Archive for the ‘Fedora’ Category
Add Color to VIM?
In Fedora 20, documents have no color coding when you edit them with vi or vim. That’s because Fedora installs vim-minimal by default. You can check what’s running with the following command at a shell prompt in the terminal:
rpm -qa | grep vim |
It should print the following to console:
vim-minimal-7.4.179-1.fc20.x86_64 |
You can download and install vim with the enhanced version by using the following syntax:
sudo yum install vim-enhanced |
Loaded plugins: langpacks, refresh-packagekit Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package vim-enhanced.x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 will be installed --> Processing Dependency: vim-common = 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 for package: 2:vim-enhanced-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 --> Processing Dependency: libgpm.so.2()(64bit) for package: 2:vim-enhanced-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 --> Running transaction check ---> Package gpm-libs.x86_64 0:1.20.7-3.fc20 will be installed ---> Package vim-common.x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 will be installed --> Processing Dependency: vim-filesystem for package: 2:vim-common-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 --> Running transaction check ---> Package vim-filesystem.x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: vim-enhanced x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 updates 1.0 M Installing for dependencies: gpm-libs x86_64 1.20.7-3.fc20 fedora 32 k vim-common x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 updates 5.9 M vim-filesystem x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 updates 11 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package (+3 Dependent packages) Total download size: 7.0 M Installed size: 23 M Is this ok [y/d/N]: y Downloading packages: (1/4): gpm-libs-1.20.7-3.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 32 kB 00:00 (2/4): vim-enhanced-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 1.0 MB 00:03 (3/4): vim-filesystem-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 11 kB 00:03 (4/4): vim-common-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 5.9 MB 00:05 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 1.3 MB/s | 7.0 MB 00:05 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Installing : 2:vim-filesystem-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 1/4 Installing : 2:vim-common-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 2/4 Installing : gpm-libs-1.20.7-3.fc20.x86_64 3/4 Installing : 2:vim-enhanced-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 4/4 Verifying : gpm-libs-1.20.7-3.fc20.x86_64 1/4 Verifying : 2:vim-common-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 2/4 Verifying : 2:vim-enhanced-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 3/4 Verifying : 2:vim-filesystem-7.4.417-1.fc20.x86_64 4/4 Installed: vim-enhanced.x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 Dependency Installed: gpm-libs.x86_64 0:1.20.7-3.fc20 vim-common.x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 vim-filesystem.x86_64 2:7.4.417-1.fc20 Complete! |
You can now type vim to edit files in color but vi will still be in black and white.
MySQL Workbench on Fedora
The early release of Fedora 20 disallowed installation of MySQL Workbench but the current version allows it. Almost like Tom Cruise’s Edge of Tomorrow without the drama. All you need to do is follow my earlier instructions for installing MySQL on Fedora 20. I’d check your kernel to know whether it’s supported. You can check that with this command:
<shell> uname -r |
My Fedora is at the following version:
3.14.8-200.fc20.x86_64 |
Then, you can install MySQL Workbench with yum, like this:
<shell> sudo yum install mysql-workbench |
It generates the following log file, and if you have Oracle 11g XE installed you can ignore the mime-type error:
Loaded plugins: langpacks, refresh-packagekit
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package mysql-workbench-community.x86_64 0:6.1.7-1.fc20 will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: libzip.so.2()(64bit) for package: mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: libvsqlitepp.so.3()(64bit) for package: mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: libtinyxml.so.0()(64bit) for package: mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: liblua-5.1.so()(64bit) for package: mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: libgtkmm-2.4.so.1()(64bit) for package: mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: libgdkmm-2.4.so.1()(64bit) for package: mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: libctemplate.so.2()(64bit) for package: mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package compat-lua-libs.x86_64 0:5.1.5-1.fc20 will be installed
---> Package ctemplate.x86_64 0:2.2-5.fc20 will be installed
---> Package gtkmm24.x86_64 0:2.24.4-2.fc20 will be installed
---> Package libzip.x86_64 0:0.11.2-1.fc20 will be installed
---> Package tinyxml.x86_64 0:2.6.2-4.fc20 will be installed
---> Package vsqlite++.x86_64 0:0.3.13-3.fc20 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
mysql-workbench-community x86_64 6.1.7-1.fc20 mysql-tools-community 24 M
Installing for dependencies:
compat-lua-libs x86_64 5.1.5-1.fc20 updates 158 k
ctemplate x86_64 2.2-5.fc20 fedora 174 k
gtkmm24 x86_64 2.24.4-2.fc20 fedora 748 k
libzip x86_64 0.11.2-1.fc20 updates 59 k
tinyxml x86_64 2.6.2-4.fc20 updates 49 k
vsqlite++ x86_64 0.3.13-3.fc20 updates 58 k
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 1 Package (+6 Dependent packages)
Total download size: 26 M
Installed size: 119 M
Is this ok [y/d/N]: y
Downloading packages:
(1/7): compat-lua-libs-5.1.5-1.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 158 kB 00:01
(2/7): ctemplate-2.2-5.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 174 kB 00:01
(3/7): tinyxml-2.6.2-4.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 49 kB 00:00
(4/7): gtkmm24-2.24.4-2.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 748 kB 00:01
(5/7): vsqlite++-0.3.13-3.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 58 kB 00:00
(6/7): libzip-0.11.2-1.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 59 kB 00:02
(7/7): mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 24 MB 00:08
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 2.9 MB/s | 26 MB 00:08
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : gtkmm24-2.24.4-2.fc20.x86_64 1/7
Installing : libzip-0.11.2-1.fc20.x86_64 2/7
Installing : vsqlite++-0.3.13-3.fc20.x86_64 3/7
Installing : ctemplate-2.2-5.fc20.x86_64 4/7
Installing : compat-lua-libs-5.1.5-1.fc20.x86_64 5/7
Installing : tinyxml-2.6.2-4.fc20.x86_64 6/7
Installing : mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64 7/7
Error in file "/usr/share/applications/oraclexe-startdb.desktop": "Application/database" is an invalid MIME type ("Application" is an unregistered media type)
Verifying : tinyxml-2.6.2-4.fc20.x86_64 1/7
Verifying : compat-lua-libs-5.1.5-1.fc20.x86_64 2/7
Verifying : ctemplate-2.2-5.fc20.x86_64 3/7
Verifying : vsqlite++-0.3.13-3.fc20.x86_64 4/7
Verifying : mysql-workbench-community-6.1.7-1.fc20.x86_64 5/7
Verifying : libzip-0.11.2-1.fc20.x86_64 6/7
Verifying : gtkmm24-2.24.4-2.fc20.x86_64 7/7
Installed:
mysql-workbench-community.x86_64 0:6.1.7-1.fc20
Dependency Installed:
compat-lua-libs.x86_64 0:5.1.5-1.fc20 ctemplate.x86_64 0:2.2-5.fc20
gtkmm24.x86_64 0:2.24.4-2.fc20 libzip.x86_64 0:0.11.2-1.fc20
tinyxml.x86_64 0:2.6.2-4.fc20 vsqlite++.x86_64 0:0.3.13-3.fc20
Complete! |
After successfully installing MySQL Workbench, you can launch it with the following command:
<shell> mysql-workbench |
It should launch the following MySQL Workbench home page (click on it to see the full size image):
Wrapping SQL*Plus
One annoying thing from installing Oracle Database 11g on Fedora, was that the up arrows for command history didn’t work. I decided to fix that today after seeing Lutz Hartmann’s article on rlwrap. Unfortunately, the epel (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) package he recommended doesn’t run on Fedora 20. You can read my tale of woe, or skip to the .bashrc function that fixed it when I installed only rlwrap.
Attempting it on yum, gave me these errors:
# yum install http://www.mirrorservice.org/sites/dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm Loaded plugins: langpacks, refresh-packagekit epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm | 14 kB 00:00 Examining /var/tmp/yum-root-5CLTPa/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm: epel-release-6-8.noarch Marking /var/tmp/yum-root-5CLTPa/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm to be installed Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package epel-release.noarch 0:6-8 will be installed --> Processing Conflict: epel-release-6-8.noarch conflicts fedora-release No package matched to upgrade: epel-release --> Finished Dependency Resolution Error: epel-release conflicts with fedora-release-20-3.noarch You could try using --skip-broken to work around the problem You could try running: rpm -Va --nofiles –nodigest |
Poking around for an epel fix wasn’t successful, so I chose to install only the rlwrap package. Here’s that command and log file:
[root@localhost ~]# yum install rlwrap Loaded plugins: langpacks, protectbase, refresh-packagekit 0 packages excluded due to repository protections Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package rlwrap.x86_64 0:0.41-1.fc20 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: rlwrap x86_64 0.41-1.fc20 updates 95 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 95 k Installed size: 204 k Is this ok [y/d/N]: y Downloading packages: rlwrap-0.41-1.fc20.x86_64.rpm | 95 kB 00:00 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction (shutdown inhibited) Installing : rlwrap-0.41-1.fc20.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : rlwrap-0.41-1.fc20.x86_64 1/1 Installed: rlwrap.x86_64 0:0.41-1.fc20 Complete! |
The next step was getting it to work. A sqlplus function wrapper inside the .bashrc file seemed the easiest. Here’s the code to the .bashrc file:
# .bashrc # Source global definitions if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then . /etc/bashrc fi # Uncomment the following line if you don't like systemctl's auto-paging feature: # export SYSTEMD_PAGER= # User specific aliases and functions . /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/xe/bin/oracle_env.sh # Wrap sqlplus with rlwrap to edit prior lines. sqlplus() { if [ "$RLWRAP" = "0" ]; then sqlplus "$@" else rlwrap sqlplus "$@" fi } # Set vi as a command line editor. set -o vi |
As always, I hope this helps some folks.
Fedora VMWare Upgrade
When a new update of VMWare comes out, and it is time to upgrade VMWare Tools. Here’s an update on the instructions for upgrading VMWare Tools 6.0.1 through 6.0.4:
- Navigate to the VMWare Menu, choose Virtual Machine and in the drop down menu Install VMWare Tools. This will mount a virtual CD in the Oracle Unbreakable Linux virtual machine and it launches the following dialog box:
- Open a terminal session by right clicking anywhere in the desktop, and then choose Open in Terminal from the context menu. You can then run the VMWare Toolkit by following these instructions as the
rootuser:
The instructions for VMWare 6.0.0 through 6.0.2 are:
cd /media/VMware\ Tools cp VMwareTools-9.6.2-1688356.tar.gz /tmp cd /tmp gunzip VMwareTools-9.6.2-1688356.tar.gz tar -xvf VMwareTools-9.6.2-1688356.tar cd vmware-tools-distrib sudo ./vmware-install.pl |
VMWare changed where the VMWare Tools CD are mounted. You can discover it by clicking on the VMware Tools in the left pane (this assumes you log on to Fedora as the student user, and the student user is a sudo-enabled user)
The instructions for VMWare Tools 6.0.4 forward are listed below. Only the first command changes. You should also note that the VMWare Tools library is the same:
cd /run/media/student/VMware\ Tools cp VMwareTools-9.6.2-1688356.tar.gz /tmp cd /tmp gunzip VMwareTools-9.6.2-1688356.tar.gz tar -xvf VMwareTools-9.6.2-1688356.tar cd vmware-tools-distrib sudo ./vmware-install.pl |
The last step requires that you reply to a set of prompts. If you’d like to accept the default at one time, you can use the following command:
sudo ./vmware-install.pl --default |
Lastly, you’ll get these instructions form the Perl script that installs the VMWare tools:
The configuration of VMware Tools 9.6.2 build-1688356 for Linux for this running kernel completed successfully. You must restart your X session before any mouse or graphics changes take effect. You can now run VMware Tools by invoking "/usr/bin/vmware-toolbox-cmd" from the command line. To enable advanced X features (e.g., guest resolution fit, drag and drop, and file and text copy/paste), you will need to do one (or more) of the following: 1. Manually start /usr/bin/vmware-user 2. Log out and log back into your desktop session; and, 3. Restart your X session. Enjoy, --the VMware team |
A/UX, NeXTSTEP, & OS X
One thing that gets tedious in the IT community and Oracle community is the penchant for Windows only solutions. While Microsoft does an excellent job in certain domains, I remain a loyal Apple customer. By the way, you can install Oracle Client software on Mac OS X and run SQL Developer against any Oracle Database server. You can even run MySQL Workbench and MySQL server natively on the Mac OS X platform, which creates a robust development platform and gives you more testing options with the MySQL monitor (the client software).
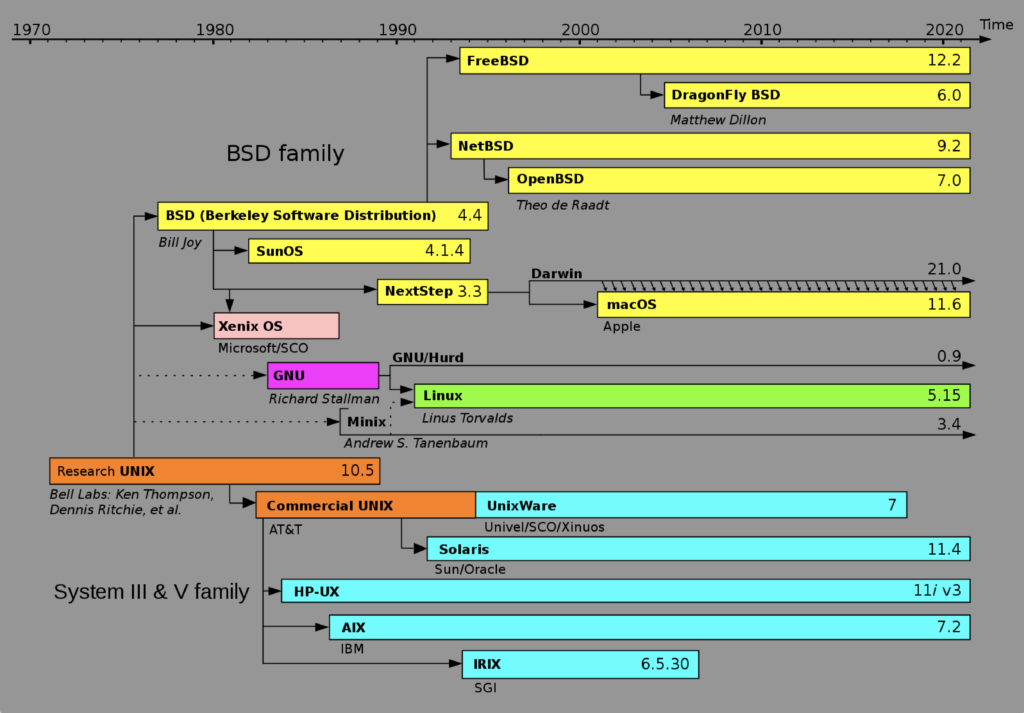
Notwithstanding, some Windows users appear to malign Apple and the Mac OS X on compatibility, but they don’t understand that it’s a derivative of the Research Unix, through BSD (Berkeley Software Distribution). This Unix lineage chart illustrates it well:
I’m probably loyal to Apple because in the early 1990’s I worked on Mac OS 6, Mac OS 7, A/UX, NeXTSTEP, and AIX/6000 (Version 3) while working at APL (American President Lines) in Oakland, California. Back then, my desktop was a pricey Macintosh Quadra 950 and today I work on a pricey Mac Pro desktop. The Mac Pro lets me use VMware virtualize development environments for Oracle Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Fedora, and as you might guess Windows 7/8. My question to those dyed in the wool Microsoft users is simple, why would you choose a single user OS like Windows over a multi-user OS like Mac OS X?
Mac Mini to the rescue
In teaching, I had a problem because my students have different base operating systems, like Windows 7, Windows 8, Linux, and Mac OS X. I needed a teaching and lecture platform that would let me teach it all (not to mention support their environments). That meant it had to virtualize any of the following with a portable device:![]()
- Windows 7 or 8 hosting natively an Oracle Database 11g XE, 11g, or 12c and MySQL Database 5.6
- Windows 7 or 8 hosting a Fedora or Oracle Unbreakable Linux VM (3 or 4 GB) with Oracle Database 11g XE, 11g, or 12c and MySQL Database 5.6
- Mac OS X hosting a Fedora or Oracle Unbreakable Linux VM (3 or 4 GB) with Oracle Database 11g XE, 11g, or 12c and MySQL Database 5.6
- Ubuntu hosting a Fedora or Oracle Unbreakable Linux VM (3 or 4 GB) with Oracle Database 11g XE, 11g, or 12c and MySQL Database 5.6
I never considered a manufacturer other than Apple for a laptop since they adopted the Intel chip. Too many of the others sell non-hyperthreaded laptop machines that they market as i5 or i7 64-bit OS machines when they’re not. Some of those vendors disable the hyperthreading facility while others provide motherboards that can’t support hyperthreading. The ones I dislike the most provide a BIOS setting that gives the impression you can enable hyperthreading when you can’t. All Apple devices, MacBook, MacBook Pro, Mac Mini, and Mac Pro do fully support a 64-bit OS and their virtualization.
A MacBook Pro came to mind but the disk space requirements were 1 TB, and that’s too pricey. I went with the Mac Mini because with 16 GB of memory and a 1 TB drive it was only $1,200. Add a wireless keyboard and mighty mouse, and an HDMI and mini-DVI connections, and I had my solution. Naturally, my desktop is a one generation old Mac Pro with 64 GB of memory and 12 TB of disk space, which supports all the virtual machines used for testing. Note to Apple marketing staff: The prior version of the Mac Pro let you pay reasonable (3rd party) prices for the additional memory and disk drives.
The Mac Mini means I can travel anywhere and plug into the console and demo tools and techniques from a myriad set of platforms without the hassle of moving on and off to frequently VM images. It’s a great solution with only one downside, HDMI to DVI sometimes creates purple toned screens. It’s unfortunate because some venues have monitors that don’t support HDMI).
Open a port on Fedora
Since MySQL Workbench 6.0 isn’t available for Fedora, Version 20, I’m having my students install it on their local Windows and Mac OS X operating systems. You can configure the /etc/sysconfig/iptables file to enable port 3306 after installing MySQL on Fedora.
You can open a port by using the firewall-config utility (easy way) or by adding the following line to the /etc/sysconfig/iptables file (Fedora’s instructions on editing iptables [hard way]). The file won’t exist initially, but you can create it by running the following command as the root superuser or sudoer:
shell> service iptables save |
You you can run the following commands as the root superuser, which saves the line in the iptables file:
shell> iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 3306 -j ACCEPT shell> iptables-save |
After making the change to the /etc/iptables file you can change the firewall by running the following command as the root superuser:
shell> service iptables restart |
Just make sure you don’t inadvertently start both iptables and ip6tables as services. You can check that only one is running by using the following commands:
shell> service iptables status shell> service ip6tables status |
MySQL Workbench Configuration
- The first thing you need to do is click on the
+symbol in the circle to the right of the MySQL Connections text label. It launches the Setup New Connection dialog.
- The second thing you need to do is enter a Connection Name, Hostname, Port, and Username. Then, click the Test Connection button.
- The Test Connection button launches the Connect to MySQL Server dialog. Enter the password for the
studentuser (or whatever user you’re interested in), and then click the OK button.
- When the credentials in the Connect to MySQL Server dialog work, you see the following confirmation dialog message. Click the OK button to continue and you’ll see a new VMWare Fedora Instance connection icon.
- Click the VMWare Fedora Instance connection to start a new connection.
- The VMWare Fedora Instance button launches the Connect to MySQL Server dialog. Like you did when configuring the connection, enter the password for the
studentuser (or whatever user you’re interested in), and then click the OK button. It launches an interactive panel that lets you run, edit, or save the SQL script file.
- Type the following two lines in the Query1 panel (at least if you have a
studentdbdatabase:USE studentdb; SELECT DATABASE();
Fedora Install of MySQL
I built a new image on VMWare Fusion for my class, which required installing MySQL 5.6 on Fedora, Version 20. If you don’t know how to add your user to the sudoers list, you should check this older and recently updated blog post.
- Download the MySQL Yum Repository and launch the downloaded RPM.
- Install MySQL on Fedora, Version 20, which you can find with the following command:
shell> rpm -qa | grep mysql mysql-community-release-fc20-5.noarch |
The fc20-5 changes with point releases, but assuming that you’re installing the fc20-5 release:
shell> sudo yum localinstall mysql-community-release-fc20-5.noarch.rpm |
- Install MySQL on Fedora with the following command:
shell> sudo yum install mysql-server |
- Start the MySQL service on Fedora with the following command:
shell> sudo service mysqld start |
- Secure the MySQL installation with the following command:
shell> mysql_secure_installation |
- Set the MySQL Service to start with the Fedora operating system with the following command (not
chkconfig):
shell> sudo systemctl enable mysqld.service |
It sets the following two links:
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service' '/etc/systemd/system/mysql.service' ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysqld.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mysqld.service' |
Restart the Fedora operating system to effect the changes.
- Reset the MySQL configuration file to enable external connections through Port 3306 with the following changes to the my:
Remark out the socket line, like this:
#socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock |
Add the bind-address and port lines below after you know the actual IP address of the server to the my.cnf file in the /etc directory.
You substitute the actual IP address for the nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn on the bind_address line with the actual IP address returned by the ifconfig command, like this:
shell> ifconfig |
Then, add these two lines to the my.cnf file.
bind-address=nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn port=3306 |
It’s actually easier to use localhost.localdomain than an IP address when you use DHCP, like:
bind-address=localhost.localdomain port=3306 |
If you plan to connect from a host system, like Windows or Mac OS X, to a virtual Linux environment using DHCP, change localhost.localdomain to 0.0.0.0:
bind-address=0.0.0.0 port=3306 |
- Restart the mysqld service with the following syntax:
shell> sudo service mysqld restart |
You can check whether MySQL is listening on Port 3306 with this syntax:
shell> sudo netstat –anp | grep 3306 |
It displays:
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1311/mysqld |
Go to this page if you want to install MySQL Workbench.
Fedora URL Changes
Somebody posted on a Gnome patching blog post for Fedora to let me know that the download URL was invalid. I poked around and it appears that the old Fedora URL at Red Hat’s site doesn’t work:
http://download.fedora.redhat.com/pub/fedora/linux
You now have to go the Fedora Project web site for the code archive, and it’s here:
http://archive.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/
If somebody knows why they made the change without any fanfare, please post a note.
Fixing my.cnf on Fedora
Working with a Fedora 16 VM for my students (next term) and found that the MySQL Server’s my.cnf file worked with a Linux socket as opposed to a listener port, and that several configuration options where missing from the file. Here’s the default /etc/my.cnf file after the package installation from the Red Hat site:
[mysqld] # Settings user and group are ignored when systemd is used. # If you need to run mysqld under different user or group, # customize your systemd unit file for mysqld according to the # instructions in http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Systemd datadir=/var/lib/mysql socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock # Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks symbolic-links=0 [mysqld_safe] log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid |
Without rebuilding the log files, this seemed like the cleanest replacement for the MySQL Server my.cnf for a development instance running on Fedora 16. If you’ve other suggestions, please let me know.
[mysqld] # Settings user and group are ignored when systemd is used. # If you need to run mysqld under different user or group, # customize your systemd unit file for mysqld according to the # instructions in http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Systemd # Default directory. datadir=/var/lib/mysql # The TCP/IP Port the MySQL Server listens on. # ------------------------------------------------------------ # Find the machine's IP address with this command run as # the root user and use the port number specified in the # my.cnf file: # [root@localhost ~]# netstat -an | grep 3306 # ------------------------------------------------------------ bind-address=nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn port=3306 # The Linux Socket the MySQL Server uses when not using a listener. # socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock # Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted security risks symbolic-links=0 # The default storage engine that will be used when creating new tables. default-storage-engine=INNODB # Set the SQL mode to strict. sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION" # Set the maximum number of connections. max_connections=100 # Set the number of open tables for all threads. table_cache=256 # Set the maximum size for internal (in-memory) temporary tables. tmp_table_size=26M # Set how many threads should be kept in a cache for reuse. thread_cache_size=8 # MyISAM configuration. myisam_max_sort_file_size=100G myisam_sort_buffer_size=52M key_buffer_size=36M read_rnd_buffer_size=256K sort_buffer_size=256K # InnoDB configuration. innodb_data_home_dir=/var/lib/mysql innodb_additional_mem_pool_size=2M innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1 innodb_log_buffer_size=1M innodb_buffer_pool_size=25M innodb_log_file_size=5M innodb_thread_concurrency=8 [mysqld_safe] log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid |
As always, I hope this helps somebody.