit utility, you click on the
Gedit Plug-in Installation
- After you install the Gedit Plug-ins, you can configure the plug-ins by launching Gedit and then click on the
geditmenu option. Then, click on the Preferences menu option to enable the new plugins, like the Embedded Terminal plug-in.
- You have four tab options when working with the Preferences menu. The first tab is the View tab, as shown to the left.
- The second tab is the Editor tab, as shown to the left.
- The third tab is the Font & Colors tab, as shown to the left.
- The fourth tab is the Plugins tab, as shown to the left. Scroll down the list and check the Embedded Terminal and Python Console plug-ins’ checkbox. The Embedded Terminal lets you edit a file and have command line access to a Terminal session from the
geditmenu; and the Python Console session from thegeditmenu.
- Click on the View menu, and then choose the Bottom Panel menu option.
- After enabling the Bottom Panel in the Gedit menu, you can edit a file and click on the Terminal by simply clicking on the subpanel. You can see the split image on the left. There’s also a set of bottom tabs that lets you switch from a Linux Terminal session to the Python console.
As always, I hope this helps those working with gedit on the Fedora operating system.
Eclipse, Java, MySQL
While I previously blogged about installing Netbeans 8, some of my students would prefer to use the Eclipse IDE. This post shows how to install and configure Eclipse IDE, include the mysql-connector-java.jar, and write Java to access the MySQL.
You can download Eclipse IDE and then open it in Fedora’s Archive Manager. You can use the Archive Manager to Extract the Eclipse IDE to a directory of your choice. I opted to extract it into my student user’s home directory, which is /home/student.
After extracting the Eclipse IDE, you can check the contents of the eclipse directory with the following command:
ls -al eclipse |
You should see the following:
drwxrwxr-x. 8 student student 4096 May 8 22:16 . drwx------. 33 student student 4096 May 8 21:57 .. -rw-rw-r--. 1 student student 119194 Mar 20 07:10 artifacts.xml drwxrwxr-x. 11 student student 4096 May 8 22:16 configuration drwxrwxr-x. 2 student student 4096 Mar 20 07:10 dropins -rwxr-xr-x. 1 student student 78782 Mar 20 07:08 eclipse -rw-rw-r--. 1 student student 315 Mar 20 07:10 eclipse.ini -rw-rw-r--. 1 student student 60 Mar 17 15:11 .eclipseproduct drwxrwxr-x. 41 student student 4096 Mar 20 07:10 features -rwxr-xr-x. 1 student student 140566 Mar 20 07:08 icon.xpm drwxrwxr-x. 4 student student 4096 Mar 20 07:09 p2 drwxrwxr-x. 12 student student 40960 Mar 20 07:10 plugins drwxrwxr-x. 2 student student 4096 Mar 20 07:10 readme |
You can launch the Eclipse IDE with the following command-line from the eclipse directory:
./eclipse & |
While you can run this from the /home/student/eclipse directory, it’s best to create an alias for the Eclipse IDE in the student user’s .bashrc file:
# Set alias for Eclipse IDE tool. alias eclipse="/home/student/eclipse/eclipse" |
The next time you start the student user account, you can launch the Eclipse IDE by entering eclipse in the search box opened by clicking on the Activities menu.
The following steps take you through installing Eclipse on Fedora Linux, which is more or less the same as any Linux distribution. It’s very similar on Windows platforms too.
Eclipse Installation
- Navigate to eclipse.org/downloads web page to download the current version of the Eclipse software. Click the Linux 32 Bit or Linux 64 Bit link, as required for your operating system.
- Click the Green Arrow to download the Eclipse software.
- The next dialog gives you an option to open or save the software. Click the Open with radio button to open the archive file.
- This the Linux Archive Manager. Click the Extract button from the menu tab to open the archive file.
- This extract button on file chooser dialog to install Eclipse into the /home/student/eclipse directory. Click the Extract button to let the Archive Manager create a copy of those files.
- The Archive Manager presents a completion dialog. Click the Close button to close the Archive Manager.
After installing the Eclipse software, you can configure Eclipse. There are sixteen steps to setup the Eclipse product. You can launch the product with the
Eclipse Setup
You need to launch the Eclipse application to perform the following steps. The syntax is the following when you did create the alias mentioned earlier in the blog post:
eclipse & |
The following steps cover setting up your workspace, project, and adding the MySQL JDBC Java archive.
- The branding dialog may display for 30 or more seconds before the Eclipse software application launches.
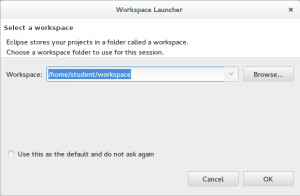
- The Workspace Launcher opens first on a new installation. You need to designate a starting folder. I’m using /home/student/workspace as my Workspace. Click the OK button when you enter a confirmed workspace.
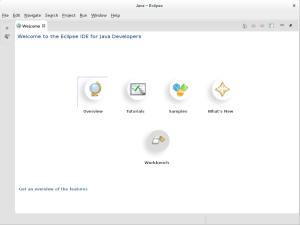
- After setting the Workspace Launcher, you open to the Eclipse Welcome page. Click second of the two icons on the left to open a working Eclipse environment. Alternatively, you can connect to Tutorials on the same page.
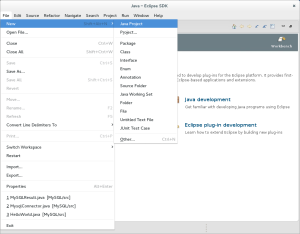
- From the developer view, click on the File menu option, the New option on the list, and the Java Project option on the floating menu. Eclipse will now create a new Java project.
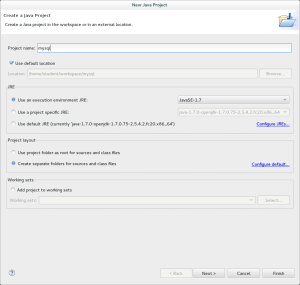
- The New Java Project dialog lets you enter a project name and it also gives you the ability to set some basic configuration details. As a rule, you simply enter the Project Name and accept the defaults before clicking the Finish button.
- After creating the new Java project, Eclipse returns you to the Welcome page. Click second of the two icons on the left to open a working Eclipse environment.
- Now you should see the working environment. Sometimes it takes the full screen but initially it doesn’t. Navigate to the lower right hand side, and expand the window to full size.
- Now you should see the full screen view of the Eclipse working environment.
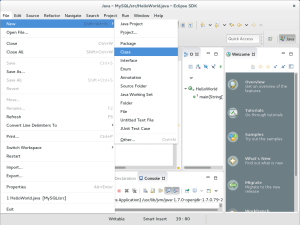
- Now you create a new Java class by navigating to the File menu options, then the New menu option, and finally choosing the Class floating menu.
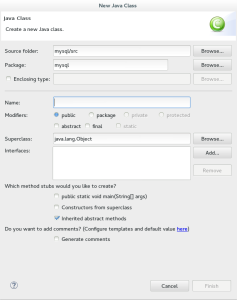
- The New Java Class dialog requires you to provide some information about the Java object you’re creating. The most important thing is the Java class name.
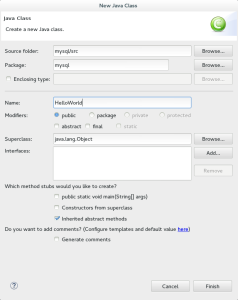
- The only difference in this copy of the New Java Class dialog is that I’ve entered HelloWorld as the Java Class’s name. Click the Finish button when you’re done.
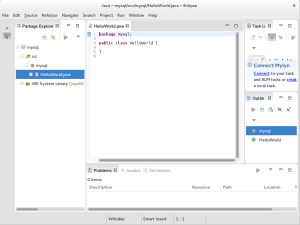
- Eclipse should show you the following
HelloWorld.javafile. It’s missing a main() method. Add a static main() method to theHelloWorld.javaclass source file.
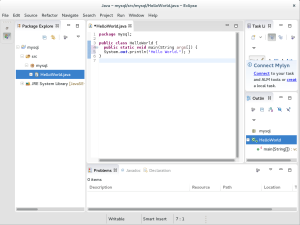
- This form shows the changes to the
HelloWorld.javafile. Specifically, it adds the It’s missing a >main() method. Add a static main() method to the HelloWorld.java class source file.
- You can click the green arrow from the tool panel or you can click the Run menu option and Run submenu choice to test your program.
1 2 3 4
// Class definition. public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("Hello World."); }}
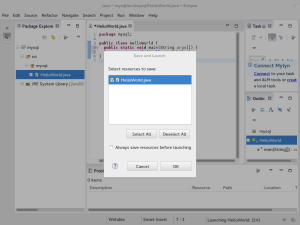
- The Save and Launch dialog tells you that you’re ready to test creating a copy of the Java class file. Click the OK button to continue.
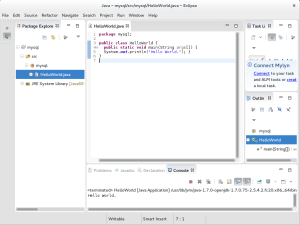
- The results from your program are written to the Console portion of the Eclipse IDE. This concludes the setup of a workspace, project, and deployment of actual Java classes.
Hello World.
Add MySQL JDBC Library
The following instructions add the MySQL Library and demonstrate how to write Java programs that connect to the MySQL database. They also use the mysql project.
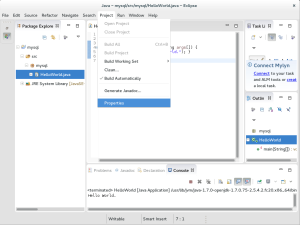
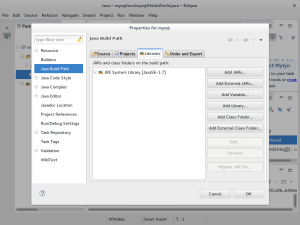
- Navigate to the Project menu and choose the Properties menu option.
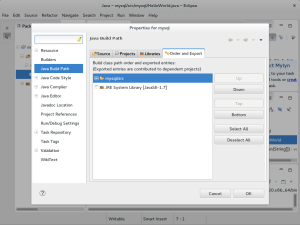
- The Properties menu option opens the Properties for the mysql project on the Order and Export tab. Click the Libraries tab to add an external library.
- In the Libraries tab click the Add Library… button on the right to add an external library.
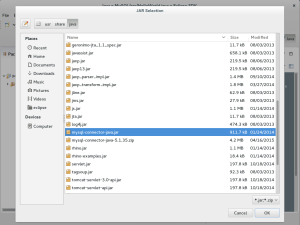
- In the JAR Selection dialog, click on Computer in the Places list, then click on usr, click on share, and click on java. The Name list should now include mysql-connector-java.jar file, and you should click on it before clicking on the OK button.
- You create new Java class file by clicking on the File menu. Then, you choose the New menu option and the Class menu option from the floating menu.
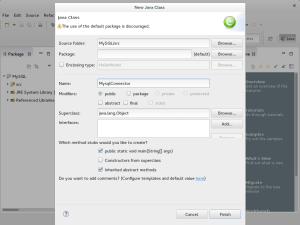
- Enter MysqlConnector as the name of the new Java class file and click the Finish button to continue.
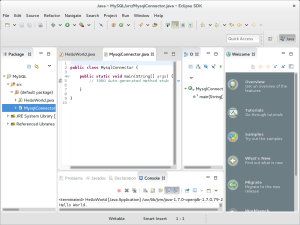
- Eclipse generates the shell of the MysqlConnector class as shown in the illustration to the left.
- You should replace the MysqlConnector class shell with the code below. Then, click the green arrow or the Run menu and Run menu option to compile and run the new MysqlConnector Java class file.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
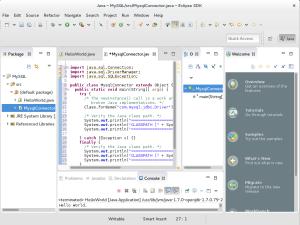
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; public class MysqlConnector extends Object { public static void main(String[] args) { try { /* The newInstance() call is a work around for some broken Java implementations. */ Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver").newInstance(); /* Verify the Java class path. */ System.out.println("===================="); System.out.println("CLASSPATH [" + System.getProperty("java.class.path") + "]"); System.out.println("===================="); } catch (Exception e) {} finally { /* Verify the Java class path. */ System.out.println("===================="); System.out.println("CLASSPATH [" + System.getProperty("java.class.path") + "]"); System.out.println("===================="); } } }
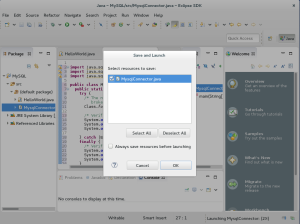
- The Save and Launch dialog informs you are saving a
MysqlConnector.javafile to yourmysqlproject. Click the OK button to continue.
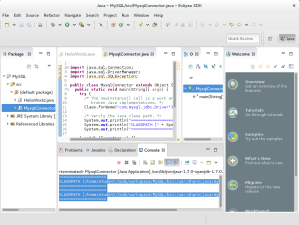
- The next screen shows that the program successfully connected to the MySQL database by printing the following information to the Console output tab.
==================== CLASSPATH [/home/student/Code/workspace/MySQL/bin:/usr/share/java/mysql-connector-java.jar] ==================== ==================== CLASSPATH [/home/student/Code/workspace/MySQL/bin:/usr/share/java/mysql-connector-java.jar] ====================
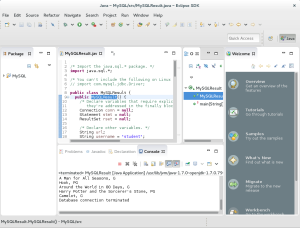
- Instead of repeating steps #5 through #10, the image displays the testing of the MysqlResults class file. The code follows below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76
/* Import the java.sql.* package. */ import java.sql.*; /* You can't include the following on Linux without raising an exception. */ // import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; public class MySQLResult { public MySQLResult() { /* Declare variables that require explicit assignments because they're addressed in the finally block. */ Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rset = null; /* Declare other variables. */ String url; String username = "student"; String password = "student"; String database = "studentdb"; String hostname = "localhost"; String port = "3306"; String sql; /* Attempt a connection. */ try { // Set URL. url = "jdbc:mysql://" + hostname + ":" + port + "/" + database; // Create instance of MySQL. Class.forName ("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver").newInstance(); conn = DriverManager.getConnection (url, username, password); // Query the version of the database, relies on *_ri2.sql scripts. sql = "SELECT i.item_title, ra.rating FROM item i INNER JOIN rating_agency ra ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id"; stmt = conn.createStatement(); rset = stmt.executeQuery(sql); System.out.println ("Database connection established"); // Read row returns for one column. while (rset.next()) { System.out.println(rset.getString(1) + ", " + rset.getString(2)); } } catch (SQLException e) { System.err.println ("Cannot connect to database server (SQLException):"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { System.err.println ("Cannot connect to database server (ClassNotFoundException)"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } catch (InstantiationException e) { System.err.println ("Cannot connect to database server (InstantiationException)"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { System.err.println ("Cannot connect to database server (IllegalAccesException)"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } finally { if (conn != null) { try { rset.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close(); System.out.println ("Database connection terminated"); } catch (Exception e) { /* ignore close errors */ } } } } /* Unit test. */ public static void main(String args[]) { new MySQLResult(); } }
After you click the green arrow or the Run menu and Run menu option to compile and run the program, you should see the following output. That is if you’re using my create_mysql_store_ri2.sql and >seed_mysql_store_ri2.sql files.
Database connection established I Remember Mama, NR Tora! Tora! Tora!, G A Man for All Seasons, G Around the World in 80 Days, G Camelot, G Christmas Carol, G I Remember Mama, G The Hunt for Red October, PG Star Wars I, PG Star Wars II, PG Star Wars II, PG The Chronicles of Narnia, PG Beau Geste, PG Hook, PG Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone, PG Scrooge, PG Harry Potter and the Sorcer's Stone, PG Harry Potter and the Sorcer's Stone, PG Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, PG Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, PG Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, PG Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, PG Harry Potter and the Half Blood Prince, PG Star Wars III, PG-13 Casino Royale, PG-13 Casino Royale, PG-13 Die Another Day, PG-13 Die Another Day, PG-13 Die Another Day, PG-13 Golden Eye, PG-13 Golden Eye, PG-13 Tomorrow Never Dies, PG-13 Tomorrow Never Dies, PG-13 The World Is Not Enough, PG-13 Clear and Present Danger, PG-13 Clear and Present Danger, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Order of the Phoenix, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows, Part 1, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows, Part 2, PG-13 Brave Heart, R The Chronicles of Narnia, E MarioKart, E Need for Speed, E Cars, E RoboCop, M Pirates of the Caribbean, T Splinter Cell, T The DaVinci Code, T Database connection terminated
As always, I hope the note helps those trying to work with the Eclipse product.
C Shared Libraries
I wrote a shared C library example to demonstrate external procedures in the Oracle Database 11g PL/SQL Programming book. I also reused the same example to demonstrate Oracle’s external procedures in the Oracle Database 12c PL/SQL Advanced Programming Techniques book last year. The example uses a C Shared Library but a PL/SQL wrapper and PL/SQL test case.
One of my students asked me to simplify the unit test case example by writing the complete unit test in the C Progamming Language. The student request seemed like a good idea, and while poking around on the web it appears there’s a strong case for a set of simple shared C library examples. This blog post isn’t meant to replace the C Programming web site and C Programming Tutorial web site, which I recommend as a great reference point.
Like most things, the best place to start is with basics of C programming because some readers may be very new to C programming. I’ll start with basic standalone programs and how to use the gcc compiler before showing you how to use shared C libraries.
The most basic program is a hello.c program that serves as a “Hello World!” program:
1 2 3 4 5 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("Hello World!\n"); return(0); } |
Assuming you put the C source files in a src subdirectory and the executable files in a bin subdirectory. You compile the program with the gcc program from the parent directory of the src and bin subdirectories, as follows:
gcc -o bin/hello src/hello.c |
Then, you execute the hello executable program from the parent directory as follows:
bin/hello |
It prints:
Hello World! |
You can modify the basic Hello World! program to accept a single input word, like this hello_whom.c program:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | #include <stdio.h> /* The executable main method. */ int main() { // Declare a character array to hold an input value. char whom[30]; /* Print a question and read a string input. */ printf("Who are you? "); scanf("%s", whom); printf("Hello %s!\n", whom); return(0); } |
You can compile the hello_whom.c program as follows:
gcc -o bin/hello_whom src/hello_whom.c |
Then, you execute the hello_whom executable program from the parent directory as follows:
bin/hello_whom
Who are you? Stuart |
It prints:
Hello Stuart! |
Alternatively, you can modify the hello_whom.c program to accept a stream of text, like the following hello_string.c program:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | #include <stdio.h> /* The executable main method. */ int main() { // Declare a character array to hold an input name. char phrase[4000]; /* Print a question and read a string input. */ printf("Hello? "); scanf("%[^\n]%*c", phrase); printf("Hello %s!\n", phrase); return(0); } |
The [] is the scan set character. The [^\n] on line 10 defines the input as not a newline with a white space, and the %*c reads the newline character from the input buffer. After you compile the program you can call it like this:
bin/hello_string
Hello? there, it reads like a C++ stream |
It would print:
Hello there, it reads like a C++ stream! |
These example, like the previous examples, assume the source files are in a src subdirectory and the executable files are in the bin subdirectory. All compilation commands are run from the parent directory of the src and bin subdirectories.
The first example puts everything into a single writingstr.c file. It defines a writestr() function prototype before the main() function and the writestr() function after the main() function.
The code follows below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | #include <stdio.h> /* Declare two integer variables. */ char path[255], message[4000]; /* Define a prototype for the writestr() function. */ void writestr(char *path, char *message); /* The executable main method. */ int main() { printf("Enter file name and message: "); scanf("%s %[^\n]%*c", &path, &message); printf("File name: %s\n", path); printf("File content: %s\n", message); writestr(path, message); return(0); } void writestr(char *path, char *message) { FILE *file_name; file_name = fopen(path,"w"); fprintf(file_name,"%s\n",message); fclose(file_name); } |
You can compile the writingstr.c function with the following syntax:
gcc -o bin/writingstr src/writingstr.c |
You can run the writingstr executable file with the following syntax:
bin/writingstr Enter file name and message: /home/student/Code/c/test.txt A string for a file. File name: /home/student/Code/c/test.txt File content: A string for a file. |
You’ll find a test.txt file written to the /home/student/Code/C directory. The file contains only the single sentence fragment entered above.
Now, let’s create a writestr.h header file, a writestr.c shared object file, and a main.c testing file. You should note a pattern between the self-contained code and the approach for using shared libraries. The prototype of the writestr() function becomes the definition of the writestr.h file, and the implementation of the writestr() function becomes the writestr.so shared library.
The main.c file contains the only the main() function from the writingstr.c file. The main() function uses the standard scanf() function to read a fully qualified file name (also known as a path) as a string and then a text stream for the content of the file.
You define the writestr.h header file as:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | #ifndef writestr_h__ #define writestr_h__ extern void writestr(char *path, char *message); #endif |
You define the writestr.c shared library, which differs from the example in the book. The difference is the #include statement of the writestr.h header file. The source code follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | #include <stdio.h> #include "writestr.h" void writestr(char *path, char *message) { FILE *file_name; file_name = fopen(path,"w"); fprintf(file_name,"%s\n",message); fclose(file_name); } |
You define the main.c testing program as:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | #include <stdio.h> #include "writestr.h" /* Declare two integer variables. */ char path[255], message[4000]; /* The executable main method. */ int main() { printf("Enter file name and message: "); scanf("%s %[^\n]%*c", &path, &message); writestr(path, message); return(0); } |
Before you begin the process to compile these, you should create an environment file that sets the $LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable or add it to your .bashrc file. You should point the $LD_LIBRARY_PATH variable to the directory where you’ve put your shared libraries.
# Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable. export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/student/Code/c/trylib/libfile |
With programs defined, you need to first compile the writestr.c shared library first. You use the following syntax from the parent directory of the src and bin subdirectories.
gcc -shared -fPIC -o bin/writestr.so src/writestr.c |
If you haven’t set the $LD_LIBRARY_PATH, you may raise an exception. There’s also an alternative to setting the $LD_LIBRARY_PATH before you call the gcc executable. You can use the -L option set the $LD_LIBRARY_PATH for a given all to the gcc executable, like:
gcc -L /home/student/Code/c/trylib/libfile -shared -fPIC -o bin/writestr.so src/writestr.c |
Then, you compile the main.c program. You must put the writestr.so shared library before you designate the main target object and main.c source files, like this:
gcc bin/writestr.so -o bin/main src/main.c |
Now, you can perform a C-only unit test case by calling the main executable. However, you must have set the $LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable at runtime too. You see the following reply to the “Enter file name and message” question when you run the main program unit:
bin/main Enter file name and message: /home/student/Code/c/trylib/libfile/test.txt A long native string is the second input to this C program. |
You can now see that the a new test.txt file has been written to the target directory, and that it contains the following string:
A long native string is the second input to this C program. |
As always, I hope this helps those you want to write shared libraries in the C programming language.
Netbeans 8 – Fedora
Some of my students want to use the Fedora image that I built for my database classes in my Java software development life cycle course. As a result, they wanted a Java development environment installed. I examined JDeveloper 11g (11.1.1.7.0) and 12c (12.1.3) but resolved on the more generic Netbeans 8 (8.0.2) IDE.
JDK 7 with Netbeans 8 Download
You can download the generic Netbeans 8 IDE or the JDK 8 with Netbeans for the Linux installation. After you download the executable program, you should follow these instructions to install the Netbeans 8 IDE on Fedora.
As the student user, you can download the file to your ~student/Downloads directory and then run these two commands:
chmod +x ./jdk-7u80-nb-8_0_2-linux-x64.sh sudo ./jdk-7u80-nb-8_0_2-linux-x64.sh |
It produces the following output log:
Configuring the installer... Searching for JVM on the system... Preparing bundled JVM ... Extracting installation data... Running the installer wizard... |
Then, it launches the installer. These screens show you how to install and create your first Java project.
JDK 7 with Netbeans 8 Installation
- The first installation dialog welcomes you to the JDK 7 Update and NetBeans 8 Installer. Click the Next button to proceed.
- The second installation dialog asks you to accept the terms in the license agreement. Click the Next button to proceed.
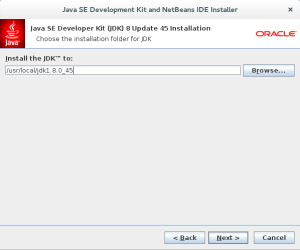
- The third installation dialog asks you to install Netbeans 8. Click the Browse button if you would like to install it in a different area. Click the Next button to proceed.
- The fourth installation dialog asks you to install another Java JDK 7 that supports the current release of Netbeans 8. Click the Browse button if you would like to install it in a different area. Click the Next button to proceed.
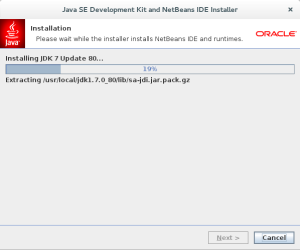
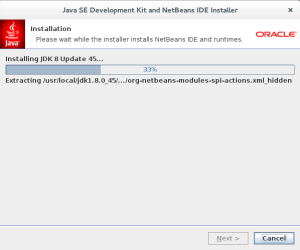
- The fifth installation dialog shows you the progress bar for installing Java JDK 7 that supports the current release of Netbeans 8. You may not need to click the Next button to proceed because it should progress to the Netbeans progress dialog. Click the Next button to proceed when it doesn’t do it automatically.
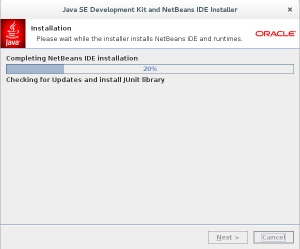
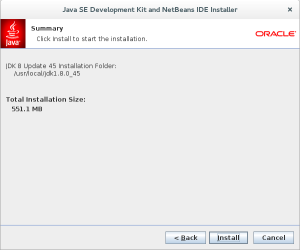
- The sixth installation dialog shows you the progress bar for installing Netbeans 8. Click the Next button to proceed when it doesn’t do it automatically.
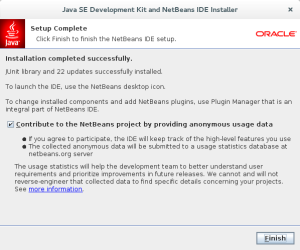
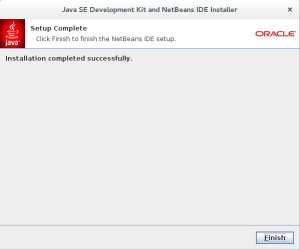
- The next screen is the final screen of the Java SE Development Kit and NetBeans IDE Installer. Click the Finish button to complete the installation.
After the installation, you need to check if the netbeans program can be found by users. It shouldn’t be found at this point because it isn’t in the default $PATH environment variable.
Configuring the student user
You can set the $PATH variable dynamically like this:
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/netbeans-8.0.2/bin |
The netbeans program location was set in Step #4 of the Netbeans installation. After setting the $PATH environment variable, you can run netbeans with this syntax:
./netbeans & |
However, the better approach is to put the following lines in your .bashrc file. This change ensures that you can access the netbeans program anytime you launch a Terminal session.
# Add netbeans to the user's PATH variable. export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/netbeans-8.0.2/bin |
After you have configured the student user’s .bashrc file, you can now use Netbeans to create a Java project.
Create a new Netbeans project
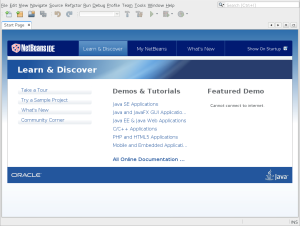
- The next screen is the Netbeans 8 Start Page. This is where you can create your first Java development project.
- You click the File menu and then the New Project menu option to open a new project.
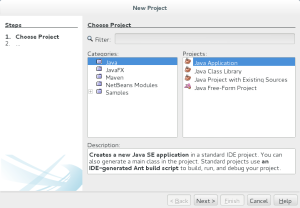
- It launches the New Project dialog at Step #1 – Choose Project, where you choose Java from your Categories list and Java Application from the Projects list. You click the Next button to continue.
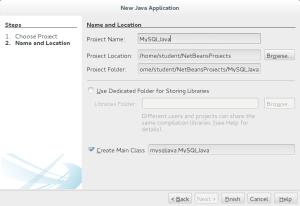
- It launches the New Project dialog at Step #2 – Name and Location, where you enter a Project Name. The example uses
MySQLJavaas the project name. You click the Next button to continue.
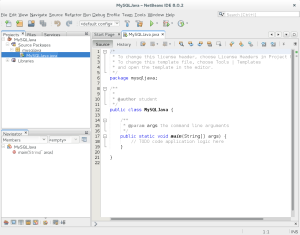
- It launches the
MySQLJava.javatab in the Netbeans 8 application. This is where you can enter your code.
You should download JDK 8 with Netbeans 8. When you install JDK 8 with Netbeans 8 into an environment with a preinstalled JDK 7 (old as it is) with Netbeans 8, the installer only adds the JDK 8.
The following segments of the post show you how to download and install JDK 8 with Netbeans 8, and how to configure Netbeans to work with the JDK 7 and JDK 8 as interchangeable libraries.
JDK 8 with Netbeans 8 Download
You can now download the JDK 8 with Netbeans for the Linux installation. After you download the executable program, you should follow these instructions to install it on Fedora.
As the student user, you can download the file to your ~student/Downloads directory and then run these two commands:
chmod +x ./jdk-8u45-nb-8_0_2-linux-x64.sh sudo ./jdk-8u45-nb-8_0_2-linux-x64.sh |
It produces the following output log:
Configuring the installer... Searching for JVM on the system... Preparing bundled JVM ... Extracting installation data... Running the installer wizard... |
Then, it launches the installer, which will be very similar to the steps you went through earlier. There are differences. There are only five screens that you navigate as opposed to the seven from the earlier JDK 7 with Netbeans 8 installation, as you’ll see below.
JDK 8 with Netbeans 8 Installation
- The first installation dialog welcomes you to the JDK 8 Update and NetBeans 8 Installer. Click the Next button to proceed.
- The second installation dialog installs the JDK 8. Click the Next button to proceed.
- The third installation dialog is a summary of what you’ll install. Click the Install button to proceed.
- The fourth installation dialog shows you a progress bar. You don’t need to do anything but watch the progress.
- The fifth installation dialog shows you the installation is complete. Click the Finish button to proceed when it doesn’t do it automatically.
After you have installed the JDK 8 SE, you can use Netbeans to add the JDK 8 platform.
Add the JDK 8 Platform to Netbeans 8
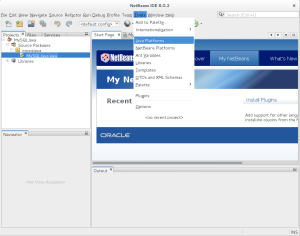
- After you open Netbeans 8, you choose the Tools menu choice. Then, you select the Java Platforms menu option.
- It launches the Java Platform Manager dialog. You click the Add Platform button to add the JDK 8 platform.
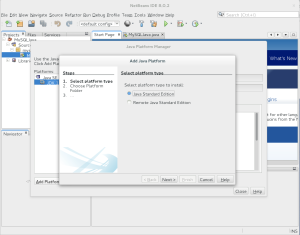
- It launches the Add Java Platform dialog. Leave the Java Standard Edition radio button checked. You click the Next button to proceed.
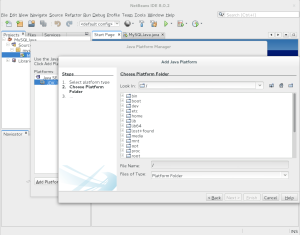
- It launches the Add Java Platform file chooser dialog. Here you navigate to find the JDK 8 software, which is located in
/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_45directory.
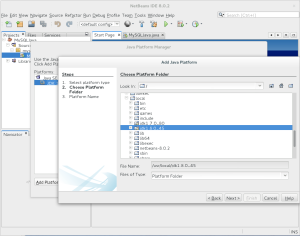
- After selecting the
/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_45directory as the platform folder, click the Next button to proceed.
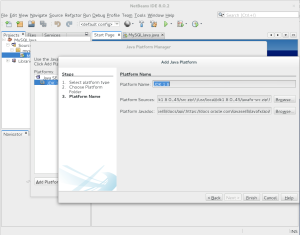
- After setting the directory, you’re asked to verify the Java Platform information. If it’s correct, click the Finish button to proceed.
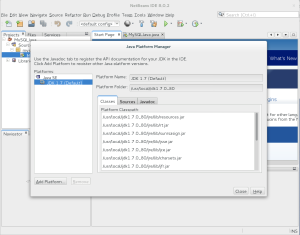
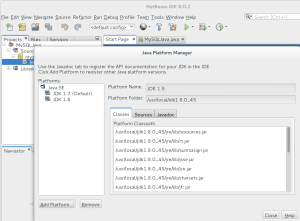
- After finishing the installation, you’ll see that you have two installed Java Platforms. Unfortunately, the first one installed is the default unless you modify the
netbeans.conffile. You click the Close button to complete the process.
Set JDK 8 Platform as the Default Java Platform for Netbeans 8
After adding the JDK 8 Java Platform, you can change the default setting my manually editing the /usr/local/netbeans-8.0.2/etc/netbeans.conf file. You simply remark out the line for JDK 7 and replace it with one for JDK 8, as shown below. The next time you boot the Netbeans application it uses Java 1.8.
netbeans_jdkhome="/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_45" |
The next time you launch Netbeans 8, it will use JDK 8 because you set that as the default Java Platform
As always, I hope this helps those looking for information like this.