Archive for the ‘Linux’ Category
Ruby+MySQL on Ubuntu
This post goes through installing and configuring Ruby and Ruby on Rails for MySQL. The first step requires updating the Ubuntu OS:
sudo apt-get update |
Interestingly, I found that the man-db service had inadvertently stopped. It raised the following error:
E: dpkg was interrupted, you must manually run 'sudo dpkg --configure -a' to correct the problem. |
You run this command to find the problem with the dpkg utility:
sudo dpkg --configure -a |
It returned:
Setting up man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Updating database of manual pages ... man-db.service is a disabled or a static unit not running, not starting it. |
The following command started the man-db service:
sudo systemctl start man-db.service |
Next, you install the prerequisite packages with this command:
sudo apt-get install -y git-core zlib1g-dev build-essential libssl-dev libreadline-dev libyaml-dev libsqlite3-dev sqlite3 libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev software-properties-common libffi-dev |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done Note, selecting 'git' instead of 'git-core' build-essential is already the newest version (12.9ubuntu3). build-essential set to manually installed. libreadline-dev is already the newest version (8.1.2-1). libreadline-dev set to manually installed. git is already the newest version (1:2.34.1-1ubuntu1.10). git set to manually installed. software-properties-common is already the newest version (0.99.22.9). zlib1g-dev is already the newest version (1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2). zlib1g-dev set to manually installed. The following additional packages will be installed: libssl3 Suggested packages: libcurl4-doc libidn11-dev libkrb5-dev libldap2-dev librtmp-dev libssh2-1-dev sqlite3-doc libssl-doc libyaml-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: libcurl4-openssl-dev libffi-dev libsqlite3-dev libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev libyaml-dev sqlite3 The following packages will be upgraded: libssl-dev libssl3 2 upgraded, 7 newly installed, 0 to remove and 18 not upgraded. Need to get 7,426 kB of archives. After this operation, 12.8 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libssl-dev amd64 3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13 [2,374 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libssl3 amd64 3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13 [1,902 kB] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libcurl4-openssl-dev amd64 7.81.0-1ubuntu1.15 [386 kB] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libsqlite3-dev amd64 3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3 [846 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libxml2-dev amd64 2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.3 [804 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libxslt1-dev amd64 1.1.34-4ubuntu0.22.04.1 [219 kB] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 sqlite3 amd64 3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3 [768 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libffi-dev amd64 3.4.2-4 [63.7 kB] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libyaml-dev amd64 0.2.2-1build2 [62.8 kB] Fetched 7,426 kB in 1s (5,467 kB/s) Preconfiguring packages ... (Reading database ... 246735 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libssl-dev_3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libssl-dev:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13) over (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.12) ... Preparing to unpack .../libssl3_3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libssl3:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13) over (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.12) ... Setting up libssl3:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13) ... Selecting previously unselected package libcurl4-openssl-dev:amd64. (Reading database ... 246735 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../0-libcurl4-openssl-dev_7.81.0-1ubuntu1.15_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libcurl4-openssl-dev:amd64 (7.81.0-1ubuntu1.15) ... Selecting previously unselected package libsqlite3-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../1-libsqlite3-dev_3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libsqlite3-dev:amd64 (3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxml2-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../2-libxml2-dev_2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxml2-dev:amd64 (2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxslt1-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../3-libxslt1-dev_1.1.34-4ubuntu0.22.04.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxslt1-dev:amd64 (1.1.34-4ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package sqlite3. Preparing to unpack .../4-sqlite3_3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking sqlite3 (3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libffi-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../5-libffi-dev_3.4.2-4_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libffi-dev:amd64 (3.4.2-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package libyaml-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../6-libyaml-dev_0.2.2-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libyaml-dev:amd64 (0.2.2-1build2) ... Setting up libyaml-dev:amd64 (0.2.2-1build2) ... Setting up libffi-dev:amd64 (3.4.2-4) ... Setting up libxml2-dev:amd64 (2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.3) ... Setting up libsqlite3-dev:amd64 (3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3) ... Setting up libcurl4-openssl-dev:amd64 (7.81.0-1ubuntu1.15) ... Setting up libssl-dev:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13) ... Setting up sqlite3 (3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3) ... Setting up libxslt1-dev:amd64 (1.1.34-4ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for install-info (6.8-4build1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.6) ... |
Use the cd command to change to the student home directory. Clone the asdf as the multiple runtime version manager with this command:
git clone https://github.com/excid3/asdf.git ~/.asdf |
The following is the output of the git clone command:
Cloning into '/home/student/.asdf'... remote: Enumerating objects: 8756, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (829/829), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (476/476), done. remote: Total 8756 (delta 428), reused 657 (delta 334), pack-reused 7927 Receiving objects: 100% (8756/8756), 3.10 MiB | 4.29 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (5148/5148), done. |
Next, you fix your .bashrc file by adding the following components:
echo '. "$HOME/.asdf/asdf.sh"' >> ~/.bashrc echo '. "$HOME/.asdf/completions/asdf.bash"' >> ~/.bashrc echo 'legacy_version_file = yes' >> ~/.asdfrc echo 'export EDITOR="code --wait"' >> ~/.bashrc |
Source the modifies shell, which you can do like this:
exec $SHELL |
or, like:
. ${HOME}/.bashrc |
Add the following asdf plug-ins:
asdf plugin add ruby asdf plugin add nodejs |
Install Ruby with the following command:
asdf install ruby 3.3.0 |
Display detailed console log →
Downloading ruby-build...
==> Downloading ruby-3.3.0.tar.gz...
-> curl -q -fL -o ruby-3.3.0.tar.gz https://cache.ruby-lang.org/pub/ruby/3.3/ruby-3.3.0.tar.gz
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 21.0M 100 21.0M 0 0 10.1M 0 0:00:02 0:00:02 --:--:-- 10.1M
==> Installing ruby-3.3.0...
-> ./configure "--prefix=$HOME/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0" --enable-shared --with-ext=openssl,psych,+
-> make -j 2
-> make install
==> Installed ruby-3.3.0 to /home/student/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0
asdf: Warn: You have configured asdf to preserve downloaded files (with always_keep_download=yes or --keep-download). But
asdf: Warn: the current plugin (ruby) does not support that. Downloaded files will not be preserved. |
Install Ruby Global with this syntax:
asdf global ruby 3.3.0 |
Update the Ruby Gems with this command:
gem update --system |
Display detailed console log →
Updating rubygems-update Fetching rubygems-update-3.5.5.gem Successfully installed rubygems-update-3.5.5 Parsing documentation for rubygems-update-3.5.5 Installing ri documentation for rubygems-update-3.5.5 Done installing documentation for rubygems-update after 1 seconds Parsing documentation for rubygems-update-3.5.5 Done installing documentation for rubygems-update after 0 seconds Installing RubyGems 3.5.5 Successfully built RubyGem Name: bundler Version: 2.5.5 File: bundler-2.5.5.gem Bundler 2.5.5 installed RubyGems 3.5.5 installed Regenerating binstubs Regenerating plugins Parsing documentation for rubygems-3.5.5 Installing ri documentation for rubygems-3.5.5 # 3.5.5 / 2024-01-18 ## Enhancements: * Installs bundler 2.5.5 as a default gem. ## Bug fixes: * Fix `require` activation conflicts when requiring default gems under some situations. Pull request [#7379](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7379) by deivid-rodriguez * Use cache_home instead of data_home in default_spec_cache_dir. Pull request [#7331](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7331) by mrkn ## Documentation: * Use squiggly heredocs in `Gem::Specification#description` documentation, so it doesn't add leading whitespace. Pull request [#7373](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7373) by bravehager # 3.5.4 / 2024-01-04 ## Enhancements: * Always avoid "Updating rubygems-update" message. Pull request [#7335](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7335) by deivid-rodriguez * Installs bundler 2.5.4 as a default gem. ## Bug fixes: * Make `gem update --system` respect ruby version constraints. Pull request [#7334](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7334) by deivid-rodriguez ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ RubyGems installed the following executables: /home/student/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0/bin/gem /home/student/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0/bin/bundle /home/student/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0/bin/bundler Ruby Interactive (ri) documentation was installed. ri is kind of like man pages for Ruby libraries. You may access it like this: ri Classname ri Classname.class_method ri Classname#instance_method If you do not wish to install this documentation in the future, use the --no-document flag, or set it as the default in your ~/.gemrc file. See 'gem help env' for details. RubyGems system software updated |
You can confirm your Ruby install with two commands. First, use the which utility to check the Ruby install:
which -a ruby |
It should return:
/home/student/.asdf/shims/ruby |
Then, check the Ruby version:
ruby -v |
It should return:
ruby 3.3.0 (2023-12-25 revision 5124f9ac75) [x86_64-linux] |
Assuming you’ve installed and configured MySQL 8 on Ubuntu, you need this additional library to support the necessary Ruby Gem:
sudo apt-get install -y libmysqlclient-dev |
Now, you can install the current MySQL Ruby Gem:
gem install mysql2 |
You can now write a mysql_connection.rb program to verify a connection to the MySQL 8 database, like:
# Include Ruby Gem libraries. require 'rubygems' require 'mysql2' begin # Create new database connection. db = Mysql2::Client.new( :host => 'localhost' \ , :username => 'student' \ , :password => 'student' \ , :database => 'studentdb') # Create a result set. stmt = db.query('SELECT version() AS version') # Read through the result set hash. stmt.each do | row | puts "#{row['version']}" end # Release the result set resources. stmt.free rescue Mysql2::Error => e # Print the error. puts "ERROR #{e.errno} (#{e.sqlstate}): #{e.error}" puts "Can't connect to the MySQL database specified." # Signal an error. exit 1 ensure # Close the connection when it is open. db.close if db end |
Call the program with this syntax:
ruby mysql_connection.rb |
It should return:
Connected to the MySQL database server. |
You can verify the version with this mysql_version.rb program:
# Include Ruby Gem libraries. require 'rubygems' require 'mysql2' begin # Create new database connection. db = Mysql2::Client.new( :host => 'localhost' \ , :username => 'student' \ , :password => 'student' \ , :database => 'studentdb') # Create a result set. rs = db.query('SELECT version() AS version') # Read through the result set hash. rs.each do | row | puts "#{row['version']}" end # Release the result set resources. rs.free rescue Mysql2::Error => e # Print the error. puts "ERROR #{e.errno} (#{e.sqlstate}): #{e.error}" puts "Can't connect to the MySQL database specified." # Signal an error. exit 1 ensure # Close the connection when it is open. db.close if db end |
On Ubuntu, it should return:
8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1 |
If you don’t know anything about the mysql2 Ruby Gem, you should read the documentation. It’s very concise and requires a basic understanding of Ruby programming. The two specific pages who may want to check for the next examples are:
- The Mysql2 Statement Class list.
- The Mysql2 Result Class List
The mysql_version.rb version uses the known string literal for columns or column aliases returned by the SQL statement, which becomes the stmt (or statement) in the program. The next program eliminates the need to enumerate with the text-based columns from the query by using the Statement#fields array values by use of a numeric index. The numeric index returns the field names from the Statement#fields class to use in as the name for values in the Result#fields value found in the row variable of the for loop.
# Include Ruby Gem libraries. require 'rubygems' require 'mysql2' # Begin block. begin # Create a new connection resource. db = Mysql2::Client.new( :host => 'localhost' \ , :username => 'student' \ , :password => 'student' \ , :database => 'studentdb') # Create a result set. stmt = db.query("SELECT DISTINCT i.item_title, ra.rating " + \ "FROM item i INNER JOIN rating_agency ra " + \ "ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id " + \ "WHERE ra.rating_agency = 'MPAA'" + \ "ORDER BY 1") # Read through the result set hash. stmt.each do | row | out = "" i = 0 while i < stmt.fields.count() # Check when not last column and use the: # - Hash returned by the result set for the value, and # - String array value returned by the statement object # as the name value of the hash by leveraging its # numeric index. if i < stmt.fields.count() - 1 out += "#{row[stmt.fields[i]]}" out += ", " else out += "#{row[stmt.fields[i]]}" end i += 1 end puts "#{out}" end # Release the result set resources. stmt.free rescue Mysql2::Error => e # Print the error. puts "ERROR #{e.errno} (#{e.sqlstate}): #{e.error}" puts "Can't connect to MySQL database specified." # Signal an error. exit 1 ensure # Close the connection when it is open. db.close if db end |
It returns the select two columns from the query:
A Man for All Seasons, G Around the World in 80 Days, G Beau Geste, PG Brave Heart, R Camelot, G Casino Royale, PG-13 ... Tomorrow Never Dies, PG-13 Tora! Tora! Tora!, G Tron, PG |
The following mysql_query_params.rb Ruby example accepts a single argument to leverage a wild card query in MySQL:
require 'rubygems' require 'mysql2' # Input external arguments. arguments = ARGV # Check for one input parameter and substitute an empty string # when one isn't found. if arguments.length == 1 argument = arguments[0] else argument = "" end # Begin block. begin # Create a new connection resource. db = Mysql2::Client.new( :host => 'localhost' \ , :username => 'student' \ , :password => 'student' \ , :database => 'studentdb') # Create a result set. stmt = db.prepare("SELECT DISTINCT i.item_title, ra.rating " + \ "FROM item i INNER JOIN rating_agency ra " + \ "ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id " + \ "WHERE ra.rating_agency = 'MPAA'" + \ "AND i.item_title LIKE CONCAT(?,'%')" + \ "ORDER BY 1") # Bind the variable into the query. rs = stmt.execute(argument) # Read through the result set hash. rs.each do | row | out = "" i = 0 while i < rs.fields.count() # Check when not last column and use the: # - Hash returned by the result set for the value, and # - String array value returned by the statement object # as the name value of the hash by leveraging its # numeric index. if i < rs.fields.count() - 1 out += "#{row[rs.fields[i]]}" out += ", " else out += "#{row[rs.fields[i]]}" end i += 1 end puts "#{out}" end # Release the result set resources. rs.free rescue Mysql2::Error => e # Print the error. puts "ERROR #{e.errno} (#{e.sqlstate}): #{e.error}" puts "Can't connect to MySQL database specified." # Signal an error. exit 1 ensure # Close the connection when it is open. db.close if db end |
If you call the mysql_query_params.rb program with this syntax:
ruby mysql_aquery_params.rb Harry |
It’ll return the following from the studentdb database:
Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, PG Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows, Part 1, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows, Part 2, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Half Blood Prince, PG Harry Potter and the Order of the Phoenix, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, PG Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone, PG |
After that, you should install Rails (check for current version beyond 1/2024). Install Ruby Global with this syntax:
gem install rails -v 7.1.3 |
Check the version installed:
rails -v |
It should return:
Rails 7.1.3 |
Run this command to enable Rails for MySQL 8:
rails new myapp -d mysql |
If you want to configure a username and password for MySQL, edit the config/database.yml file.
As always, I hope this helps somebody looking for step-by-step guide.
VSCode & $PYTHONPATH
About 4 years ago, I demonstrated how to develop Python functions with a relative src directory in this old blog post. I thought it might be possible to do with VSCode. Doing a bit of research, it appeared all that was required was adding the PythonPath to VSCode’s Python settings in:
/home/student/.vscode/extensions/ms-python.python-2023.22.0/pythonFiles/.vscode/settings.json |
It contained:
{"files.exclude":{"**/__pycache__/**":true,"**/**/*.pyc":true},"python.formatting.provider":"black"} |
I added a configuration for the PYTHONPATH, as shown:
{"files.exclude":{"**/__pycache__/**":true,"**/**/*.pyc":true},"python.formatting.provider":"black","python.pythonPath": "/home/student/Lib"} |
As you can tell from the embedded VSCode Terminal output below, the PYTHONPATH is not found. You can manually enter it and retest your code successfully. There is no way to use a relative PYTHONPATH like the one you can use from an shell environment file.
This is the hello_whom5.py code:
#!/usr/bin/python # Import the basic sys library. import sys from input import parse_input # Assign command-line argument list to variable. whom = parse_input(sys.argv) # Check if string isn't empty and use dynamic input. if len(whom) > 0: # Print dynamic hello salutation. print("Hello " + whom + "!\n") else: # Print default saluation. print("Hello World!") |
This is the input.py library module:
# Parse a list and return a whitespace delimited string. def parse_input(input_list): # Assign command-line argument list to variable. cmd_list = input_list[1:] # Declare return variable. result = "" # Check whether or not their are parameters beyond the file name. if isinstance(input_list,list) and len(input_list) != 0: # Loop through the command-line argument list and print it. for element in cmd_list: if len(result) == 0: result = element else: result = result + " " + element # Return result variable as string. return result |
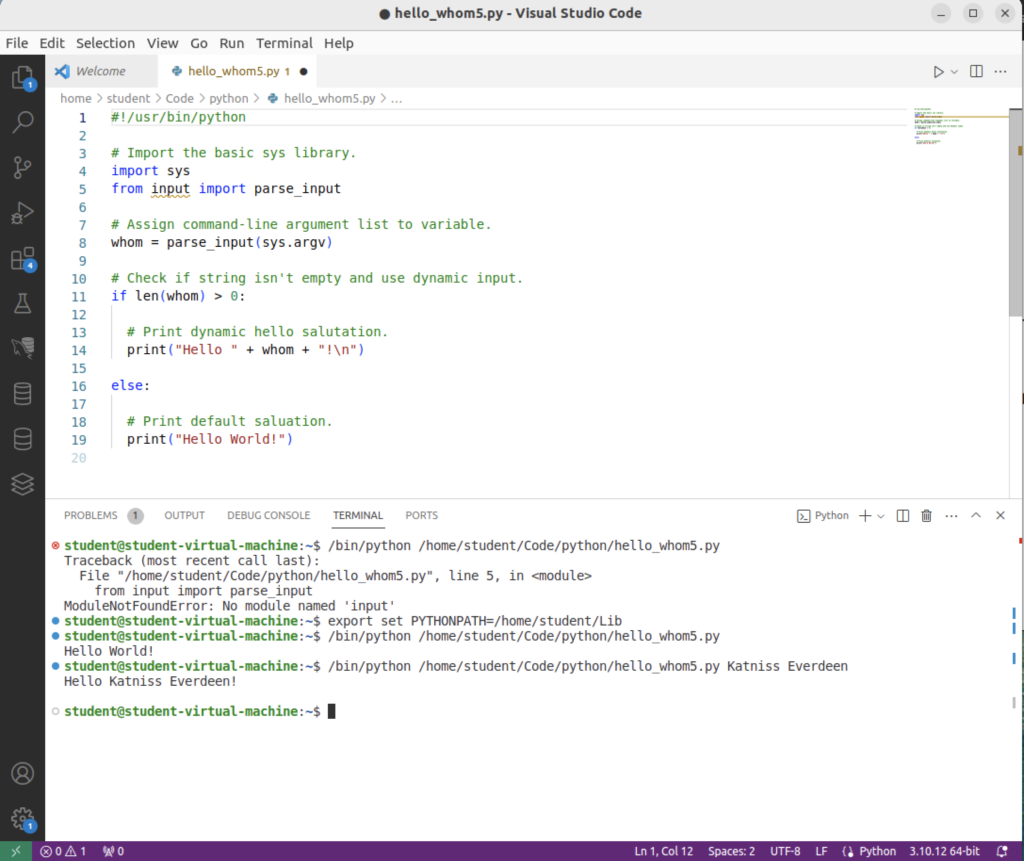
This is the Terminal output from VSCode:
student@student-virtual-machine:~$ /bin/python /home/student/Code/python/hello_whom5.py Traceback (most recent call last): File "/home/student/Code/python/hello_whom5.py", line 5, in <module> from input import parse_input ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'input' student@student-virtual-machine:~$ export set PYTHONPATH=/home/student/Lib student@student-virtual-machine:~$ /bin/python /home/student/Code/python/hello_whom5.py Hello World! student@student-virtual-machine:~$ /bin/python /home/student/Code/python/hello_whom5.py Katniss Everdeen Hello Katniss Everdeen! student@student-virtual-machine:~$ |
The VSCode image for the test follows below:
As always, I hope this helps somebody working the same issue. However, if somebody has a better solution, please let me know.
Ubuntu, R, RScript & RStudio
Installed R, Rscript, and RStudio on my student Ubuntu instance. You use the following command to install R a
sudo apt install -y r-base-core |
Then, you can check the version with the following command:
R --version |
It should return:
R version 4.1.2 (2021-11-01) -- "Bird Hippie" Copyright (C) 2021 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit) R is free software and comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. You are welcome to redistribute it under the terms of the GNU General Public License versions 2 or 3. For more information about these matters see https://www.gnu.org/licenses/. |
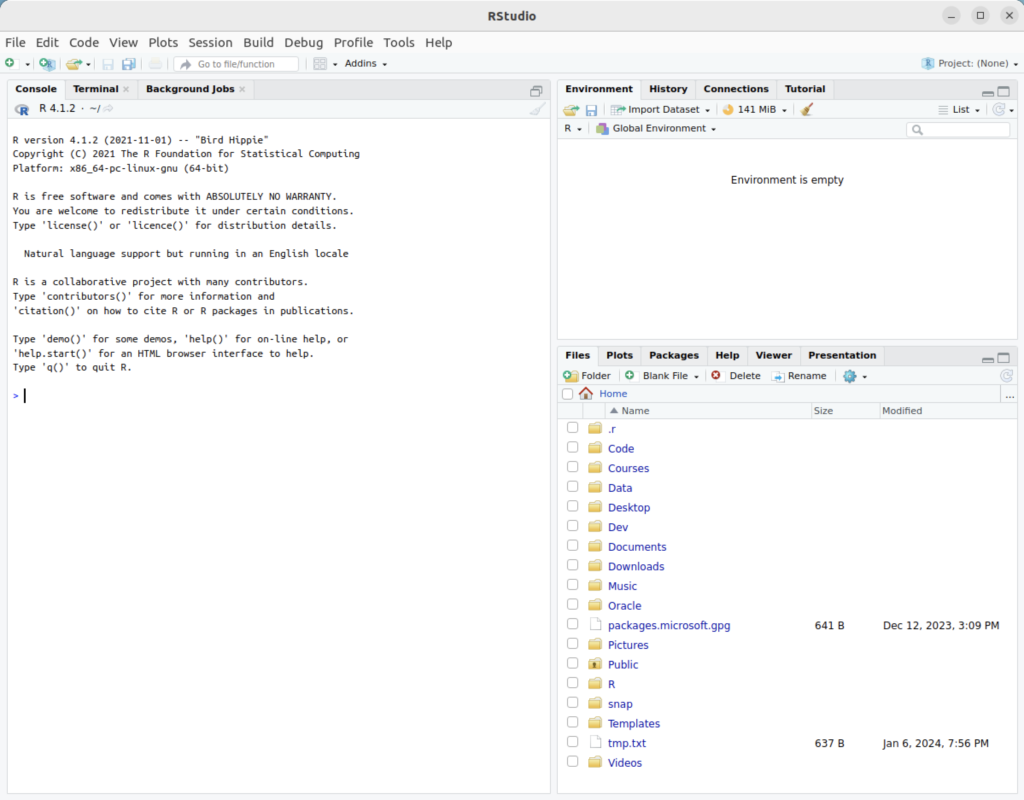
You also can run the interactive R environment by simply typing “R” at the command-line interface (CLI). It will display the following after entering the environment, quitting the environment, and discarding the workspace:
R version 4.1.2 (2021-11-01) -- "Bird Hippie" Copyright (C) 2021 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit) R is free software and comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. You are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions. Type 'license()' or 'licence()' for distribution details. Natural language support but running in an English locale R is a collaborative project with many contributors. Type 'contributors()' for more information and 'citation()' on how to cite R or R packages in publications. Type 'demo()' for some demos, 'help()' for on-line help, or 'help.start()' for an HTML browser interface to help. Type 'q()' to quit R. > q() Save workspace image? [y/n/c]: n |
You can write and run a hello.r script file as follows in a Linux environment:
#!/usr/bin/Rscript
# Print a string.
print("Hello World!") |
It prints what you would expect:
[1] "Hello World!" |
The RStudio comes in two versions. One is Free and the other costs money. These are not hosted in the Ubuntu repository, and you must download them manually to apply them. You can go to RStudio web site or run the following command to download RStudio Free edition:
wget https://download1.rstudio.org/electron/jammy/amd64/rstudio-2023.12.0-369-amd64.deb |
After downloading the package, you can’t quite install RStudio until you install two likely uninstalled dependencies, which are:
libclang-dev libclang-14-dev libclang1-14 libclang-common-14-dev lib32gcc-s1 lib32stdc++6 libc6-i386 libobjc4 libobjc-11-dev libssl-dev |
Therefore, the prestep is:
sudo apt install -y libssl-dev libclang-dev libclang-14-dev libobjc-11-dev libclang1-14 libclang-common-14-dev lib32gcc-s1 lib32stdc++6 libc6-i386 libobjc4 |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done Suggested packages: libssl-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: lib32gcc-s1 lib32stdc++6 libc6-i386 libclang-14-dev libclang-common-14-dev libclang-dev libclang1-14 libobjc-11-dev libobjc4 libssl-dev 0 upgraded, 10 newly installed, 0 to remove and 14 not upgraded. 1 not fully installed or removed. Need to get 44.2 MB of archives. After this operation, 382 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libssl-dev amd64 3.0.2-0ubuntu1.12 [2,373 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libobjc4 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [48.6 kB] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libobjc-11-dev amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [196 kB] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libclang1-14 amd64 1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1 [6,792 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libc6-i386 amd64 2.35-0ubuntu3.5 [2,837 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 lib32gcc-s1 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [63.9 kB] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 lib32stdc++6 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [740 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libclang-common-14-dev amd64 1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1 [5,975 kB] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libclang-14-dev amd64 1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1 [25.2 MB] Get:10 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/universe amd64 libclang-dev amd64 1:14.0-55~exp2 [3,138 B] Fetched 44.2 MB in 3s (17.1 MB/s) Selecting previously unselected package libssl-dev:amd64. (Reading database ... 242640 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../0-libssl-dev_3.0.2-0ubuntu1.12_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libssl-dev:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.12) ... Selecting previously unselected package libobjc4:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../1-libobjc4_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libobjc4:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libobjc-11-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../2-libobjc-11-dev_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libobjc-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libclang1-14. Preparing to unpack .../3-libclang1-14_1%3a14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libclang1-14 (1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libc6-i386. Preparing to unpack .../4-libc6-i386_2.35-0ubuntu3.5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libc6-i386 (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Selecting previously unselected package lib32gcc-s1. Preparing to unpack .../5-lib32gcc-s1_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking lib32gcc-s1 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package lib32stdc++6. Preparing to unpack .../6-lib32stdc++6_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking lib32stdc++6 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libclang-common-14-dev. Preparing to unpack .../7-libclang-common-14-dev_1%3a14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libclang-common-14-dev (1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libclang-14-dev. Preparing to unpack .../8-libclang-14-dev_1%3a14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libclang-14-dev (1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libclang-dev. Preparing to unpack .../9-libclang-dev_1%3a14.0-55~exp2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libclang-dev (1:14.0-55~exp2) ... Setting up libclang1-14 (1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1) ... Setting up libobjc4:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libssl-dev:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.12) ... Setting up libc6-i386 (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Setting up libobjc-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up lib32gcc-s1 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up lib32stdc++6 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libclang-common-14-dev (1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1) ... Setting up libclang-14-dev (1:14.0.0-1ubuntu1.1) ... Setting up libclang-dev (1:14.0-55~exp2) ... Setting up rstudio (2023.12.0+369) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... |
Then, you can install RStudio with this command from the directory where you downloaded it:
sudo dpkg -i rstudio-2023.12.0-369-amd64.deb |
Display detailed console log →
Selecting previously unselected package rstudio. (Reading database ... 239285 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack rstudio-2023.12.0-369-amd64.deb ... Unpacking rstudio (2023.12.0+369) ... Setting up rstudio (2023.12.0+369) ... Processing triggers for mailcap (3.70+nmu1ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.26-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for hicolor-icon-theme (0.17-2) ... Processing triggers for shared-mime-info (2.1-2) ... |
After a successful installation, you can launch RStudio with the following command:
rstudio |
You will get the following console:
As always, I hope this helps those trying to do something that should be simple but isn’t quite simple.
Ubuntu, Perl & MySQL
Configuring Perl to work with MySQL is straight forward. While Perl is installed generally, you may need to install the libdbd-mysql-perl library.
You install it as a sudoer user with this syntax:
sudo apt install -y libdbd-mysql-perl |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: libmysqlclient21 The following NEW packages will be installed: libdbd-mysql-perl libmysqlclient21 0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 12 not upgraded. Need to get 1,389 kB of archives. After this operation, 7,143 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libmysqlclient21 amd64 8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1 [1,301 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libdbd-mysql-perl amd64 4.050-5ubuntu0.22.04.1 [87.6 kB] Fetched 1,389 kB in 1s (1,213 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package libmysqlclient21:amd64. (Reading database ... 235085 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libmysqlclient21_8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libmysqlclient21:amd64 (8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libdbd-mysql-perl:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../libdbd-mysql-perl_4.050-5ubuntu0.22.04.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libdbd-mysql-perl:amd64 (4.050-5ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Setting up libmysqlclient21:amd64 (8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Setting up libdbd-mysql-perl:amd64 (4.050-5ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... |
You can find the Perl version with the following version.pl program:
1 2 3 4 | #!/usr/bin/perl -w # Print the version. print "Perl ".$]."\n"; |
The first line lets you call the program without prefacing the program name with perl. The first line invokes a subshell of perl by default. You just need to ensure the file has read and execute privileges to run by using the
chmod 755 version.pl |
You call it with this:
./version.pl |
It prints:
Perl 5.034000 |
The following static_query.pl Perl program uses the Perl DBI library to query and return a data set based on a static query.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | #!/usr/bin/perl -w # Use the DBI library. use DBI; use strict; use warnings; # Create a connection. my $dbh = DBI->connect("DBI:mysql:database=studentdb;host=localhost:3306" ,"student","student",{'RaiseError' => 1}); # Create SQL statement. my $sql = "SELECT i.item_title , ra.rating , cl.common_lookup_meaning FROM item i INNER JOIN common_lookup cl ON i.item_type = cl.common_lookup_id INNER JOIN rating_agency ra ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id WHERE i.item_title LIKE 'Harry%' AND cl.common_lookup_type = 'BLU-RAY'"; # Prepare SQL statement. my $sth = $dbh->prepare($sql); # Execute statement and read result set. $sth->execute() or die $DBI::errstr; # Read through returned rows, assign elements explicitly to match SELECT-list. while (my @row = $sth->fetchrow_array()) { my $item_title = $row[0]; my $rating = $row[1]; my $lookup_meaning = $row[2]; print "$item_title, $rating, $lookup_meaning\n"; } # Close resources. $sth->finish(); |
It returns the following rows from the sample database:
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone, PG, Blu-ray Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, PG, Blu-ray Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, PG, Blu-ray Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, PG-13, Blu-ray |
The following dynamic_query.pl Perl program uses the Perl DBI library to prepare a query, bind a local variable into the query, and return a data set based on a dynamic query.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | #!/usr/bin/perl -w # Use the DBI library. use DBI; use strict; use warnings; # Mimic a function parameter by using a local variable. my $item_title_in = 'Star'; # Create a connection. my $dbh = DBI->connect("DBI:mysql:database=studentdb;host=localhost:3306" ,"student","student",{'RaiseError' => 1}); # Create SQL statement. my $sql = "SELECT i.item_title , ra.rating , cl.common_lookup_meaning FROM item i INNER JOIN common_lookup cl ON i.item_type = cl.common_lookup_id INNER JOIN rating_agency ra ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id WHERE i.item_title LIKE CONCAT(?,'%') AND cl.common_lookup_type = 'BLU-RAY'"; # Prepare SQL statement. my $sth = $dbh->prepare($sql); # Bind a variable to first parameter in the query string. $sth->bind_param(1, $item_title_in); # Execute statement and read result set. $sth->execute() or die $DBI::errstr; # Read through returned rows, assign elements explicitly to match SELECT-list. while (my @row = $sth->fetchrow_array()) { my $item_title = $row[0]; my $rating = $row[1]; my $lookup_meaning = $row[2]; print "$item_title, $rating, $lookup_meaning\n"; } # Close resources. $sth->finish(); |
It returns the following rows from the sample database:
Star Wars II, PG, Blu-ray |
You can replace lines 34 through 40 with the following to read any number of columns into a comma-delimited row return:
34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | # Read through returned rows, assign elements explicitly to match SELECT-list. while (my @row = $sth->fetchrow_array()) { # Read through a dynamic column list for column separated display. my $result = ''; foreach(@row) { if (length($result) == 0) { $result = $_; } else { $result .= ", " . $_; } } # Print comma-separted values by row. print $result . "\n" } |
It returns the following rows from the sample database:
Star Wars II, PG, Blu-ray |
As always, I hope this helps the reader solve a problem.
Native sqlplus editing
I have to remind myself from time to time that Ubuntu is a Desktop or Workstation and by default can go missing key server software, like ssh. This became evident when I wanted to check whether I could run sqlplus from my Mac OS terminal through my Ubuntu VM and internally embedded Oracle Database 23c Free docker instance.
If like me you forgot to add it, you can add the ssh service with the following commands to your Ubuntu VM:
sudo apt update sudo apt install -y openssh-server sudo systemctl start ssh.service |
Then, you can test the installation with an ssh call to localhost, like:
ssh localhost |
You should see the following, where you need to enter the sudoer’s password to continue. Your localhost target causes an authenticity check, like:
The authenticity of host 'localhost (127.0.0.1)' can't be established. ED25519 key fingerprint is SHA256:js8knEf/lOE1rSss3u8lP4Ii634Y0CkUz+oJM5dt3w4. This key is not known by any other names Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? |
Enter yes to continue:
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes |
It will now add localhost to the list of known hosts provide standard messages, as shown below.
Warning: Permanently added 'localhost' (ED25519) to the list of known hosts. student@localhost's password: Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS (GNU/Linux 6.2.0-39-generic x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled. 9 updates can be applied immediately. 5 of these updates are standard security updates. To see these additional updates run: apt list --upgradable Enable ESM Apps to receive additional future security updates. See https://ubuntu.com/esm or run: sudo pro status The programs included with the Ubuntu system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Ubuntu comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law. |
Having verified the installation and functionality of ssh in the Ubuntu VM. Then, I launched a Terminal session on my MacBookPro base operating system. Using the Ubuntu instance ssh and a customized Bash function, I discovered its IP address.
The following is the get_ip() user-defined function in the Ubuntu instance’s student user’s customized .bashrc file:
# Return the local instance's IP address. get_ip () { echo `hostname -I | cut -f1 -d' '` } |
In this instance, it returned:
192.168.195.155 |
With the IP address, I secured shelled into my Ubuntu sudoer student user like this:
ssh student@192.168.195.155 |
It’ll prompt you for the remote server’s student password, like:
student@192.168.195.155's password: |
After entering the correct password, I got the standard reply of a valid connection:
Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS (GNU/Linux 6.2.0-39-generic x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com * Management: https://landscape.canonical.com * Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled. 9 updates can be applied immediately. 5 of these updates are standard security updates. To see these additional updates run: apt list --upgradable Enable ESM Apps to receive additional future security updates. See https://ubuntu.com/esm or run: sudo pro status Last login: Fri Jan 5 18:13:21 2024 from 127.0.0.1 |
Next, I connected to the Ubuntu Docker Oracle Database 23c Free instance with this syntax:
docker exec -it --user student oracle23c bash |
At the prompt for the Docker instance of Oracle Database 23c Free, you can type sqlplus to work directly against the Oracle Database 23c Free instance with a pluggable c##student database user.
sqlplus c##student/student SQL*Plus: Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Production on Sat Jan 6 01:38:06 2024 Version 23.3.0.23.09 Copyright (c) 1982, 2023, Oracle. All rights reserved. Last Successful login time: Sat Dec 23 2023 04:30:00 +00:00 Connected to: Oracle Database 23c Free Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Develop, Learn, and Run for Free Version 23.3.0.23.09 |
Now, I can interactively edit my files with vi in the Docker Oracle Database 23c Free directory. The following demonstrates using the sandboxed student() function from my earlier Oracle 23c Free SQL*Plus blog post and connects as a sandboxed student user in the Docker Oracle 23c Free container. The image uses a different Mac OS and different Ubuntu VM from the earlier entries in this blog post from the earlier examples.
You can edit and test the files in the Docker Oracle 23c Free instance through the command-line interface (CLI). You can further automate the ssh connection by making the Ubuntu instance’s IP address a static address instead of a DCHP-assigned address; and then you can put it in the Mac OS’s /etc/hosts file which lets you resolve it by name (through file versus DNS resolution).
As always, I hope this helps those looking for a solution.
Ubuntu DaaS VM
Completed the build of my new Ubuntu Virtual Machine (VM) with Oracle 23c installed in a Docker instance, and MySQL and PostgreSQL installed locally. The VM image also provides a LAMP stack with Apache2, PHP 8.1 with MySQLi and PDO modules. Since the original post, I’ve added a number of items to support our program courses and the Data Science degrees.
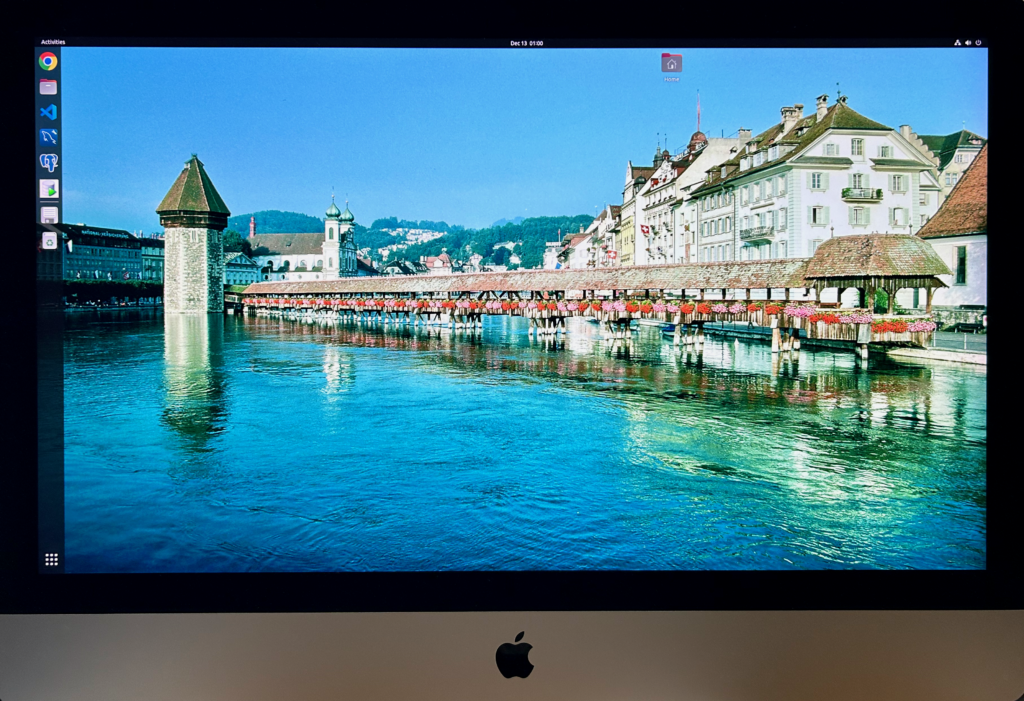
There are lots of tricks and techniques in the blog associated with creating the build. I took the background photograph of Chapel Bridge early on Sunday morning August 30, 1987 in Lucerne Switzerland (with a Canon A1 and ASA 64 slide film that subsequently digitized well).
Next step: roll it out into an AWS image for the students to use for their courses.
Related blog posts:
- Installing and configuring Apache2 and PHP 8.1 on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing and configuring Docker on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing and configuring MySQL 8 on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing Oracle Database 23c Free in a Docker container with space allocation techniques
- Installing and configuring PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing and configuring pgAdmin4
- Installing and configuring Python for MySQL 8
- Installing and configuring Python for PostgreSQL driver on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing and configuring SQL Developer on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing the rlwrap utility to access command history in SQL*Plus (sqlplus) inside Docker container.
- How to add PostGIS to an existing PostgreSQL 14 Install on Ubuntu 22.0.4
- How to create a sandboxed user and wrap sqlplus inside the Docker version of Oracle 23c Free
- How to install, configure, and create a persistent SQLite 3 database and access it with Python.
As always, I hope the post and information helps others.
Apache2 on Ubuntu
It’s always interesting when I build new instances. Ubuntu 22.0.4 was no different but I ran into an issue with installing Apache2 and eventually loading the mysqli module.
The Apache2 error was an issue with an unsupported module or hidden prerequisite. The MySQLi required an Apache reload after installation. Contrary to some erroneous posts the mysqli driver is supported on PHP 8.1.
Apache2 installation starts first and the mysqli module reload and verification script follows. On Ubuntu, you install Apache2 if you’re unaware of the hidden pre-requisite, otherwise install the pre-requisite first and avoid the error.
This is the command to install the apache2 module:
sudo apt-get install -y apache2 |
It generated the following error message:
apache2: Syntax error on line 146 of /etc/apache2/apache2.conf: Syntax error on line 1 of /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/wsgi.load: Cannot load /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_wsgi.so into server: /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_wsgi.so: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory Action 'start' failed. The Apache error log may have more information. |
Line 146 in the /etc/apache2/apache2.conf file contains the instruction to load modules. The error says it can’t find the mod_wsgi.so library, which was originally part of the deprecated Python 2.7 release.
IncludeOptional mods-enabled/*.load |
The first step I pursued was finding the missing library, which appeared to be in the libapache2-mod-wsgi package. However, it became clear there is no installation candidate for that module, which supported Python 3.x. A little more research led me to find the appropriate library version for Python 3, which is found in the libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 package.
I installed the libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 package with the following syntax:
sudo apt-get install -y libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following NEW packages will be installed: libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 10 not upgraded. Need to get 106 kB of archives. After this operation, 304 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 amd64 4.9.0-1ubuntu0.1 [106 kB] Fetched 106 kB in 1s (135 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3. (Reading database ... 228859 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3_4.9.0-1ubuntu0.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 (4.9.0-1ubuntu0.1) ... Setting up libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 (4.9.0-1ubuntu0.1) ... apache2_invoke wsgi: already enabled |
After applying it, I was able to start Apache2. Then, typing in localhost returns the Apache2 index.htm page, like:
After creating the following file in the default directory:
<?php phpinfo(); ?> |
Typing in localhost/infophp returns the Apache2 info.php page, like:
After the basics for PHP, the next step is the mysqli module for the MySQL database. This can be done in two steps on Ubuntu.
- Install the MySQLi software with the following syntax on Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install -y php8.1-mysql
If you forget and use the old php-mysqli, it will redirect to the new PHP 8.1 MySQL module.
- You need to reload the Apache configuration with the following syntax:
sudo systemctl reload apache2
Now, you can use the following PHP program to verify that the mysqli and pdo drivers are installed:
<html>
<header>
<title>Module Verification</title>
</header>
<body>
<?php
if (!function_exists('mysqli_init') && !extension_loaded('mysqli')) {
print 'mysqli not installed.'; }
else {
print 'mysqli installed.'; }
if (!function_exists('pdo_init') && !extension_loaded('pdo')) {
print '<p>pdo not installed.</p>'; }
else {
print '<p>pdo installed.</p>'; }
?>
</script>
</body>
</html> |
If everything is correct, it should return the following in a browser when you query it from localhost/the-file-name and the file is in the /var/www/html directory:
mysqli installed. pdo installed. |
This means you can now write PHP applications, like the following example for my students:
I also have some demonstration programs that upload PNG files. As usual, I forgot about that while building the Ubuntu installation with MySQL 8, PHP 8.1 and Apache2. Fortunately, I solved it back in the day when moving from PHP 5.7 to 7.1 and here are the equivalent steps for Ubuntu:
I installed the libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 package with the following syntax:
sudo apt-get install -y php-gd |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: php8.1-gd The following NEW packages will be installed: php-gd php8.1-gd 0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 13 not upgraded. Need to get 34.7 kB of archives. After this operation, 158 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 php8.1-gd amd64 8.1.2-1ubuntu2.14 [32.9 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 php-gd all 2:8.1+92ubuntu1 [1,828 B] Fetched 34.7 kB in 1s (39.3 kB/s) sh: 0: getcwd() failed: No such file or directory sh: 0: getcwd() failed: No such file or directory sh: 0: getcwd() failed: No such file or directory sh: 0: getcwd() failed: No such file or directory Selecting previously unselected package php8.1-gd. (Reading database ... 228928 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../php8.1-gd_8.1.2-1ubuntu2.14_amd64.deb ... Unpacking php8.1-gd (8.1.2-1ubuntu2.14) ... Selecting previously unselected package php-gd. Preparing to unpack .../php-gd_2%3a8.1+92ubuntu1_all.deb ... Unpacking php-gd (2:8.1+92ubuntu1) ... Setting up php8.1-gd (8.1.2-1ubuntu2.14) ... Creating config file /etc/php/8.1/mods-available/gd.ini with new version Setting up php-gd (2:8.1+92ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for libapache2-mod-php8.1 (8.1.2-1ubuntu2.14) ... Processing triggers for php8.1-cli (8.1.2-1ubuntu2.14) ... |
Then, I restarted the Apache2 server to incorporate the php-gd library in my PHP module with this syntax:
sudo systemctl restart apache2.service |
Retesting the PHP form to upload and render a PNG image file with this code (note that the only thing you can display is the html header and converted image, as shown on lines 64 and 65):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 | <?php /* ConvertBlobToImage.php * by Michael McLaughlin * * This script queries an image from a BLOB column and * converts it to a PNG image. * * ALERT: * * The header must be inside the PHP script tag because nothing * can be rendered before the header() function call that signals * this is a PNG file. */ // Database credentials must be set manually because an include_once() function // call puts something ahead of the header, which causes a failure when rendering // an image. // Include the credential library. include_once("MySQLCredentials.inc"); // Return successful attempt to connect to the database. if (!$c = @mysqli_connect(HOSTNAME,USERNAME,PASSWORD,DATABASE)) { // Print user message. print "Sorry! The connection to the database failed. Please try again later."; // Assign the OCI error and format double and single quotes. print mysqli_error(); // Kill the resource. die(); } else { // Declare input variables. $id = (isset($_GET['id'])) ? (int) $_GET['id'] : 1023; // Initialize a statement in the scope of the connection. $stmt = mysqli_stmt_init($c); // Declare a SQL SELECT statement returning a MediumBLOB. $sql = "SELECT item_blob FROM item WHERE item_id = ?"; // Prepare statement and link it to a connection. if (mysqli_stmt_prepare($stmt,$sql)) { mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt,"i",$id); // Execute the PL/SQL statement. if (mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)) { // Bind result to local variable. mysqli_stmt_bind_result($stmt, $image); // Read result. mysqli_stmt_fetch($stmt); } } // Disconnect from database. mysqli_close($c); // Print the header first. header('Content-type: image/png'); imagepng(imagecreatefromstring($image)); } ?> |
The call to the ConvertMySQLBlobToImage.php is handled in an image tag, as shown:
<img src="ConvertMySQLBlobToImage.php?id='.$id.'"> |
Rendering a web page, like:
As always, I hope this explains something worthwhile.
OracleDB Python Tutorial 1
This shows you how to get Python working with the Oracle Database 23c in Docker or Podman on Ubuntu. You can find useful connection strings for this in Oracle Database Free Get Started.
- First step requires you to install the pip3/span> utility on Ubuntu.
sudo apt install -y python3-pip
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu build-essential dpkg-dev fakeroot g++ g++-11 gcc gcc-11 javascript-common libalgorithm-diff-perl libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libalgorithm-merge-perl libasan6 libbinutils libc-dev-bin libc-devtools libc6-dev libcc1-0 libcrypt-dev libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libdpkg-perl libexpat1-dev libfakeroot libfile-fcntllock-perl libgcc-11-dev libitm1 libjs-jquery libjs-sphinxdoc libjs-underscore liblsan0 libnsl-dev libpython3-dev libpython3.10-dev libquadmath0 libstdc++-11-dev libtirpc-dev libtsan0 libubsan1 linux-libc-dev lto-disabled-list make manpages-dev python3-dev python3-distutils python3-setuptools python3-wheel python3.10-dev rpcsvc-proto zlib1g-dev Suggested packages: binutils-doc debian-keyring g++-multilib g++-11-multilib gcc-11-doc gcc-multilib autoconf automake libtool flex bison gcc-doc gcc-11-multilib gcc-11-locales apache2 | lighttpd | httpd glibc-doc bzr libstdc++-11-doc make-doc python-setuptools-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu build-essential dpkg-dev fakeroot g++ g++-11 gcc gcc-11 javascript-common libalgorithm-diff-perl libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libalgorithm-merge-perl libasan6 libbinutils libc-dev-bin libc-devtools libc6-dev libcc1-0 libcrypt-dev libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libdpkg-perl libexpat1-dev libfakeroot libfile-fcntllock-perl libgcc-11-dev libitm1 libjs-jquery libjs-sphinxdoc libjs-underscore liblsan0 libnsl-dev libpython3-dev libpython3.10-dev libquadmath0 libstdc++-11-dev libtirpc-dev libtsan0 libubsan1 linux-libc-dev lto-disabled-list make manpages-dev python3-dev python3-distutils python3-pip python3-setuptools python3-wheel python3.10-dev rpcsvc-proto zlib1g-dev 0 upgraded, 53 newly installed, 0 to remove and 9 not upgraded. Need to get 62.2 MB of archives. After this operation, 220 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 binutils-common amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [222 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libbinutils amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [662 kB] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libctf-nobfd0 amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [107 kB] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libctf0 amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [103 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [2,327 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 binutils amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [3,190 B] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libc-dev-bin amd64 2.35-0ubuntu3.5 [20.3 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 linux-libc-dev amd64 5.15.0-91.101 [1,332 kB] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libcrypt-dev amd64 1:4.4.27-1 [112 kB] Get:10 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 rpcsvc-proto amd64 1.4.2-0ubuntu6 [68.5 kB] Get:11 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libtirpc-dev amd64 1.3.2-2ubuntu0.1 [192 kB] Get:12 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libnsl-dev amd64 1.3.0-2build2 [71.3 kB] Get:13 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libc6-dev amd64 2.35-0ubuntu3.5 [2,098 kB] Get:14 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libcc1-0 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [48.3 kB] Get:15 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libitm1 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [30.2 kB] Get:16 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libasan6 amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [2,282 kB] Get:17 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 liblsan0 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [1,069 kB] Get:18 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libtsan0 amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [2,260 kB] Get:19 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libubsan1 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [976 kB] Get:20 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libquadmath0 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [154 kB] Get:21 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libgcc-11-dev amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [2,517 kB] Get:22 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 gcc-11 amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [20.1 MB] Get:23 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 gcc amd64 4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1 [5,112 B] Get:24 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libstdc++-11-dev amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [2,101 kB] Get:25 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 g++-11 amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [11.4 MB] Get:26 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 g++ amd64 4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1 [1,412 B] Get:27 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 make amd64 4.3-4.1build1 [180 kB] Get:28 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libdpkg-perl all 1.21.1ubuntu2.2 [237 kB] Get:29 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 lto-disabled-list all 24 [12.5 kB] Get:30 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 dpkg-dev all 1.21.1ubuntu2.2 [922 kB] Get:31 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 build-essential amd64 12.9ubuntu3 [4,744 B] Get:32 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libfakeroot amd64 1.28-1ubuntu1 [31.5 kB] Get:33 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 fakeroot amd64 1.28-1ubuntu1 [60.4 kB] Get:34 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 javascript-common all 11+nmu1 [5,936 B] Get:35 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libalgorithm-diff-perl all 1.201-1 [41.8 kB] Get:36 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl amd64 0.04-6build3 [11.9 kB] Get:37 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libalgorithm-merge-perl all 0.08-3 [12.0 kB] Get:38 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libc-devtools amd64 2.35-0ubuntu3.5 [28.9 kB] Get:39 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libexpat1-dev amd64 2.4.7-1ubuntu0.2 [147 kB] Get:40 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libfile-fcntllock-perl amd64 0.22-3build7 [33.9 kB] Get:41 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libjs-jquery all 3.6.0+dfsg+~3.5.13-1 [321 kB] Get:42 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libjs-underscore all 1.13.2~dfsg-2 [118 kB] Get:43 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libjs-sphinxdoc all 4.3.2-1 [139 kB] Get:44 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 zlib1g-dev amd64 1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2 [164 kB] Get:45 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libpython3.10-dev amd64 3.10.12-1~22.04.3 [4,762 kB] Get:46 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libpython3-dev amd64 3.10.6-1~22.04 [7,166 B] Get:47 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 manpages-dev all 5.10-1ubuntu1 [2,309 kB] Get:48 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 python3.10-dev amd64 3.10.12-1~22.04.3 [507 kB] Get:49 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 python3-distutils all 3.10.8-1~22.04 [139 kB] Get:50 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 python3-dev amd64 3.10.6-1~22.04 [26.0 kB] Get:51 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 python3-setuptools all 59.6.0-1.2ubuntu0.22.04.1 [339 kB] Get:52 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 python3-wheel all 0.37.1-2ubuntu0.22.04.1 [32.0 kB] Get:53 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 python3-pip all 22.0.2+dfsg-1ubuntu0.4 [1,305 kB] Fetched 62.2 MB in 35s (1,781 kB/s) Extracting templates from packages: 100% Selecting previously unselected package binutils-common:amd64. (Reading database ... 221117 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../00-binutils-common_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking binutils-common:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libbinutils:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../01-libbinutils_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libbinutils:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libctf-nobfd0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../02-libctf-nobfd0_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libctf-nobfd0:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libctf0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../03-libctf0_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libctf0:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu. Preparing to unpack .../04-binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package binutils. Preparing to unpack .../05-binutils_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking binutils (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libc-dev-bin. Preparing to unpack .../06-libc-dev-bin_2.35-0ubuntu3.5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libc-dev-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Selecting previously unselected package linux-libc-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../07-linux-libc-dev_5.15.0-91.101_amd64.deb ... Unpacking linux-libc-dev:amd64 (5.15.0-91.101) ... Selecting previously unselected package libcrypt-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../08-libcrypt-dev_1%3a4.4.27-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libcrypt-dev:amd64 (1:4.4.27-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package rpcsvc-proto. Preparing to unpack .../09-rpcsvc-proto_1.4.2-0ubuntu6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking rpcsvc-proto (1.4.2-0ubuntu6) ... Selecting previously unselected package libtirpc-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../10-libtirpc-dev_1.3.2-2ubuntu0.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libtirpc-dev:amd64 (1.3.2-2ubuntu0.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libnsl-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../11-libnsl-dev_1.3.0-2build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libnsl-dev:amd64 (1.3.0-2build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libc6-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../12-libc6-dev_2.35-0ubuntu3.5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libc6-dev:amd64 (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Selecting previously unselected package libcc1-0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../13-libcc1-0_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libcc1-0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libitm1:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../14-libitm1_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libitm1:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libasan6:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../15-libasan6_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libasan6:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package liblsan0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../16-liblsan0_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking liblsan0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libtsan0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../17-libtsan0_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libtsan0:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libubsan1:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../18-libubsan1_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libubsan1:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libquadmath0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../19-libquadmath0_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libquadmath0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libgcc-11-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../20-libgcc-11-dev_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libgcc-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package gcc-11. Preparing to unpack .../21-gcc-11_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking gcc-11 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package gcc. Preparing to unpack .../22-gcc_4%3a11.2.0-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking gcc (4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libstdc++-11-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../23-libstdc++-11-dev_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libstdc++-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package g++-11. Preparing to unpack .../24-g++-11_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking g++-11 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package g++. Preparing to unpack .../25-g++_4%3a11.2.0-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking g++ (4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package make. Preparing to unpack .../26-make_4.3-4.1build1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking make (4.3-4.1build1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libdpkg-perl. Preparing to unpack .../27-libdpkg-perl_1.21.1ubuntu2.2_all.deb ... Unpacking libdpkg-perl (1.21.1ubuntu2.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package lto-disabled-list. Preparing to unpack .../28-lto-disabled-list_24_all.deb ... Unpacking lto-disabled-list (24) ... Selecting previously unselected package dpkg-dev. Preparing to unpack .../29-dpkg-dev_1.21.1ubuntu2.2_all.deb ... Unpacking dpkg-dev (1.21.1ubuntu2.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package build-essential. Preparing to unpack .../30-build-essential_12.9ubuntu3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking build-essential (12.9ubuntu3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libfakeroot:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../31-libfakeroot_1.28-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libfakeroot:amd64 (1.28-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package fakeroot. Preparing to unpack .../32-fakeroot_1.28-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking fakeroot (1.28-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package javascript-common. Preparing to unpack .../33-javascript-common_11+nmu1_all.deb ... Unpacking javascript-common (11+nmu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libalgorithm-diff-perl. Preparing to unpack .../34-libalgorithm-diff-perl_1.201-1_all.deb ... Unpacking libalgorithm-diff-perl (1.201-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl. Preparing to unpack .../35-libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl_0.04-6build3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl (0.04-6build3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libalgorithm-merge-perl. Preparing to unpack .../36-libalgorithm-merge-perl_0.08-3_all.deb ... Unpacking libalgorithm-merge-perl (0.08-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libc-devtools. Preparing to unpack .../37-libc-devtools_2.35-0ubuntu3.5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libc-devtools (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Selecting previously unselected package libexpat1-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../38-libexpat1-dev_2.4.7-1ubuntu0.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libexpat1-dev:amd64 (2.4.7-1ubuntu0.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libfile-fcntllock-perl. Preparing to unpack .../39-libfile-fcntllock-perl_0.22-3build7_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libfile-fcntllock-perl (0.22-3build7) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-jquery. Preparing to unpack .../40-libjs-jquery_3.6.0+dfsg+~3.5.13-1_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-jquery (3.6.0+dfsg+~3.5.13-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-underscore. Preparing to unpack .../41-libjs-underscore_1.13.2~dfsg-2_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-underscore (1.13.2~dfsg-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-sphinxdoc. Preparing to unpack .../42-libjs-sphinxdoc_4.3.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-sphinxdoc (4.3.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package zlib1g-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../43-zlib1g-dev_1%3a1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking zlib1g-dev:amd64 (1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libpython3.10-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../44-libpython3.10-dev_3.10.12-1~22.04.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libpython3.10-dev:amd64 (3.10.12-1~22.04.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libpython3-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../45-libpython3-dev_3.10.6-1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libpython3-dev:amd64 (3.10.6-1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package manpages-dev. Preparing to unpack .../46-manpages-dev_5.10-1ubuntu1_all.deb ... Unpacking manpages-dev (5.10-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3.10-dev. Preparing to unpack .../47-python3.10-dev_3.10.12-1~22.04.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking python3.10-dev (3.10.12-1~22.04.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-distutils. Preparing to unpack .../48-python3-distutils_3.10.8-1~22.04_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-distutils (3.10.8-1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-dev. Preparing to unpack .../49-python3-dev_3.10.6-1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking python3-dev (3.10.6-1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-setuptools. Preparing to unpack .../50-python3-setuptools_59.6.0-1.2ubuntu0.22.04.1_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-setuptools (59.6.0-1.2ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-wheel. Preparing to unpack .../51-python3-wheel_0.37.1-2ubuntu0.22.04.1_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-wheel (0.37.1-2ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-pip. Preparing to unpack .../52-python3-pip_22.0.2+dfsg-1ubuntu0.4_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-pip (22.0.2+dfsg-1ubuntu0.4) ... Setting up python3-distutils (3.10.8-1~22.04) ... Setting up javascript-common (11+nmu1) ... Setting up manpages-dev (5.10-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up lto-disabled-list (24) ... Setting up python3-setuptools (59.6.0-1.2ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Setting up libfile-fcntllock-perl (0.22-3build7) ... Setting up libalgorithm-diff-perl (1.201-1) ... Setting up binutils-common:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up linux-libc-dev:amd64 (5.15.0-91.101) ... Setting up libctf-nobfd0:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up python3-wheel (0.37.1-2ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Setting up libfakeroot:amd64 (1.28-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up libasan6:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up fakeroot (1.28-1ubuntu1) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/fakeroot-sysv to provide /usr/bin/fakeroot (fakeroot) in auto mode Setting up libtirpc-dev:amd64 (1.3.2-2ubuntu0.1) ... Setting up rpcsvc-proto (1.4.2-0ubuntu6) ... Setting up make (4.3-4.1build1) ... Setting up libquadmath0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up python3-pip (22.0.2+dfsg-1ubuntu0.4) ... Setting up libdpkg-perl (1.21.1ubuntu2.2) ... Setting up libubsan1:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libnsl-dev:amd64 (1.3.0-2build2) ... Setting up libcrypt-dev:amd64 (1:4.4.27-1) ... Setting up libjs-jquery (3.6.0+dfsg+~3.5.13-1) ... Setting up libbinutils:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up libc-dev-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Setting up libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl (0.04-6build3) ... Setting up libcc1-0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up liblsan0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libitm1:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libc-devtools (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Setting up libjs-underscore (1.13.2~dfsg-2) ... Setting up libalgorithm-merge-perl (0.08-3) ... Setting up libtsan0:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libctf0:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up libjs-sphinxdoc (4.3.2-1) ... Setting up libgcc-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libc6-dev:amd64 (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Setting up binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up binutils (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up dpkg-dev (1.21.1ubuntu2.2) ... Setting up libexpat1-dev:amd64 (2.4.7-1ubuntu0.2) ... Setting up libstdc++-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up zlib1g-dev:amd64 (1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2) ... Setting up gcc-11 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up g++-11 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up gcc (4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up libpython3.10-dev:amd64 (3.10.12-1~22.04.3) ... Setting up python3.10-dev (3.10.12-1~22.04.3) ... Setting up g++ (4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/g++ to provide /usr/bin/c++ (c++) in auto mode Setting up build-essential (12.9ubuntu3) ... Setting up libpython3-dev:amd64 (3.10.6-1~22.04) ... Setting up python3-dev (3.10.6-1~22.04) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ...
- Second step requires that you pip3 install the oracledb library:
sudo pip3 install oracledb --upgrade
Display detailed console log →
Defaulting to user installation because normal site-packages is not writeable Collecting oracledb Downloading oracledb-1.4.2-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl (8.6 MB) ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 8.6/8.6 MB 2.7 MB/s eta 0:00:00 Requirement already satisfied: cryptography>=3.2.1 in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from oracledb) (3.4.8) Installing collected packages: oracledb Successfully installed oracledb-1.4.2 - Third step requires you write a Python program to test your connection to Oracle Database 23c Free, like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
#!/usr/bin/python # Import the Oracle library. import oracledb try: # Create a connection to local Docker or Podman installation. db = oracledb.connect(user='c##student', password='student', dsn='localhost:51521/FREE') # Print a connection message. print("Connected to the Oracle", db.version, "database.") except oracledb.DatabaseError as e: error, = e.args print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Code:", error.code) print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Message:", error.message) finally: # Close connection. db.close()
The 51521 port is the recommended port when setting up Docker or Podman services, however, it can be set to any port above 1024.
It should print:
Connected to the Oracle 23.3.0.23.9 database.
- Fourth step requires you write a Python program to test querying data from an Oracle Database 23c Free instance. I created the following avenger table and seeded it with six Avengers.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
/* Conditionally drop the table. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS avenger; /* Create the table. */ CREATE TABLE avenger ( avenger_id NUMBER , first_name VARCHAR2(20) , last_name VARCHAR2(20) , character_name VARCHAR2(20)); /* Seed the table with data. */ INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (1,'Anthony','Stark','Iron Man'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (2,'Thor','Odinson','God of Thunder'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (3,'Steven','Rogers','Captain America'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (4,'Bruce','Banner','Hulk'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (5,'Clinton','Barton','Hawkeye'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (6,'Natasha','Romanoff','Black Widow');
Then, I extended the program logic to include a cursor and for loop to read the values from the avenger table:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
#!/usr/bin/python # Import the Oracle library. import oracledb try: # Create a connection to local Docker or Podman installation. db = oracledb.connect(user='c##student', password='student', dsn='localhost:51521/FREE') # Create a cursor. cursor = db.cursor() # Execute a query. cursor.execute("SELECT character_name " + ", first_name " + ", last_name " + "FROM avenger " + "ORDER BY character_name") # Read the contents of the cursor. for row in cursor: print(row[0] + ':',row[2] + ',',row[1]) except oracledb.DatabaseError as e: error, = e.args print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Code:", error.code) print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Message:", error.message) finally: # Close cursor and connection. cursor.close() db.close()
The 51521 port is the recommended port when setting up Docker or Podman services, however, it can be set to any port above 1024.
It should print:
Black Widow: Romanoff, Natasha Captain America: Rogers, Steven God of Thunder: Odinson, Thor Hawkeye: Barton, Clinton Hulk: Banner, Bruce Iron Man: Stark, Anthony
- Fifth step requires you write a Python program to test querying data filtered by a local variable from an Oracle Database 23c Free instance. This example looks only for the Hulk among the six Avengers.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
#!/usr/bin/python # Import the Oracle library. import oracledb try: # Create a connection to local Docker or Podman installation. db = oracledb.connect(user='c##student', password='student', dsn='localhost:51521/FREE') # Create a cursor. cursor = db.cursor() # Execute a query. stmt = "SELECT character_name " \ ", first_name " \ ", last_name " \ "FROM avenger " \ "WHERE character_name = :avenger " \ "ORDER BY character_name" # Execute with bind variable. cursor.execute(stmt, avenger = "Hulk") # Read the contents of the cursor. for row in cursor: print(row[0] + ':',row[2] + ',',row[1]) except oracledb.DatabaseError as e: error, = e.args print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Code:", error.code) print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Message:", error.message) finally: # Close cursor and connection. cursor.close() db.close()
It should print:
Hulk: Banner, Bruce
As always, I hope this puts everything together for setting up Python with Oracle Database 23c Free.
pgAdmin4 on Ubuntu
Installing pgAdmin4 is qualified by the pgAdmin4 (APT) web page, which relies on the curl utility. Ubuntu doesn’t install curl by default, so you need to install it before you can download and install pgAdmin4:
- Download and install curl utility
sudo apt-get install -y curl
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following NEW packages will be installed: curl 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 5 not upgraded. Need to get 194 kB of archives. After this operation, 454 kB of additional disk space will be used. Ign:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 curl amd64 7.81.0-1ubuntu1.14 Err:1 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 curl amd64 7.81.0-1ubuntu1.14 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.91.38 80] E: Failed to fetch http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/c/curl/curl_7.81.0-1ubuntu1.14_amd64.deb 404 Not Found [IP: 91.189.91.38 80] E: Unable to fetch some archives, maybe run apt-get update or try with --fix-missing? student@student-virtual-machine:~$ sudo apt-get update Hit:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates InRelease [119 kB] Get:3 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease [110 kB] Get:4 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease [1,825 B] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease [109 kB] Get:6 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/main i386 Packages [376 kB] Get:7 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable/main amd64 Packages [1,081 B] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 Packages [1,244 kB] Get:9 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/main amd64 Packages [1,016 kB] Get:10 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/main Translation-en [195 kB] Get:11 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/restricted amd64 Packages [1,179 kB] Get:12 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/universe i386 Packages [577 kB] Get:13 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/universe amd64 Packages [815 kB] Get:14 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/universe Translation-en [152 kB] Get:15 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main i386 Packages [543 kB] Get:16 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main Translation-en [257 kB] Get:17 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/restricted amd64 Packages [1,226 kB] Get:18 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/restricted Translation-en [199 kB] Get:19 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe i386 Packages [675 kB] Get:20 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 Packages [1,018 kB] Get:21 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe Translation-en [226 kB] Get:22 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports/universe amd64 Packages [27.8 kB] Get:23 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports/universe i386 Packages [16.8 kB] Fetched 10.1 MB in 26s (386 kB/s) Reading package lists... Done
- Download and install the public key for the repository (if not done previously):
sudo curl -fsS https://www.pgadmin.org/static/packages_pgadmin_org.pub | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/packages-pgadmin-org.gpg
It may find an existing key and require you to confirm its replacement:
File '/usr/share/keyrings/packages-pgadmin-org.gpg' exists. Overwrite? (y/N) y
- Create the repository configuration file:
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/packages-pgadmin-org.gpg] https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/$(lsb_release -cs) pgadmin4 main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgadmin4.list && apt update'
Display detailed console log →
Hit:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease Hit:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates InRelease Hit:3 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease Hit:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease Hit:5 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease Get:6 https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/jammy pgadmin4 InRelease [4,217 B] Get:7 https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/jammy pgadmin4/main all Packages [4,637 B] Get:8 https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/jammy pgadmin4/main amd64 Packages [7,693 B] Fetched 16.5 kB in 2s (7,404 B/s) Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done 21 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them. student@student-virtual-machine:~$ sudo apt-get update Hit:1 http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security InRelease Hit:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy InRelease Hit:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates InRelease Hit:4 https://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb stable InRelease Hit:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-backports InRelease Hit:6 https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/jammy pgadmin4 InRelease Reading package lists... Done
- Install the pgadmin4 Desktop:
sudo apt install pgadmin4-desktop
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: pgadmin4-server The following NEW packages will be installed: pgadmin4-desktop pgadmin4-server 0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 21 not upgraded. Need to get 203 MB of archives. After this operation, 0 B of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/jammy pgadmin4/main amd64 pgadmin4-server amd64 8.0 [93.5 MB] Get:2 https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/pgadmin/pgadmin4/apt/jammy pgadmin4/main amd64 pgadmin4-desktop amd64 8.0 [110 MB] Fetched 203 MB in 49s (4,163 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package pgadmin4-server. (Reading database ... 204519 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../pgadmin4-server_8.0_amd64.deb ... Unpacking pgadmin4-server (8.0) ... Selecting previously unselected package pgadmin4-desktop. Preparing to unpack .../pgadmin4-desktop_8.0_amd64.deb ... Unpacking pgadmin4-desktop (8.0) ... Setting up pgadmin4-server (8.0) ... Setting up pgadmin4-desktop (8.0) ... Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.26-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for hicolor-icon-theme (0.17-2) ... Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for mailcap (3.70+nmu1ubuntu1) ...
- You can launch your pgadmin4 program file or by clicking the pgAdmin4 icon in the other applications menu:
- It takes a couple moments to launch the pgadmin4 desktop. The initial screen will look like:

- After pgadmin4 launches, you’re prompted for a master password. Enter the password and click the OK button to proceed or simply let it sit for a couple minutes to avoid entering a password.
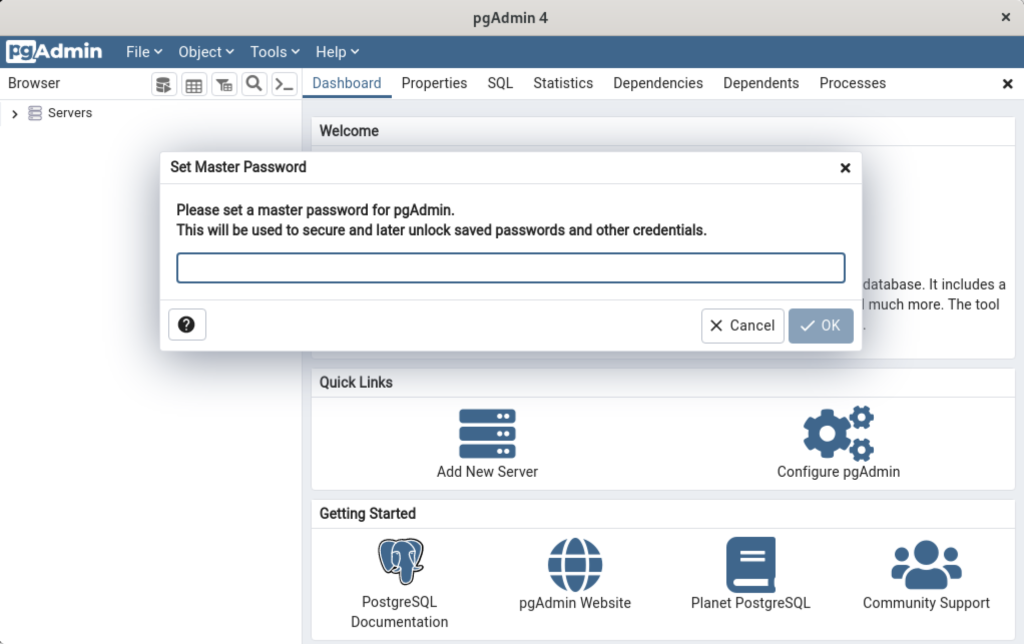
- After entering the password or skipping its entry you arrive at the base dialog, as shown.
- Click the Add New Server link, which prompts you to register your database. Enter videodb in the Name field and click the Connection tab to the right of the General tab.
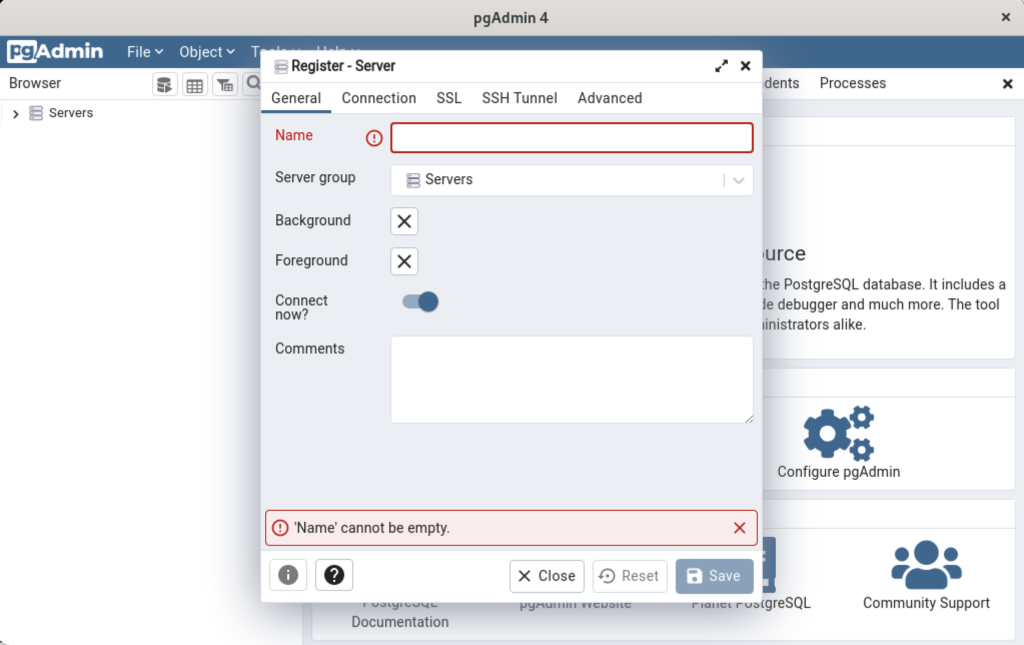
- In the Connection dialog, enter the following values:
- Host name/address: localhost
- Port: 5432
- Maintenance database: postgres
- Username: student
- Password: student

Enter a name for your database. In this example, videodb is the Server Name. Click the Save button to proceed.
- Having completed the configuration, you now see the home page.

This completes the instructions for installing, configuring, and using PostgreSQL on AlmaLinux. As always, I hope it helps those looking for instructions.
Python3 on PostgreSQL
The necessary Python 3 driver for connections to the PostgreSQL database is python3-psycopg2, as qualified by this earlier post with full test examples for Red Hat distributions. You can install it on Ubuntu with the following command:
sudo apt-get install -y python3-psycopg2 |
Display detailed console log →
python3-psycopg2 Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done Suggested packages: python-psycopg2-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: python3-psycopg2 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 4 not upgraded. Need to get 136 kB of archives. After this operation, 483 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 python3-psycopg2 amd64 2.9.2-1build2 [136 kB] Fetched 136 kB in 1s (146 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package python3-psycopg2. (Reading database ... 204321 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../python3-psycopg2_2.9.2-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking python3-psycopg2 (2.9.2-1build2) ... Setting up python3-psycopg2 (2.9.2-1build2) ... |
As always, I hope this helps those looking for a solution. Also, remember the referenced post above provides Linux distribution neutral full solutions.