Archive for the ‘Oracle 18c’ Category
Oracle Docker Container
Install, configure, and use an Oracle Docker Container
Installing a Docker instance isn’t quite straightforward nor is it terribly difficult. It can be quite overwhelming if you’re unfamiliar with the technology of virtualization and containerization. This essay shows you how to create, configure, and manage an Oracle Database 18c XE Docker instance on the macOS. There are some slight differences when you install it on Windows OS.
Installation
You need to download the Oracle Database 18c XE file for Linux. You will find it on Oracle’s OTN website at https://www.oracle.com/downloads/. Click the Database link under the Developer Downloads banner. You want to download the Oracle Database Express Edition (XE), Release 18.4.0.0.0 (18c) file.
The file is a Linux Red Hat Package Manager (rpm) file. The file is approximately 2.5 GB in size, which means you may want to take a break while downloading it. Whether you take a break or not, this step may take more time than you like.
While downloading the Oracle database, you want to work on the two other tasks concurrently. You need to download and install Docker and Homebrew software, which aren’t installed from Apple’s Application Store. Many macOS systems disallow by default software from outside the comfy boundaries and inspections of the Apps Store. You may need to change your system preferences to install Docker and Homebrew.
You can download Docker for the macOS from the following website:
https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-mac/install/
The Homebrew (the missing package manager for macOS) website will tell you to install it from the macOS Command Line Interface (CLI). Please note that you must already have the Xcode Command Line Tools installed before you install Homebrew. The following Homebrew installation will update your Command Line Tools to macOS Mojave Version 10.14.
Open a Terminal session from your finder and run this command:
bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)" |
After you install Homebrew in the Terminal, type the following to go to your user’s home folder (or directory):
cd |
In your home directory (/Users/username [~]), create the docker-images directory from the available GitHub docker containers with these two commands (separated by the semicolon):
cd ~/; git clone https://github.com/oracle/docker-images.git |
Move the Oracle Database XE 18c rpm file from your Downloads folder to the target docker-images subfolder with the following command:
mv ~/Downloads/oracle-database-xe-18c-1.0-1.x86_64-2.rpm \ ~/docker-images/OracleDatabase/SingleInstance/dockerfiles/18.4.0/. |
Change your present working directory with the following cd command:
cd docker-images/OracleDatabase/SingleInstance/dockerfiles |
Build the Docker image with the following command (from the directory where the buildDockerImage.sh shell script is found):
./buildDockerImage.sh -v 18.4.0 -x |
The Docker image build takes quite some time. It may take more than 10 minutes on some macOS computers. After it completes, you should see that it was successfully built and tagged in the Terminal. You can confirm the image build with this command:
docker images |
It should return something like this:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE oracle/database 18.4.0-xe 926f4349b277 12 minutes ago 5.89GB oraclelinux 7-slim 153f8d73287e 8 weeks ago 131MB |
Before you start your Docker container, you need to open a Terminal session. You will be in your home directory, which should give you a prompt like:
machine_name:~ username$ |
If you issue a pwd command, you should see the following:
/Users/username |
Create an oracle directory as subdirectory:
mkdir oracle |
While you might wonder about the oracle directory at this point, it’s to help keep straight Docker containers on the macOS file system. For example, when you install Docker instances for MySQL and PostgreSQL, you can see the Docker file systems as:
/Users/username/mysql /Users/username/oracle /Users/username/postgres |
Now, you start the Docker container with the following command:
sudo \ docker run --name videodb -d -p 51521:1521 -p 55500:5500 -e ORACLE_PWD=cangetin \ -e ORACLE_CHARACTERSET=AL32UTF8 -v ~/oracle:/home oracle/database:18.4.0-xe |
After starting the Docker container, you check the container’s status the following command:
docker ps |
Congratulations, you have successfully installed the Docker container.
Configure
The standard docker container prepares a base platform for you. It doesn’t create a schema or containerized user. It simply installs the Oracle Database Management System (DBMS) and Oracle Listener. You need to configure your Linux environment and your database.
You connect to the container as the root user, like:
docker exec -it videodb bash |
You should update any of the older packages with the following command:
yum update |
Next, you should install the openssh-server and vim packages. They’re not installed as part of the docker container’s default configuration. You’ll need them when you create non-root users and edit configuration files. This command installs them both:
yum openssh-server vim |
There are a number of things for you to do at this point. They don’t all have to be done in the order that this essay takes. Like any other installation of Oracle on Linux, there is an oracle user who owns the installation. The oracle user is a non-login user. A non-login user doesn’t have a password and disallows a ssh connection. You need to first become the root user before you can use the su (substitute user) command to become the oracle user. Only superuser accounts hold the privileges to su without credentials because they’re trusted users.
The easiest thing to do while you’re the root user is test your ability to connect to the Oracle database’s system schema. You set the system schema’s password to cangetin when you ran the docker run command. At the command prompt, type the following to connect to the database:
sqlplus system/cangetin@xe |
You should see the following when you connect as the system user:
SQL*Plus: Release 18.0.0.0.0 - Production on Sun Sep 13 02:48:44 2020 Version 18.4.0.0.0 Copyright (c) 1982, 2018, Oracle. All rights reserved. Last Successful login time: Sat Sep 12 2020 21:13:33 +00:00 Connected to: Oracle Database 18c Express Edition Release 18.0.0.0.0 - Production Version 18.4.0.0.0 SQL> |
Please note that only the oracle user can connect without referencing the @xe service identifier, which is defined in the $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.ora file. You can read more about the SQL*Net configuration in the documentation. The quit command exits the SQL*Plus Command Line Interface. At this point, as root, lets you create a missing vi symbolic link to the vim utility you installed earlier.
ln -s /usr/bin/vim /usr/bin/vi |
With vi configured, let’s su to the oracle user and create an .bashrc file for it. You should note that a non-login user doesn’t have a .bashrc file by default. You become the oracle user with the following command:
su oracle |
You may notice that you’re not in the oracle user’s home directory. Let’s change that by moving to the correct home directory.
The home directory for any user is configured in the /etc/passwd file and available by using the echo command to see the $HOME environment variable’s value. This is true for Red Hat, Oracle Unbreakable Linux, CentOS, and Fedora distributions. They create users’ home directories as subdirectories in the /home directory.
The .bashrc file is a hidden file. Hidden files have no file name before the period and are not visible with an ls (list) command. You can find them by using a -al flag value with the ls command
ls -al |
You can use the vi editor to create a .bashrc file like this:
vi .bashrc |
A minimal oracle .bashrc (bash resource) file should look like this:
# Source global definitions if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then . /etc/bashrc fi # User specific environment if ! [[ "$PATH" =~ "$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:" ]] then PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:$PATH" fi export PATH # Set Prompt export PS1="[\u@localhost \W]\$ " # Change to home directory. cd $HOME # Uncomment the following line if you don't like systemctl's auto-paging feature: # export SYSTEMD_PAGER= # User specific aliases and functions |
If you know about the Linux CLI prompt, the localhost string may seem odd. It’s there to suppress the random string otherwise provided by the docker container.
A number of other Oracle environment parameters have already been set. You can see them with this command:
env | grep -i oracle |
You can connect as the privileged sysdba role, once known as the internal user, to start and stop the database instance without stopping the docker container. That command syntax is:
sqlplus / as sysdba |
Only the oracle user has privileges to connect with the sysdba role by default. That’s because the oracle user is the owner of the Oracle database installation.
While connected as the oracle user, you should make three changes. One change to oracle executable file permissions and two changes to the glogin.sql default configuration file.
The initial permissions on the $ORACLE_HOME/bin/oracle executable file in the docker container are shown below.
-rwxr-x--x 1 oracle oinstall 437755981 Oct 18 2018 oracle |
The setuid bit is disabled when the user’s permissions are rwx. The oracle executable should always run with the permissions and ownership of the oracle user. That only happens when the setuid bit is enabled. You set the setuid. bit with the following syntax as the oracle user or privileged root superuser (from the $ORACLE_HOME/bin directory):
chmod u+s oracle |
Relisting the file in a long list view (ls -al) after the change, you should see the following:
-rwsr-x--x 1 oracle oinstall 437755981 Oct 18 2018 oracle |
The setuid bit is enabled when the user permissions are rws. Connections to the database by non-privileged Oracle users may raise ORA-01017 and ORA-12547 errors when the setuid bit is unset.
The glogin.sql file is read and processed with every connection to the database. Therefore, you should put little in there, and some would argue nothing in there. You’re going to enter the command that lets you interactively launch vi from a SQL> command prompt and set a SQL*Plus environment variable. The SQL*Plus environment variable lets you see debug messages raised by your PL/SQL programs.
To edit the glogin.sql file, change your terminal directory as follows:
cd $ORACLE_HOME/sqlplus/admin |
Add the following two lines at the bottom of the glogin.sql file:
define _editor=vi SET SERVEROUTPUT ON SIZE UNLIMITED |
That’s it for configuring the oracle user’s account. Type exit to return to the root user shell. Type exit again, this time to leave the root user’s account and return to your hosting macOS.
The next configuration step sets up a non-privileged student account in Linux. You setup the student user with the following Docker command (for reference, it can’t be done from within the docker container):
sudo \ docker exec -it videodb bash -c "useradd -u 501 -g dba -G users \ -d /home/student -s /bin/bash -c "Student" -n student" |
You will be prompted for a password when this command runs. Try to keep the password simple. Using a password like cangetin is recommended when it’s a development instance. You can connect with the following docker command:
docker exec -it --user student videodb bash |
After logging in to the docker container as the student user, you need to configure the .bashrc file. You should use the following minimal .bashrc file in the /home/student directory, which you can create with the vi editor.
# Source global definitions if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then . /etc/bashrc fi # User specific environment if ! [[ "$PATH" =~ "$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:" ]] then PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:$PATH" fi export PATH # Set Prompt export PS1="[\u@localhost \W]\$ " # Change to home directory. cd $HOME # Uncomment the following line if you don't like systemctl's auto-paging feature: # export SYSTEMD_PAGER= # User specific aliases and functions # Set Oracle environment variables. export ORACLE_SID=XE export ORACLE_BASE=/opt/oracle export ORACLE_HOME=/opt/oracle/product/18c/dbhomeXE |
As the c##student user, you need to connect to the system schema and provision a c##student container database. You can connect to the system schema with the following syntax:
sqlplus system/cangetin@xe |
There are four steps required to provision a container database. These steps are different than the steps for previous non-container databases. In non-container databases, you could grant privileges directly to database users. Oracle now requires that you create database roles, which bundle privileges together. Then, you grant roles to users. The four provisioning steps are:
- Create a user, which must adhere to the following naming convention from Oracle Database 12c forward. The database user’s name must start with the letter
cand two#(pound) symbols followed by a character and then a string of letters and numbers. - Create a role, which must use the same naming convention as containerized users. Failure to use the correct naming convention raises an
ORA-65096error. - Grant database privileges to a role.
- Grant a database role to a user.
You create a c##student container database user with the following syntax:
CREATE USER c##student IDENTIFIED BY student DEFAULT TABLESPACE users QUOTA 100M ON users TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp; |
Next, you create a c##studentrole container role with the following syntax:
CREATE ROLE c##studentrole CONTAINER = ALL; |
Then, you grant the following privileges to your newly created c##studentrole role:
GRANT CREATE CLUSTER, CREATE INDEXTYPE, CREATE PROCEDURE, CREATE SEQUENCE, CREATE SESSION, CREATE TABLE, CREATE TRIGGER, CREATE TYPE, CREATE VIEW TO c##studentrole; |
Finally, you grant a c##studentrole role (bundle of privileges) to a c##videodb user:
GRANT c##studentrole TO c##student; |
After completing these tasks, you should use the quit command to exit the SQL*Plus CLI. Please note that unlike some database CLIs, you do not need to add a semicolon to quit the connection. Oracle divides its CLI commands into SQL*Plus and SQL commands; and the quit command is a SQL*Plus command. SQL*Plus commands do not require the terminating semicolon. SQL commands do require the semicolon or a line return and forward slash, which dispatches the SQL command to the SQL engine.
You should confirm that the provisioning worked by reconnecting to the Oracle database as the c##student user with this syntax:
sqlplus c##student/student@xe |
You have now provisioned and verified the connection to a database container user. Use the quit command to disconnect from the Oracle database, and the exit command to return to your host operating system.
At this point you have a couple options for using the docker container. You can install a proprietary Integrated Development Environment (IDE), like Oracle’s free SQL Developer. There are several others and some support more than one database engine. Unfortunately, all the others have annual licensing costs.
Post Install: Access Tools
Oracle’s SQL Developer is a Java-based solution that runs on numerous platforms. You can download SQL Developer from Oracle’s OTN web site:
https://www.oracle.com/downloads/
Click on the Developer Tools link to find the current version of the SQL Developer. Before you install SQL Developer on your macOS, you will need to download and install the Java 8 Software Development Kit (SDK) from this web site:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/
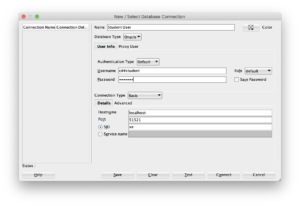
You configure a SQL Developer connection with the following values: use localhost as the host, c##student as the user, xe as the network service identifier, and 51521 as the port address. Click the plus button to add a connection where you enter these values, like shown below:
While the Java code in SQL Developer supports a port connection, Docker maps the port to the Oracle docker container. You don’t need to resolve the connection between SQL Developer and the Oracle Database listener through the network layer because this solution uses an Internal Process Control (IPC) model, based on socket to socket communication.
With virtualization you would need to install the Oracle Instant Client software on the hosting operating system. Then, you would configure your /etc/hosts file on both the hosting (macOS) and hosted (Oracle Linux) operating systems. Alternatively, you could add both IP addresses to a DNS server. The IP addresses let you map the connection between your physical macOS system and the Docker container running Oracle Linux. You can find further qualification of the connection mechanisms and repackaging in the Oracle Docker User Guide.
Containers map a local directory to operating system inside the container. Based on the earlier instructions the ~/oracle directory maps to the /home directory in the docker container. You have the ability to edit and move files within this portion of the file system’s hierarchy, which means you have complete control of the portion of the file system owned by the student user.
The next few steps help you verify the dual access to this portion of the docker container. Open a Terminal session and check your present working directory (with the pwd utility).
macName:~ username$ pwd |
It should return:
/Users/username |
During the installation, you created two subdirectories in the /Users/username directory. They were the oracle and docker-images subdirectories. In your host macOS, you should list (with the ls utility) the contents of your oracle subdirectory:
ls ~/oracle |
It should return the following:
oracle student |
As mentioned, your macOS /Users/username/oracle directory holds the contents of your docker container’s /home directory. That means that your /Users/username/oracle/student directory mirrors the /home/student directory in your docker container.
Assume your GitHub code repository for Oracle development is in a directory on your macOS side. The local mapping to the ~/oracle/student directly lets you put symbolic links in the hosted student user’s subdirectories. These symbolic links would point to the editable code on the macOS file system, which can be concurrently linked to your GitHub code repository.
Misleading Oracle Errors
It’s always interesting when you get in a hurry, have multiple terminal sessions open and type the wrong thing in the wrong terminal session. This is especially true when working with the Oracle database.
In this case, it was implementing a Docker Container of Oracle Database 18c on macOS. I typed the following to connect as the privileged system user:
sqlplus system/cangetin |
It generated the following error stack:
[student@localhost ~]$ sqlplus system/cangetin SQL*Plus: Release 18.0.0.0.0 - Production on Tue Sep 15 15:02:30 2020 Version 18.4.0.0.0 Copyright (c) 1982, 2018, Oracle. All rights reserved. ERROR: ORA-27140: attach to post/wait facility failed ORA-27300: OS system dependent operation:invalid_egid failed with status: 1 ORA-27301: OS failure message: Operation not permitted ORA-27302: failure occurred at: skgpwinit6 ORA-27303: additional information: startup egid = 54321 (oinstall), current egid = 54322 (dba) |
Really, that’s suppose to help an end-user or even an average DBA? Shouldn’t it really return an error that says the OS user isn’t the owner of the database? Naturally, there’s nothing wrong with connecting as the system privileged user when you’re OS account is not the owner provided you use the network service identifier, like
sqlplus system/cangetin@xe |
It works fine with the xe network service identifier. I hope this helps anybody confused by the error stack.
Correlated Updates
It’s always interesting when I answer questions. This question was how to you perform a correlated UPDATE statement. My answer was assuming you’re updating the rating_id foreign key column in the rating table with the value from an item_rating column in the item table where on or another column value in the rating table match the item_rating column value in the item table match, you would write a correlated UPDATE statement like:
UPDATE item i SET i.rating_id = r.rating_id WHERE EXISTS (SELECT NULL FROM rental r WHERE r.rating = i.item_rating OR r.description = i.item_rating); |
This works in Oracle, MySQL, MariaDB, and MS SQL Server. I thought my work was done but I was wrong. The individual was trying to write a correlated UPDATE statement for PostgreSQL. The statement returned the following error:
ERROR: syntax error at or near "WHERE"
LINE 3: WHERE EXISTS
^ |
I did didn’t find an article to point the individual to after quick Google and DuckDuckGo searches. So, I thought I’d provide how you do it in PostgreSQL:
UPDATE item i SET rating_id = r.rating_id FROM rating r WHERE r.rating = i.item_rating OR r.description = i.item_rating; |
In short, PostgreSQL doesn’t do what most expect because the UPDATE statement supports a FROM clause. Let’s give them the prize for different dialect. While I hope that I’m not a syntax bigot because I use MySQL more, I think the default syntax should always be supported in SQL dialects. After all, MySQL has a far superior named-notation INSERT statement alternative to the standard with the assignment method but MySQL also supports the standard syntax.
While I’ve shown you how to do it in PostgreSQL, what do you think? Should PostgreSQL be as responsible as MySQL is in maintaining standard SQL approaches?
Wrap Oracle SQL*Plus
One of the key problems with Oracle’s deployment is that you can not use the up-arrow key to navigate the sqlplus command-line history. Here’s little Bash shell function that you can put in your .bashrc file. It requires you to have your system administrator install the rlwrap package, which wraps the sqlplus command-line history.
You should also set the $ORACLE_HOME environment variable before you put this function in your .bashrc file.
sqlplus () { # Discover the fully qualified program name. path=`which rlwrap 2>/dev/null` file='' # Parse the program name from the path. if [ -n ${path} ]; then file=${path##/*/} fi; # Wrap when there is a file and it is rewrap. if [ -n ${file} ] && [[ ${file} = "rlwrap" ]]; then rlwrap sqlplus "${@}" else echo "Command-line history unavailable: Install the rlwrap package." $ORACLE_HOME/bin/sqlplus "${@}" fi } |
If you port this shell script to an environment where rlwrap is not installed, it simply prints the error message and advises you to install the rlwrap package.
As always, I hope this helps those looking for a solution.
Create Student User
It’s amazing how old some of my students’ computers are. The oldest with least memory are the foreign students. Fortunately, I kept copies of the old Oracle Database 10g XE. I give it to some students who need to run the smallest possible option. Then, again I have students who get emotional about having to use Unix or Linux as an operating system, which means I now also support Oracle Database 18c.
Anyway, I had to write a script that would support building a small 200 MB student schema in any of the Express Edition databases from 10g to 18c. Here’s the script for those who would like to use it. It sets up a student schema for Oracle Database 10g and 11g databases and a c##student schema for Oracle’s Containized Database 12c and 18c.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 | DECLARE /* Control variable. */ container BOOLEAN := FALSE; /* Weakly structured system reference cursor. */ container_sql SYS_REFCURSOR; /* Constant required for pre-container databases to avoid a a compile time error. */ sql_statement CONSTANT VARCHAR2(50) := 'SELECT cdb FROM v$database WHERE cdb = ''YES'''; BEGIN /* Check if the current user is the superuser. */ FOR i IN (SELECT USER FROM dual) LOOP /* Perform tasks as superuser. */ IF i.USER = 'SYSTEM' THEN /* Check for a container-enabled column, which enables this to work in both pre-container Oracle databases, like 10g and 11g. */ FOR j IN (SELECT DISTINCT column_name FROM dba_tab_columns WHERE column_name = 'CDB') LOOP /* Check for a container database, set control variable and exit when found. */ OPEN container_sql FOR sql_statement; LOOP container := TRUE; EXIT WHEN container_sql%FOUND; END LOOP; END LOOP; /* Conditionally drop existing user and role. */ IF container THEN /* Conditionally drop a container user. */ FOR j IN (SELECT username FROM dba_users WHERE username = 'C##STUDENT') LOOP EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'DROP USER c##student CASCADE'; END LOOP; /* Conditionally rop the container c##studentrole role. */ FOR j IN (SELECT ROLE FROM dba_roles WHERE ROLE = 'C##STUDENTROLE') LOOP EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'DROP ROLE c##studentrole'; END LOOP; /* Create a container user with 200 MB of space. */ EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'CREATE USER c##student'||CHR(10) || 'IDENTIFIED BY student'||CHR(10) || 'DEFAULT TABLESPACE users'||CHR(10) || 'QUOTA 200M ON users'||CHR(10) || 'TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp'; /* Create a container role. */ EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'CREATE ROLE c##studentrole CONTAINER = ALL'; /* Grant privileges to a container user. */ EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'GRANT CREATE CLUSTER, CREATE INDEXTYPE,'||CHR(10) || 'CREATE PROCEDURE, CREATE SEQUENCE,'||CHR(10) || 'CREATE SESSION, CREATE TABLE,'||CHR(10) || 'CREATE TRIGGER, CREATE TYPE,'||CHR(10) || 'CREATE VIEW TO c##studentrole'; /* Grant role to user. */ EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'GRANT c##studentrole TO c##student'; ELSE /* Conditonally drop the non-container database user. */ FOR j IN (SELECT username FROM dba_users WHERE username = 'STUDENT') LOOP EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'DROP USER student CASCADE'; END LOOP; /* Create the student database. */ EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'CREATE USER student'||CHR(10) || 'IDENTIFIED BY student'||CHR(10) || 'DEFAULT TABLESPACE users'||CHR(10) || 'QUOTA 200M ON users'||CHR(10) || 'TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp'; /* Grant necessary privileges to the student database. */ EXECUTE IMMEDIATE 'GRANT CREATE CLUSTER, CREATE INDEXTYPE,'||CHR(10) || 'CREATE PROCEDURE, CREATE SEQUENCE,'||CHR(10) || 'CREATE SESSION, CREATE TABLE,'||CHR(10) || 'CREATE TRIGGER, CREATE TYPE,'||CHR(10) || 'CREATE VIEW TO student'; END IF; ELSE /* Print an message that the user lacks privilegs. */ dbms_output.put_line('You must be the SYSTEM user to drop and create a user.'); END IF; END LOOP; END; / |
As always, I hope this helps those looking for a solution beyond Quest’s Toad for Oracle, APEX, or SQL Developer. Let me know if you like it.
MySQL Linux to Windows
My students want to transfer their course setup MySQL files from the Linux VM that I provide to Microsoft Windows 10. This post explains how because I found a couple small errors in the Google’d posts they would most likely see.
The first step is required because when I didn’t assign a name or domain to the the Fedora VM, which allows it to run as localhost on any student machine. In tandem, I didn’t assign a static IP address but opted for dynamic IP assignment. That means, the first step to securely copy the files requires you to find the assigned IP address. You can do that with the following Linux command:
ifconfig -a | grep 'inet[[:blank:]]' | head -1 | cut -c 14-30 |
It would return something like:
192.168.147.198 |
After you have discovered the IP address, you need to download PuTTy from their web site because includes the pscp (PuTTy Secure Copy) utility. I recommend you click on the MSI (Microsoft Installer Package) file, and install it on your Windows machine. As a rule, you should accept the default location, which is C:\Program Files\PuTTy.
While you could alter your system-level %PATH% environment variable after you install the software, I recommend you only include it in the %PATH% within the scope of a Command (cmd) shell. Navigate to your Windows Start and enter cmd in the search field. It should launch the Command Prompt terminal, which is a terminal emulator.
In the terminal editor, type the following case sensitive command to add the PuTTy directory to your path (yes, it’s case sensitive):
SET PATH=%PATH%;%ProgramFiles%\PuTTy |
Now, you can securely copy the files and directory structure from Linux to Windows with the following command (where you replace the traditional server name with the dynamically assigned IP address). You should also be in the target directory where you want the files and directories copied:
C:\Data\cit225>pscp -r student@192.168.147.198:/home/student/Data/cit225/mysql . |
After entering the password for the student on the Linux VM, you should see the following copy over:
Raiders2.png | 99 kB | 99.5 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% LordOfTheRings3.png | 119 kB | 119.8 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter4.png | 103 kB | 103.9 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% Raiders1.png | 92 kB | 92.4 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% Raiders3.png | 123 kB | 123.9 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% LordOfTheRings2.png | 111 kB | 111.7 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% LordOfTheRings1.png | 103 kB | 104.0 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter2.png | 118 kB | 118.7 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter7.png | 150 kB | 150.2 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter3.png | 106 kB | 106.1 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter5.png | 82 kB | 82.5 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter6.png | 129 kB | 129.9 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter1.png | 118 kB | 118.8 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter8.png | 150 kB | 150.9 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter8.txt | 8 kB | 8.5 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter3.txt | 5 kB | 5.8 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter5.txt | 7 kB | 7.9 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter1.txt | 6 kB | 6.6 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter2.txt | 7 kB | 7.8 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% Raiders3.txt | 5 kB | 5.6 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter4.txt | 7 kB | 7.5 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter7.txt | 5 kB | 5.4 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% HarryPotter6.txt | 7 kB | 7.4 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% LOTRFellowship.txt | 4 kB | 5.0 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% apply_store_base.sql | 1 kB | 1.6 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% query_membership.sql | 0 kB | 0.3 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% apply_mysql_lab1.sql | 1 kB | 1.9 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% configure_mysql_web.sql | 37 kB | 37.1 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% seed_mysql_store_ri2.sql | 58 kB | 58.5 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% cleanup_mysql_store.sql | 5 kB | 5.4 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% create_mysql_store_ri2.sq | 21 kB | 21.1 kB/s | ETA: 00:00:00 | 100% |
My students will need to repeat this step to transfer all of the sample PHP files that demonstrate web application patterns. They also need to inspect individual files to ensure any path referencing commands are manually converted to their new Windows equivalent.
They can move the physical files as the root superuser with the following pscp command provide you haven’t stored the files somewhere other than the default location:
C:\Data\temp>pscp -r root@192.168.147.198:/var/lib/mysql . |
As always, I hope this helps those trying to sort things out.
Session Variables
In MySQL and Oracle, you set a session variable quite differently. That means you should expect there differences between setting a session variable in Postgres. This blog post lets you see how to set them in all three databases. I’m always curious what people think but I’m willing to bet that MySQL is the simplest approach. Postgres is a bit more complex because you must use a function call, but Oracle is the most complex.
The difference between MySQL and Postgres is an “@” symbol versus a current_setting() function call. Oracle is more complex because it involves the mechanics in Oracle’s sqlplus shell, SQL dialect, and PL/SQL language (required to assign a value to a variable).
MySQL
MySQL lets you declare a session variable in one step and use it one way in a SQL statement or stored procedure.
- You set a session variable on a single line with the following command:
SET @my_variable_name := 'My Value';
- You can query a variable from the pseudo table
dualor as a comparison value in theSELECT-listSELECT @my_variable_name AS "The Value" FROM dual;
or
WHEREclauseSELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name = @my_variable_name;
Postgres
Postgres lets you declare a session variable in one step and use it one way in a SQL statement or stored procedure.
- You set a session variable in a single line. It iss critical to note that you must use double quotes around the session variable name and single quotes for the value. You raise an error when you use a single quote instead a double quote around the session variable name. The syntax is:
SET SESSION "videodb.table_name" = 'new_hire';
- You can query a variable from the pseudo table
dualor as a comparison value in theSELECT-list with thecurrent_setting()function call.SELECT current_setting('videodb.table_name') AS "The Value";
or
WHEREclauseSELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name = current_setting('videodb.table_name');
Oracle
There are two steps required to declare a session variable in Oracle. First, you need to define the variable in the SQL*Plus session. Oracle lets you define a variable like you would define a variable in the C language, using extern before the variable’s type. Second, you assign a value to the session variable in an anonymous PL/SQL block. There is no single line statement to declare a variable with an initial value.
- You set a session variable by using the
VARIABLEkeyword, a variable name, and data type. The supported data types are:BLOB,BFILE,BINARY_DOUBLE,BINARY_FLOAT,CHAR,CLOB,NCHAR,NCLOB,NVARCHAR2,REFCURSOR, andVARCHAAR2. You define a variable with the following syntax:VARIABLE bv_variable_name VARCHAR2(30)
- You assign a value to the bind variable inside an anonymous block by prefacing the variable name with a colon. You assign values inside PL/SQL with the walrus operator (
:=) and a string enclosed by single quotes. Anonymous blocks start with aBEGINand end with anENDfollowed by a semicolon (;) and a forward slash (/) to dispatch the block for execution. The following example shows a full block:BEGIN :bv_variable_name := 'Some Value'; END; /
- You can query any declared variable from the pseudo table
dualor as a comparison value in theSELECT-listSELECT :bv_variable_name FROM dual;
or
WHEREclauseSELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE column_name = :bv_variable_name;
Misleading ORA- Message
Oracle error messages are more or less the best in the industry but time-to-time they saddle you with a bad or misleading message. For example, I was running one of the code modules from my Oracle Database 12c PL/SQL Programming book for a class exercise and got this error message:
BEGIN * ERROR AT line 1: ORA-22288: FILE OR LOB operation failed ORA-06512: AT "STUDENT.LOAD_CLOB_FROM_FILE", line 71 ORA-06512: AT line 11 |
Oddly enough, it was simple to identify generally. It failed on a call to the DBMS_LOB.LOADCLOBFROMFILE procedure. However, the better question is why did it fail because the virtual directory resolved and the permissions worked.
The first test was to try another file, which worked perfectly with the same code. That meant it had to be something with the physical file. I took a look and sure enough I found a character set problem, like the following:
… he reveals that the Nazgûl, or Ringwraiths, have left Mordor to capture the Ring and kill whoever carries it.
and,
The group flees to the elvish realm of Lothlórien …
The “û” and “ó” characters were incompatible with the default NLS_LANG setting of the database and a CLOB limits the use of non-standard character sets. It’s ashamed that Oracle didn’t through a character set error, which would have expedited resolution of the problem.
As always, I hope this helps those looking for solutions.