Archive for the ‘Oracle Developer’ tag
Updating Nested ADTs
The first part of this series showed how you can leverage Oracle’s SQL syntax with UDT columns and collection columns. It would be nice if Oracle gave you some SQL to work with the elements of ADT collections, but they don’t. After all, that’s why you have this article.
While you could change the setup of the prior example table, it’s easier to create a new customer table. The new customer table drops the address column. There’s also a new pizza table. The pizza table includes an ingredient ADT collection column, which by design holds a unique set of ingredients for each pizza.
Realistically, ADT collections of numbers, characters, and dates have little value by themselves. That’s because those data types typically don’t have much meaning. A set of unique strings can be useful for certain use cases.
You create the list ADT type with this syntax:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 TYPE list IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(20); 3 / |
You create the customer and pizza tables, and customer_s and pizza_s sequences with the following syntax:
SQL> CREATE TABLE customer 2 ( customer_id NUMBER 3 , first_name VARCHAR2(20) 4 , last_name VARCHAR2(20) 5 , CONSTRAINT pk_customer PRIMARY KEY (customer_id)); SQL> CREATE SEQUENCE customer_s; SQL> CREATE TABLE pizza 2 ( pizza_id NUMBER 3 , customer_id NUMBER 4 , pizza_size VARCHAR2(10) 5 , ingredients LIST 6 , CONSTRAINT pk_pizza PRIMARY KEY (pizza_id) 7 , CONSTRAINT ck_pizza_size 8 CHECK (pizza_size IN ('Mini','Small','Medium','Large','Very Large'))) 9 NESTED TABLE ingredients STORE AS ingredient_table; SQL> CREATE SEQUENCE pizza_s; |
The customer table only has scalar columns. The pizza table has the ingredient ADT collection column. Line 9 creates a nested ingredient_table for the ingredient ADT collection column.
There is a primary and foreign key relationship between the customer and pizza tables. That relationship between the tables requires that you insert rows into the customer table before you insert rows into the pizza table.
The sample script populates the customer table with characters from the Green Arrow television show, as follows:
Customer
ID # Last Name First Name
-------- ---------- ----------
1 Queen Oliver
2 Queen Thea
3 Queen Moira
4 Lance Dinah
5 Lance Quentin
6 Diggle John
7 Wilson Slade |
Next, you can insert three rows into the pizza table. Each has different ingredients in the ingredient ADT column.
The following is the syntax for the INSERT statements:
SQL> INSERT INTO pizza 2 VALUES 3 ( pizza_s.NEXTVAL 4 ,(SELECT c.customer_id FROM customer c 5 WHERE c.first_name = 'Quentin' AND c.last_name = 'Lance') 6 ,'Large' 7 , list('Cheese','Marinara Sauce','Sausage','Salami')); SQL> INSERT INTO pizza 2 VALUES 3 ( pizza_s.NEXTVAL 4 ,(SELECT c.customer_id FROM customer c 5 WHERE c.first_name = 'Thea' AND c.last_name = 'Queen') 6 ,'Medium' 7 , list('Cheese','Marinara Sauce','Canadian Bacon','Pineapple')); SQL> INSERT INTO pizza 2 VALUES 3 ( pizza_s.NEXTVAL 4 ,(SELECT c.customer_id FROM customer c 5 WHERE c.first_name = 'John' AND c.last_name = 'Diggle') 6 ,'Small' 7 , list('Cheese','BBQ Sauce','Chicken')); |
Querying results from tables with nested ADT columns provides interesting results. An ordinary query, like this:
SQL> COL pizza_id FORMAT 99999 HEADING "Pizza|ID #" SQL> COL pizza_size FORMAT A6 HEADING "Pizza|Size" SQL> COL ingredients FORMAT A64 HEADING "Ingredients" SQL> SELECT pizza_id 2 , pizza_size 3 , ingredients 4 FROM pizza; |
… returns the following results with a flattened object type:
Pizza Pizza
ID # Size Ingredients
------ ------ ----------------------------------------------------------------“
1 Large LIST('Cheese', 'Marinara Sauce', 'Sausage', 'Salami')
2 Medium LIST('Cheese', 'Marinara Sauce', 'Canadian Bacon', 'Pineapple')
3 Small LIST('Cheese', 'BBQ Sauce', 'Chicken') |
If you use a CROSS JOIN it multiplies each row times the number of items in the ADT collection column. The multiplication hides the results.
The best solution for displaying results from an ADT collection requires that you serialize the results. The following serialize_set PL/SQL function creates a serialized comma separated list:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 FUNCTION serialize_set (pv_list LIST) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS 3 /* Declare a return string as large as you need. */ 4 lv_comma_string VARCHAR2(60); 5 BEGIN 6 /* Read list of values and serialize them in a string. */ 7 FOR i IN 1..pv_list.COUNT LOOP 8 IF NOT i = pv_list.COUNT THEN 9 lv_comma_string := lv_comma_string || pv_list(i) || ', '; 10 ELSE 11 lv_comma_string := lv_comma_string || pv_list(i); 12 END IF; 13 END LOOP; 14 RETURN lv_comma_string; 15 END serialize_set; |
You can now write a query that uses your PL/SQL function to format the ADT collection column values into a single row. The syntax for the query is:
SQL> SELECT pizza_id 2 , pizza_size 3 , serialize_set(ingredients) AS ingredients 4 FROM pizza; |
It returns:
Pizza Pizza
ID # Size Ingredients
------ ------ -----------------------------------------------------------
1 Large Cheese, Marinara Sauce, Sausage, Salami
2 Medium Cheese, Marinara Sauce, Canadian Bacon, Pineapple
3 Small Cheese, BBQ Sauce, Chicken |
At this point, you know how to create a table with an ADT collection column and how to insert values. The Oracle documentation says you can only replace the whole content of the ADT column in an UPDATE statement. That’s true in practice but not in principle.
The principal differs because you can write PL/SQL functions that add, change, or remove elements from the ADT collection that works in an UPDATE statement. The trick is quite simple. You achieve it by:
- Passing the current ADT collection as a IN-only mode parameter
- Passing any new parameters when you add or change elements
- Passing any old parameters when you change or remove elements
Now, you will learn how to create the add_elements, change_elements, and remove_elements PL/SQL functions. They let you use an UPDATE statement to add, change, or remove elements from an ADT collection column.
Adding ADT elements with an UPDATE statement
This section shows you how to add elements to an ADT collection column with an UPDATE statement. The add_elements PL/SQL function can add one or many elements to an ADT collection column. That’s possible because the new element or elements are passed to the function inside an ADT collection parameter.
The merit of this type of solution is that you only need one function to accomplish two tasks. The test cases show you how to pass one new element or a set of new elements.
An alternative solution would have you write two functions. One would accept a collection parameter and a variable length string, and the other would accept two collection parameters. Many developers might choose to do that because they would like to leverage overloading inside PL/SQL packages. You should ask yourself one question when you make the decision about your approach to this problem: Which is easier to maintain and use?
The following creates the add_elements PL/SQL function:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 FUNCTION add_elements 3 ( pv_list LIST 4 , pv_element LIST ) RETURN LIST IS 5 /* Declare local return collection variable. */ 6 lv_list LIST; 7 BEGIN 8 /* Check for instantiated collection and initialize when necessary. */ 9 IF pv_list IS NULL THEN 10 lv_list := list(); 11 ELSE 12 /* Assign parameter collection to local collection variable. */ 13 lv_list := pv_list; 14 FOR i IN 1..pv_element.COUNT LOOP 15 /* Check to avoid duplicates, allocate memory and assign value. */ 16 IF NOT list(pv_element(i)) SUBMULTISET OF lv_list THEN 17 lv_list.EXTEND; 18 lv_list(lv_list.COUNT) := pv_element(i); 19 END IF; 20 END LOOP; 21 END IF; 22 23 /* Return new collection. */ 24 RETURN lv_list; 25 END add_elements; 26 / |
Line 3 and 4 define the two parameters of the add_elements function as ADT collections. Line 4 also designates the return type of the function, which is the same ADT collection.
Line 6 declares a local ADT collection variable. You need a local lv_list ADT collection variable because you want to accept two collections and merge them into the local ADT collection variable. Then, you return the local ADT collection variable as the function outcome.
Line 9 checks whether the pv_list parameter is null. Line 10 initializes the lv_list variable when it is null to avoid an unitialized error when you try to assign values to it. Line 13 assigns an initialized ADT collection column’s value to the local lv_list variable. Line 14 starts a loop through the ADT collection you want to add to the ingredient column’s list of values.
Line 16 use the SUBMULTISET set operator to ensure that only new add elements when they don’t already exist in the ingredient ADT collection column. Line 17 allocates memory space in the lv_list variable, and line 18 assigns a new element to it.
You could extend memory for the total count of elements but that would make the index assignment on line 18 more complex. Combining them increments the count of items and lets you use the count as the index value. Line 24 returns the local ADT collection and replaces the original ingredient column value.
The test case for the function should ensure that only unique values are assigned to the ingredient ADT collection column value. This can be done by a three-step test case. The test queries the values in the ADT collection column, updates them, and re-queries them.
The following query shows you the contents of the row:
SQL> SELECT pizza_id, pizza_size 2 , serialize_set(ingredients) AS ingredients 3 FROM pizza 4 WHERE customer_id = 5 ( SELECT customer_id FROM customer 6 WHERE first_name = 'Quentin' AND last_name = 'Lance' ); |
It returns:
Pizza Pizza
ID # Size Ingredients
------ ------ -----------------------------------------------------------
1 Large Cheese, Marinara Sauce, Sausage, Salami |
You can update the ADT collection column’s values with the following UPDATE statement. It attempts to add Sausage and Italian Sausage to the list of values. The function should add only Italian Sausage because Sausage already exists in the list of values. When you re-query the row you will see that the add_elements added only the element Italian Sausage.
You would use the following UPDATE statement:
SQL> UPDATE pizza 2 SET ingredients = 3 add_elements(ingredients,list('Italian Sausage','Sausage')) 4 WHERE customer_id = 5 (SELECT customer_id FROM customer 6 WHERE first_name = 'Quentin' AND last_name = 'Lance'); |
Line 3 calls the add_elements PL/SQL function with the ingredient ADT collection column’s value as the first parameter. The second parameter is a dynamically created list of the elements. It contains the element or elements you want to add to the ingredient column’s values.
Re-querying the row, you should see that the UPDATE statement added only the Italian Sausage element to the row. You should see the following output:
Pizza Pizza
ID # Size Ingredients
------ ------ -----------------------------------------------------------
1 Large Cheese, Marinara Sauce, Sausage, Salami, Italian Sausage' |
As you can see, the call to the add_elements function adds only Italian Sausage to the list of values in the ingredient column, while a comma delimited list of single quote delimited strings allows you to add multiple elements. You add one element by making it the only single quote delimited item in the list constructor call.
Updating ADT elements with an UPDATE statement
This section shows you how to change elements in an ADT collection column with an UPDATE statement. The change_elements PL/SQL function can change one to many elements in an ADT collection column. That’s possible because the change element or elements are passed to the function inside ADT collection parameters.
Unlike the add_elements function, the change_elements function requires an ADT collection parameter and a UDT collection element. The UDT collection needs to hold an old and new value.
The alternative approach would require you to try and synchronize two ADT collection value sets. One would hold all the old values and the other would hold all the new values, and they would both need to be synchronized in mirrored positional order.
You define a pair UDT object type such as the following:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 TYPE pair IS OBJECT 3 ( old VARCHAR2(20) 4 , NEW VARCHAR2(20)); 5 / |
Next, you define a change UDT collection type:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 TYPE change IS TABLE OF pair; 3 / |
You define the change_element function as shown below:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 FUNCTION change_elements 3 ( pv_list LIST 4 , pv_element CHANGE ) RETURN LIST IS 5 /* Declare local return collection variable. */ 6 lv_list LIST; 7 BEGIN 8 /* Check for instantiated collection and initialize when necessary. */ 9 IF pv_list IS NULL THEN 10 lv_list := list(); 11 ELSE 12 /* Assign parameter collection to local collection variable. */ 13 lv_list := pv_list; 14 FOR i IN 1..pv_element.COUNT LOOP 15 /* Check to avoid duplicates, allocate memory and assign value. */ 16 IF NOT list(pv_element(i).old) SUBMULTISET OF lv_list THEN 17 lv_list.EXTEND; 18 lv_list(lv_list.COUNT) := pv_element(i).NEW; 19 END IF; 20 END LOOP; 21 END IF; 22 23 /* Return new collection. */ 24 RETURN lv_list; 25 END change_elements; 26 / |
Line 3 and 4 define the two parameters of the change_elements function. The first pv_list parameter uses the list ADT collection type and the list type that matches the ingredient column’s data type. Line 4 defines a parameter that uses the change UDT collection type, which is a collection of the pair UDT type.
Line 6 declares a local ADT collection variable, such as the add_elements function. The lv_list variable also serves the same purpose as it does in the add_elements function.
Line 9 checks whether the pv_list parameter is null. Line 10 initializes the lv_list variable when it is null to avoid an unitialized error when you try to assign values to it. Line 13 assigns an initialized ADT collection column’s value to the local lv_list variable. Line 14 starts a loop through the ADT collection you want to add to the ingredient column’s list of values.
Line 16 uses the SUBMULTISET set operator to ensure that the old element exists in the ingredient ADT collection column. Line 17 allocates memory space in the lv_list variable, and line 18 assigns the new element to it.
The change_elements function couples the memory allocation with the assignment of new values. Line 24 returns the local ADT collection and replaces the original ingredient column value.
The test case shows you how to pass one old and one new element or a set of old and new elements. The initial query shows you the data before the update:
SQL> SELECT pizza_id, pizza_size 2 , serialize_set(ingredients) AS ingredients 3 FROM pizza 4 WHERE customer_id = 5 (SELECT customer_id FROM customer 6 WHERE first_name = 'Thea' AND last_name = 'Queen'); |
It returns:
Pizza Pizza
ID # Size Ingredients
------ ------ -----------------------------------------------------------
2 Medium Cheese, Marinara Sauce, Canadian Bacon |
You now update the row with the following query:
SQL> UPDATE pizza 2 SET ingredients = 3 change_elements(ingredients 4 ,change(pair(old => 'Italian Sausage' 5 ,NEW => 'Linguica'))) 6 WHERE customer_id = 7 ( SELECT customer_id FROM customer 8 WHERE first_name = 'Thea' AND last_name = 'Queen' ); |
When you re-query the row, it shows you the following:
Pizza Pizza
ID # Size Ingredients
------ ------ -----------------------------------------------------------
2 Medium Cheese, Marinara Sauce, Canadian Bacon, Linguica |
As you can see, the call to the change_elements function changes onlyItalian Sausage to Linguica in the list of values in the ingredient column, while a comma delimited list of pair UDT values allows you to change multiple elements. You change one element by making it the only pair UDT in the change constructor call.
Removing ADT elements with an UPDATE statement
This section shows you how to remove elements from an ADT collection column with an UPDATE statement. The remove_elements PL/SQL function can remove one to many elements from an ADT collection column.
The remove_elements function works much like the add_elements function. It uses the same ADT collections as the add_elements function.
The code for the remove_elements function is:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 FUNCTION remove_elements 3 ( pv_list LIST 4 , pv_elements LIST ) RETURN LIST IS 5 /* Declare local return collection variable. */ 6 lv_list LIST; 7 BEGIN 8 /* Check for instantiation and element membership. */ 9 IF NOT (pv_list IS NULL AND pv_elements IS NULL) AND 10 (pv_list.COUNT > 0 AND pv_elements.COUNT > 0) THEN 11 /* Assign parameters to local variables. */ 12 lv_list := pv_list; 13 /* Remove any elements from a collection. */ 14 FOR i IN 1..lv_list.COUNT LOOP 15 FOR j IN 1..pv_elements.COUNT LOOP 16 IF lv_list(i) = pv_elements(j) THEN 17 lv_list.DELETE(i); 18 EXIT; 19 END IF; 20 END LOOP; 21 END LOOP; 22 END IF; 23 24 /* Return modified collection. */ 25 RETURN lv_list; 26 END remove_elements; 27 / |
Lines 3, 4, and 6 work like the add_elements function. Lines 9 and 10 differ because they check for initialized collections that hold at least one element each. Line 12 mimics the behavior of line 13 in the add_elements function. Lines 14 through 16 implements a nested loop and filtering IF-statement. The IF-statement checks for a valid element to remove from the ingredient ADT column’s list of values.
Line 17 removes an element from the list. Line 18 exits the inner loop to skip the evaluation of other non-matches. It’s possible to do this because the add_elements and change_elements functions ensure a unique list of string values in the ingredient ADT collection.
The test case for the remove_elements function works like the earlier tests. You query the row that you will update to check its values; for instance:
SQL> SELECT pizza_id, pizza_size 2 , serialize_set(ingredients) AS ingredients 3 FROM pizza 4 WHERE customer_id = 5 (SELECT customer_id FROM customer 6 WHERE first_name = 'Thea' AND last_name = 'Queen'); |
It should return:
Pizza Pizza
ID # Size Ingredients
------ ------ ----------------------------------------------------------------
2 Medium Cheese, Marinara Sauce, Canadian Bacon, Linguica |
You would remove an element from the ingredient ADT collection column with the following UPDATE statement:
SQL> UPDATE pizza 2 SET ingredients = 3 remove_elements(ingredients,list('Canadian Bacon')) 4 WHERE customer_id = 5 ( SELECT customer_id FROM customer 6 WHERE first_name = 'Thea' AND last_name = 'Queen' ); |
When you re-query the row, you should see that Canadian Bacon is no longer an element in the ingredient ADT collection column. Like this:
Pizza Pizza
ID # Size Ingredients
------ ------ ----------------------------------------------------------------
2 Medium Cheese, Marinara Sauce, Linguica |
This two article series has shown you the differences between working with ADT and UDT collection. It has also shown you how to create PL/SQL functions to enable you to add, change, and remove elements from ADT column inside an UPDATE statement.
The next step would be for you to put the serialize_set, add_elements, change_elements, and remove_elements functions into an adt package. That package would look like:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 PACKAGE adt IS 3 4 FUNCTION add_elements 5 ( pv_list LIST 6 , pv_element LIST ) RETURN LIST; 7 8 FUNCTION change_elements 9 ( pv_list LIST 10 , pv_element CHANGE ) RETURN LIST; 11 12 FUNCTION remove_elements 13 ( pv_list LIST 14 , pv_elements LIST ) RETURN LIST; 15 16 FUNCTION serialize_set 17 (pv_list LIST) RETURN VARCHAR2; 18 19 END adt; 20 / |
Beyond writing an ADT package to manage a list of variable length strings, you have the opportunity to extend behaviors further through overloading. Overloading lets you define functions that use the same name with different parameter lists.
For example, you could define the LIST_D, LIST_N, and LIST_S as SQL ADT where they would implement ADTs of dates, numbers, and strings respectively. Then, you would write three versions of the preceding four functions. Each set of functions would work with one of the type specific ADTs, and provide you with a powerful utility package to add, change, remove, and serialize the values of date, number, and string ADTs.
When you put all the related functions into a package you simplify access and organize for reusability. That way you have all the tools you need inside a single adt package to write advanced UPDATE statements against ADT nested tables.
Updating Nested Tables
This two-part series covers how you update User-Defined Types (UDTs) and Attribute Data Types (ADTs). There are two varieties of UDTs. One is a column of a UDT object type and the other a UDT collection of a UDT object type.
You update nested UDT columns by leveraging the TABLE function. The TABLE function lets you create a result set, and access a UDT object or collection column. You need to combine the TABLE function and a CROSS JOIN to update elements of a UDT collection column.
ADTs are collections of a scalar data types. Oracle’s scalar data types are DATE, NUMBER, CHAR and VARCHAR2 (or, variable length strings). ADTs are unique and from some developer’s perspective difficult to work with.
The first article in this series shows you how to work with a UDT object type column and a UDT collection type. The second article will show you how to work with an ADT collection type.
PL/SQL uses ADT collections all the time. PL/SQL also uses User-Defined Types (UDTs) collections all the time. UDTs can be record or object types, or collections of records and objects. Record types are limited, and only work inside a PL/SQL scope. Object types are less limited and you can use them in a SQL or PL/SQL scope.
Object types come in two flavors. One acts as a typical record structure and has no methods and the other acts like an object type in any object-oriented programming language (OOPL). This article refers only to object types like typical record structures. That means when you read ADTs you should think of a SQL collection of a scalar data type, and when you read UDTs you should think of a SQL collection of an object type without methods.
You can create tables that hold nested tables. Nested tables can use a SQL ADT or UDT data type. Inserting data into nested tables is straightforward when you understand the syntax, but updating nested tables can be complex. The complexity exists because Oracle treats nested tables of ADTs differently than UDTs. My article series will show you how to simplify updating ADT columns.
That’s why it has two parts:
- How you insert and update rows with UDT columns and collection columns
- How you insert and update rows with ADT collection columns
If you’re asking yourself why there isn’t a section for deleting rows, that’s simple. You delete them the same way as you would any other row, using the DELETE statement.
How you insert and update rows with UDT columns and collection columns
This section shows you how to create a table with a UDT column and a UDT collection column. It also shows you how to insert and update the embedded columns.
You insert into any ordinary UDT column by prefacing the data with a constructor name. A constructor name is the same as a UDT name. The following creates an address_type UDT that you will use inside a customer table:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 TYPE address_type IS OBJECT 3 ( street VARCHAR2(20) 4 , city VARCHAR2(30) 5 , state VARCHAR2(2) 6 , zip VARCHAR2(5)); 7 / |
You should take note that the address_type UDT doesn’t have any methods. All object types without methods have a default constructor. The default constructor follows the same rules as tables in the database.
Create the sample customer table with an address column that uses the address_type UDT as its data type; for instance:
SQL> CREATE TABLE customer 2 ( customer_id NUMBER 3 , first_name VARCHAR2(20) 4 , last_name VARCHAR2(20) 5 , address ADDRESS_TYPE 6 , CONSTRAINT pk_customer PRIMARY KEY (customer_id)); |
Line 5 defines the address column with the address_type UDT. You insert a row with an embedded address_type data record as follows:
SQL> INSERT 2 INTO customer 3 VALUES 4 ( customer_s.NEXTVAL 5 ,'Oliver' 6 ,'Queen' 7 , address_type( street => '1 Park Place' 8 , city => 'Starling City' 9 , state => 'NY' 10 , zip => '10001')); |
Lines 7 through 10 includes the constructor call to the address_type UDT. The address_type constructor uses named notation rather than positional notation. You should always try to use named notation for object type constructor calls.
Updating an element of a UDT object structure is straightforward, because you simply refer to the column and a member of the UDT object structure. The syntax for that type of UPDATE statement follows:
SQL> UPDATE customer c 2 SET c.address.state = 'NJ' 3 WHERE c.first_name = 'Oliver' 4 AND c.last_name = 'Queen'; |
The address_type UDT works for an object structure but not for a UDT collection. You need to add a column to differentiate between rows of the nested collection. You can redefine the address_type UDT as follows:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 TYPE address_type IS OBJECT 3 ( status VARCHAR2(8) 4 , street VARCHAR2(20) 5 , city VARCHAR2(30) 6 , state VARCHAR2(2) 7 , zip VARCHAR2(5)); 8 / |
After creating the UDT object type, you need to create an address_table UDT collection of the address_type UDT object type. You use the following syntax to create the SQL collection:
SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE 2 TYPE address_table IS TABLE OF address_type; 3 / |
Having both the UDT object and collection types, you can drop and create the customer table with the following syntax:
SQL> CREATE TABLE customer 2 ( customer_id NUMBER 3 , first_name VARCHAR2(20) 4 , last_name VARCHAR2(20) 5 , address ADDRESS_TABLE 6 , CONSTRAINT pk_customer PRIMARY KEY (customer_id)) 7 NESTED TABLE address STORE AS address_tab; |
Line 5 defines the address column as a UDT collection. Line 7 instructs how to store the UDT collection as a nested table. You designate the address column as the nested table and store it as an address_tab table. You can access the nested table only through its container, which is the customer table.
You can insert rows into the customer table with the following syntax. This example stores a single row with two elements of the address_type in the nested table:
SQL> INSERT 2 INTO customer 3 VALUES 4 ( customer_s.NEXTVAL 5 ,'Oliver' 6 ,'Queen' 7 , address_table( 8 address_type( status => 'Obsolete' 9 , street => '1 Park Place' 10 , city => 'Starling City' 11 , state => 'NY' 12 , zip => '10001') 13 , address_type( status => 'Current' 14 , street => '1 Dockland Street' 15 , city => 'Starling City' 16 , state => 'NY' 17 , zip => '10001'))); |
Lines 7 through 17 have two constructor calls for the address_type UDT object type inside the address_table UDT collection. After you insert an address_table UDT collection, you can query an element by using the SQL built-in TABLE function and a CROSS JOIN. The TABLE function returns a SQL result set. The CROSS JOIN lets you create cross product that you can filter inside the WHERE clause.
A CROSS JOIN between two tables or a table and result set from a nested table matches every row in the customer table with every row in the nested table. A best practice would include a WHERE clause that filters the nested table to a single row in the result set.
The syntax for such a query is complex, and follows below:
SQL> COL first_name FORMAT A8 HEADING "First|Name" SQL> COL last_name FORMAT A8 HEADING "Last|Name" SQL> COL street FORMAT A20 HEADING "Street" SQL> COL city FORMAT A14 HEADING "City" SQL> COL state FORMAT A5 HEADING "State" SQL> SELECT c.first_name 2 , c.last_name 3 , a.street 4 , a.city 5 , a.state 6 FROM customer c CROSS JOIN TABLE(c.address) a 7 WHERE a.status = 'Current'; |
As mentioned, the TABLE function on line 6 translates the UDT collection into a SQL result set, which acts as a temporary table. The alias a becomes the name of the temporary table. Lines 3, 4, 5, and 7 all reference the temporary table.
The query should return the following for the customer and their current address value:
First Last Name Name Street City State -------- -------- -------------------- -------------- ----- Oliver Queen 1 Dockland Street Starling City NY |
Oracle thought through the fact that you should be able to update UDT collections. The same TABLE function lets you update elements in the nested table. You can update the elements in nested UDT tables provided you create a unique key, such as a natural key or primary key. Oracle’s syntax doesn’t support constraints on nested tables, which means you need to implement it by design and protect by carefully controlling inserts and updates to the nested table.
You can update the state value of the current address with the following UPDATE statement:
SQL> UPDATE TABLE(SELECT c.address 2 FROM customer c 3 WHERE c.first_name = 'Oliver' 4 AND c.last_name = 'Queen') a 5 SET a.state = 'NJ' 6 WHERE a.status = 'Current'; |
Line 5 sets the current state value in the address_table UDT nested table. Line 6 filters the nested table to the current address element. You need to ensure that any UDT object type holds a member attribute or set of member attributes that holds a unique value. That’s because you need to ensure that there’s a way to find a unique element within a UDT collection. If you require the table, you should see the change inside the nested table.
Oracle does not provide equivalent syntax for such a change in an ADT collection type. The second article in this series show you how to implement PL/SQL functions to solve that problem.
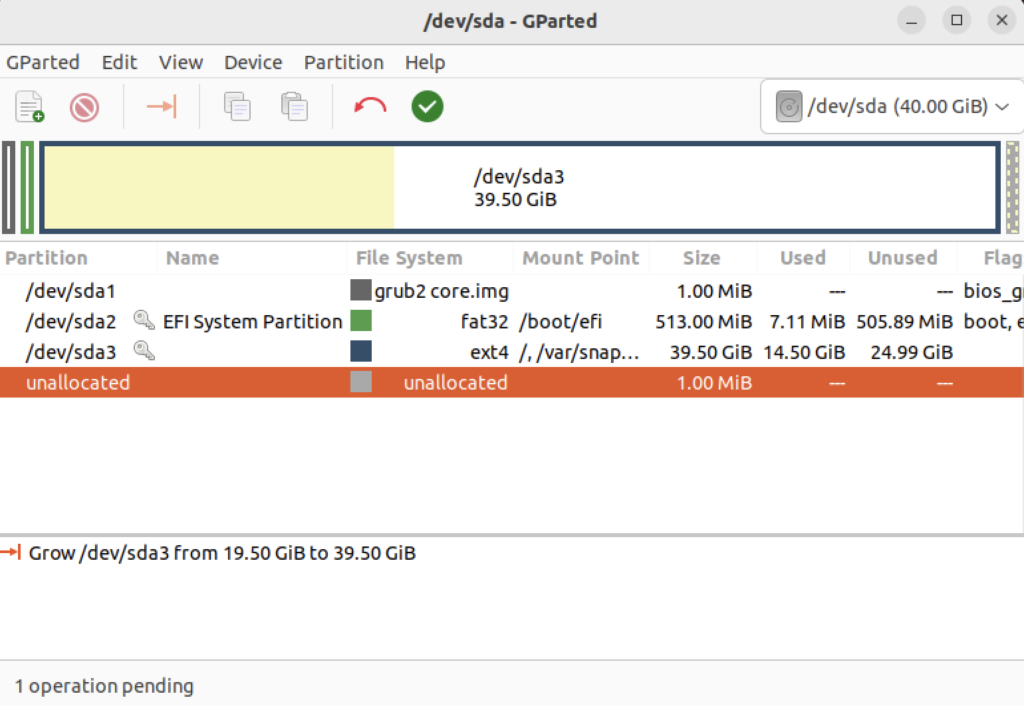
Oracle23ai Ubuntu Install

What to do with a Late 2015 iMac with an i7 Quad CPU running at 3.4 GHz, 32 GB or RAM, a 5K Display and an almost warn out hybrid 1 TB hard disk? You could sell it to Apple for pennies, but why enrich them. I opted to upgrade it with an OWC kit that had a 2 TB SSD Disk. Then, I installed Ubuntu 22.0.4 and built a DaaS (Database as a Service) machine with Oracle Database 23ai in a Docker container, and MySQL 8 and PostgreSQL 14 natively.
I’ve posted on installing MySQL 8 and PostgreSQL 14 on Ubuntu before when I repurposed my late 2014 MacBook Pro. This post covers the installation of Docker and Oracle Database 23ai.
Install Docker
Contrary to the instructions, you should do the following as a sudoer user:
sudo apt install -y docker.io |
Install all dependency packages using the following command:
sudo snap install docker |
You should see the following:
docker 20.10.24 from Canonical✓ installed |
You can verify the Docker install with the following command:
sudo docker --version |
It should show something like this:
Docker version 24.0.5, build 24.0.5-0ubuntu1~22.04.1 |
You can check the pulled containers with the following command but at this point there should be no pulled containers.
sudo docker images |
At this point, a docker group already exists but you need to add your user to the docker group with the following command:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER |
Using the Docker Commands:
- To activate the logging, utilize the -f parameter.
- To divide JSON, use Docker by default; to extract individual keys, use JQ.
- In your Container file, there are quite a few areas where commands may be specified.
- Posting to the volumes could be more effective while the picture is being built.
- Docker offers a highly efficient way to create an alias for its own built-in commands. This makes it easier to set up and handle lengthy and enormous orders. These alias values are stored in the directories /.bashrc or and /.bash_aliases.
- Docker offers further assistance to remove unused code fragments from the installation of the container.
- Docker always favors reading statements from the container file that have not changed. Therefore, time savings may be realized by arranging what is shown in the container file in a way that ensures the elements that are susceptible to change are shown towards the end of the document and those that are most likely to undergo change are shown at the top.
Install Oracle Database 23ai Free in a Docker container
Use the following command to pull and install the Oracle Database 23ai container:
sudo docker run --name oracle23ai -p 1521:1521 -p 5500:5500 -e ORACLE_PWD=cangetin container-registry.oracle.com/database/free:latest |
After installing the Oracle Database 23ai Free container, you can access it as the root user by default with this syntax:
docker exec -it -u root oracle23ai bash |
At the root prompt, you can connect to the system schema with the following command:
sqlplus system/cangetin@FREE |
You should see the following:
SQL*Plus: RELEASE 23.0.0.0.0 - Production ON Thu May 9 03:56:57 2024 Version 23.4.0.24.05 Copyright (c) 1982, 2024, Oracle. ALL rights reserved. LAST SUCCESSFUL login TIME: Wed Apr 24 2024 21:23:00 +00:00 Connected TO: Oracle DATABASE 23ai Free RELEASE 23.0.0.0.0 - Develop, Learn, AND Run FOR Free Version 23.4.0.24.05 SQL> |
Create a c##student as a sandbox user:
After you create and provision the Oracle Database 21ai Free, you can create a c##student sand-boxed user with the following two step process.
- Create a c##student Oracle user account with the following command as the system user:
CREATE USER c##student IDENTIFIED BY student DEFAULT TABLESPACE users QUOTA 200M ON users TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp;
- Grant necessary privileges to the newly created c##student user:
GRANT CREATE CLUSTER, CREATE INDEXTYPE, CREATE OPERATOR , CREATE PROCEDURE, CREATE SEQUENCE, CREATE SESSION , CREATE TABLE, CREATE TRIGGER, CREATE TYPE , CREATE VIEW TO c##student;
- Connect to the sandboxed user with the following syntax (by the way it’s a pluggable user account as qualified in Oracle Database 12c forward):
SQL> CONNECT c##student/student@FREE
or, disconnect and reconnect with this syntax:
sqlplus system/cangetin@FREE
Set Docker Oracle 23ai to start always
Assuming that your container name was oracle23ai, as qualified above, you can run the following command to automatically restart the Docker container:
docker update --restart=always `docker ps -aqf "name=oracle23ai"` |
The docker command inside the backquotes uses the Docker instance’s name to return the Docker container_id value, which can also be seen when you run the following command:
docker ps |
which returns:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES b211f494e692 container-registry.oracle.com/database/free:latest "/bin/bash -c $ORACL…" 13 days ago Up 18 minutes (healthy) 0.0.0.0:1521->1521/tcp, :::1521->1521/tcp, 0.0.0.0:5500->5500/tcp, :::5500->5500/tcp oracle23ai |
The Docker container_id value is required when you perform a Docker update operation.
Configuring your Docker Oracle 23ai environment
Unless you like memorizing the Docker command-line, you may automate connecting as the root user or add a sand boxed user. The root user typically has more power than you need to perform ordinary development and use-case testing tasks.
A sand boxed user has narrow access, can’t start and stop the database instance or perform Oracle Datasbase 23ai administration. In this segment, you’ll learn how to create a couple local Bash functions to simplify your use of the Oracle Database 23ai container; and how to extend the configuration of Oracle’s Docker container:
- Adding a student user to the Docker container and configuring it to access the Oracle Database 23ai locally from within the Docker container using a direct sqlplus connection.
- Configuring the Docker container to support external files and leverage a shared directory with your base operating system.
Automating Docker instance connections:
The following shows you how to add a local Bash function to automate access to the Docker container from the Linux command-line. You put the following Bash function in your base Linux operating system’s user .bashrc file:
- Create the following Bash function:
# User defined function to launch Oracle 23 ai container # as the root user. admin () { # Discover the fully qualified program name. path=`which docker 2>/dev/null` file='' # Parse the program name from the path. if [ -n ${path} ]; then file=${path##/*/} fi # Wrap when there is a file and it is rewrap. if [ -n ${file} ] && [[ ${file} = "docker" ]]; then python -c "import subprocess; subprocess.run(['docker exec -it --user root oracle23ai bash'], shell=True)" else echo "Docker is unavailable: Install the docker package." fi }
- After you source the .bashrc file or simply reconnect as to the terminal as your user, which resources the .bashrc file, you can access the oracle23ai Docker instance with this command:
admin
It will display a new prompt with the root user and the Docker container_id value, like:
[root@b211f494e692 oracle]#
You can exit the Docker container by typing exit at the Linux command line. If you curious what version of Linux you’re using inside the Docker instance, you can’t use the uname command because it returns the hosting Linux distribution (distro). You must use the following when inside the Docker instance:
cat /etc/os-release
or, outside the Docker instance you can use the following docker command:
docker exec oracle23ai cat /etc/os-release
Either way, for an Oracle Database 23ai container, it should return:
NAME="Oracle Linux Server" VERSION="8.9" ID="ol" ID_LIKE="fedora" VARIANT="Server" VARIANT_ID="server" VERSION_ID="8.9" PLATFORM_ID="platform:el8" PRETTY_NAME="Oracle Linux Server 8.9" ANSI_COLOR="0;31" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:oracle:linux:8:9:server" HOME_URL="https://linux.oracle.com/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://github.com/oracle/oracle-linux" ORACLE_BUGZILLA_PRODUCT="Oracle Linux 8" ORACLE_BUGZILLA_PRODUCT_VERSION=8.9 ORACLE_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="Oracle Linux" ORACLE_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION=8.9
Unfortunately, Oracle has appeared to block updates to the Oracle Unbreakable Linux 8 instance inside the container, which makes native SQL*Plus use more difficult. That’s because you’ll need to install the Oracle SQL*Plus client in the hosting Operating System.
I’ve written a separate blog post that instructs you on how to install and use Oracle SQL*Plus client on Ubuntu.
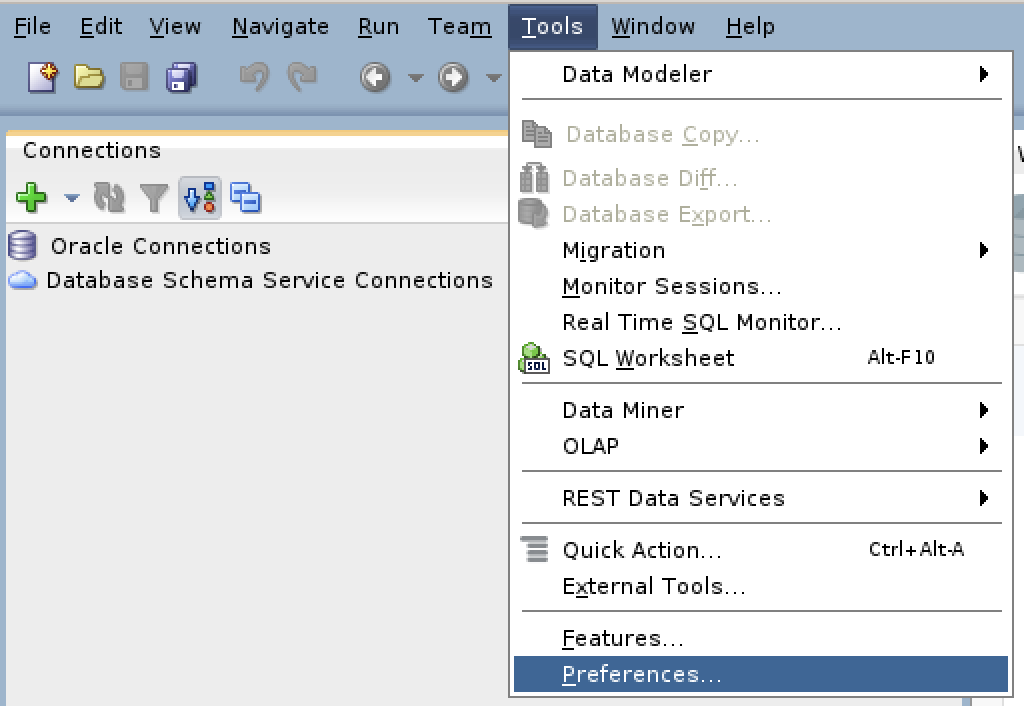
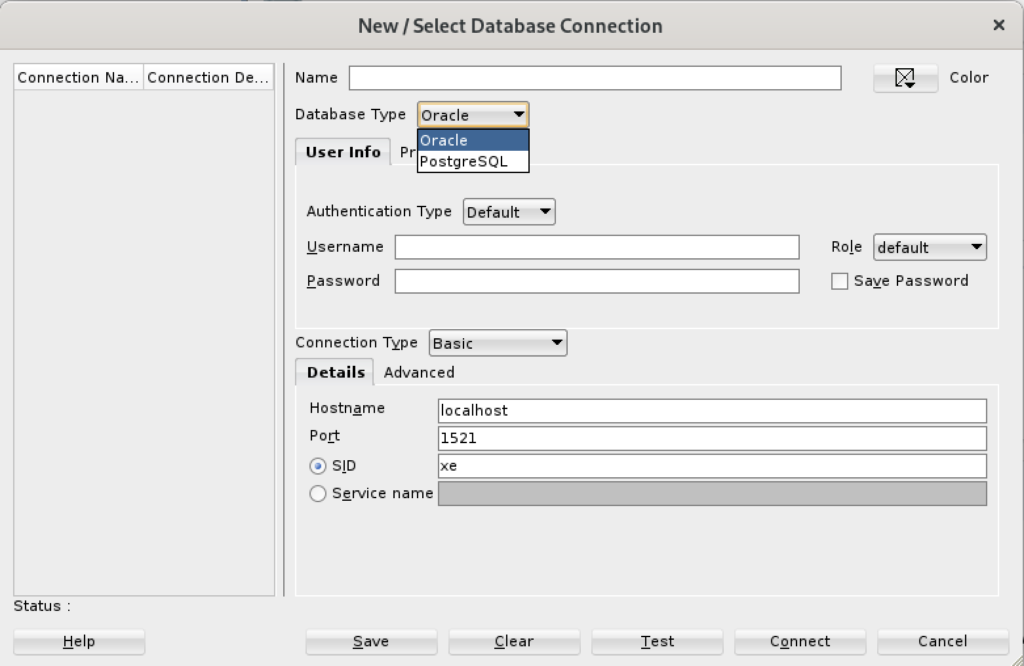
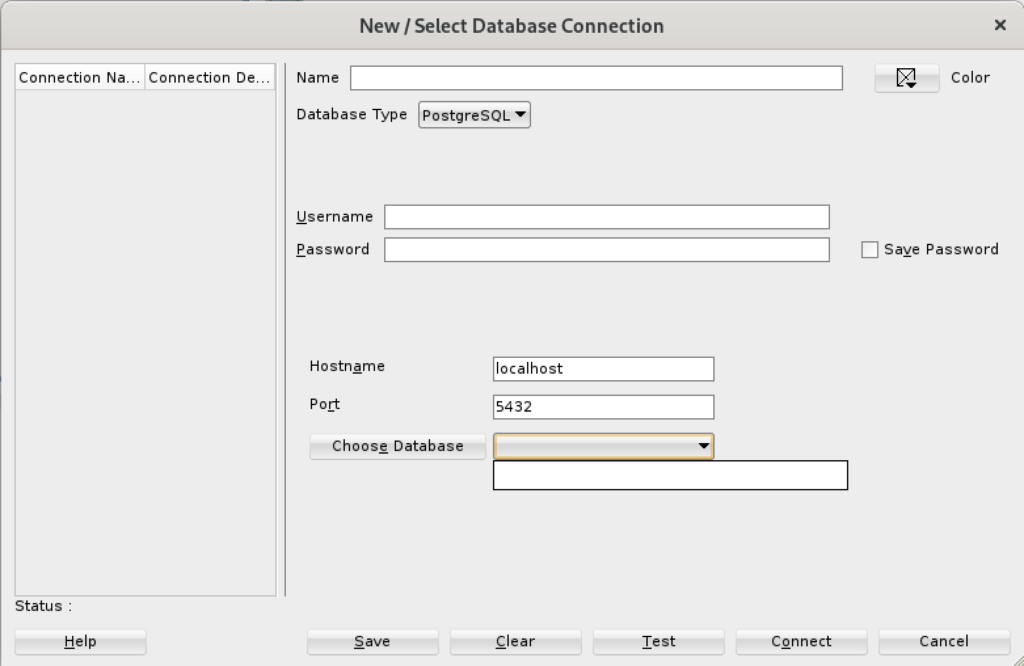
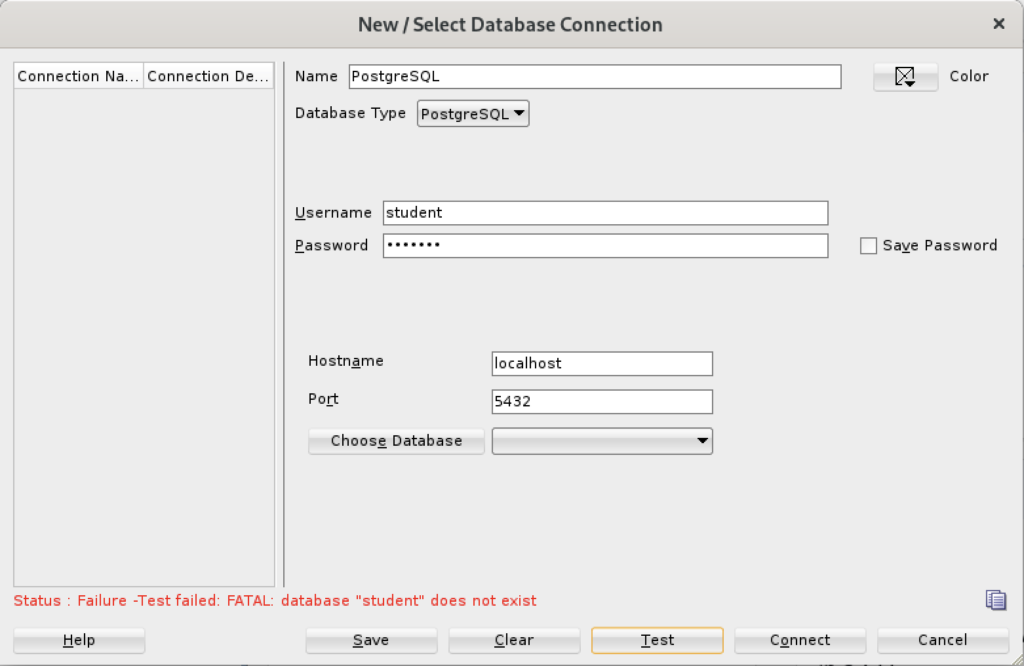
Install SQL Developer in the base Linux operating system
The first steps are installing the Java Runtime Environment and Java Development Kit, and then downloading, installing and configuring SQL Developer. These are the required steps:
- Install the Java Runtime Environment:
sudo apt install default-jre
The log file for this is:
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: ca-certificates-java default-jre-headless fonts-dejavu-extra java-common libatk-wrapper-java libatk-wrapper-java-jni openjdk-11-jre openjdk-11-jre-headless Suggested packages: fonts-ipafont-gothic fonts-ipafont-mincho fonts-wqy-microhei | fonts-wqy-zenhei The following NEW packages will be installed: ca-certificates-java default-jre default-jre-headless fonts-dejavu-extra java-common libatk-wrapper-java libatk-wrapper-java-jni openjdk-11-jre openjdk-11-jre-headless 0 upgraded, 9 newly installed, 0 to remove and 4 not upgraded. Need to get 44.9 MB of archives. After this operation, 185 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 java-common all 0.72build2 [6,782 B] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 openjdk-11-jre-headless amd64 11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04 [42.5 MB] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 default-jre-headless amd64 2:1.11-72build2 [3,042 B] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 ca-certificates-java all 20190909ubuntu1.2 [12.1 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 openjdk-11-jre amd64 11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04 [214 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 default-jre amd64 2:1.11-72build2 [896 B] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 fonts-dejavu-extra all 2.37-2build1 [2,041 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libatk-wrapper-java all 0.38.0-5build1 [53.1 kB] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libatk-wrapper-java-jni amd64 0.38.0-5build1 [49.0 kB] Fetched 44.9 MB in 14s (3,270 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package java-common. (Reading database ... 203118 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../0-java-common_0.72build2_all.deb ... Unpacking java-common (0.72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package openjdk-11-jre-headless:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../1-openjdk-11-jre-headless_11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04_amd64 .deb ... Unpacking openjdk-11-jre-headless:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package default-jre-headless. Preparing to unpack .../2-default-jre-headless_2%3a1.11-72build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking default-jre-headless (2:1.11-72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package ca-certificates-java. Preparing to unpack .../3-ca-certificates-java_20190909ubuntu1.2_all.deb ... Unpacking ca-certificates-java (20190909ubuntu1.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package openjdk-11-jre:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../4-openjdk-11-jre_11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking openjdk-11-jre:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package default-jre. Preparing to unpack .../5-default-jre_2%3a1.11-72build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking default-jre (2:1.11-72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package fonts-dejavu-extra. Preparing to unpack .../6-fonts-dejavu-extra_2.37-2build1_all.deb ... Unpacking fonts-dejavu-extra (2.37-2build1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libatk-wrapper-java. Preparing to unpack .../7-libatk-wrapper-java_0.38.0-5build1_all.deb ... Unpacking libatk-wrapper-java (0.38.0-5build1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libatk-wrapper-java-jni:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../8-libatk-wrapper-java-jni_0.38.0-5build1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libatk-wrapper-java-jni:amd64 (0.38.0-5build1) ... Setting up java-common (0.72build2) ... Setting up fonts-dejavu-extra (2.37-2build1) ... Setting up libatk-wrapper-java (0.38.0-5build1) ... Setting up libatk-wrapper-java-jni:amd64 (0.38.0-5build1) ... Setting up default-jre-headless (2:1.11-72build2) ... Setting up openjdk-11-jre-headless:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java to provid e /usr/bin/java (java) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jjs to provide /usr/bin/jjs (jjs) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/keytool to pro vide /usr/bin/keytool (keytool) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/rmid to provid e /usr/bin/rmid (rmid) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/rmiregistry to provide /usr/bin/rmiregistry (rmiregistry) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/pack200 to pro vide /usr/bin/pack200 (pack200) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/unpack200 to p rovide /usr/bin/unpack200 (unpack200) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/lib/jexec to provi de /usr/bin/jexec (jexec) in auto mode Setting up openjdk-11-jre:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up default-jre (2:1.11-72build2) ... Setting up ca-certificates-java (20190909ubuntu1.2) ... head: cannot open '/etc/ssl/certs/java/cacerts' for reading: No such file or dir ectory Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_1_G3.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_E46.pem Adding debian:T-TeleSec_GlobalRoot_Class_3.pem Adding debian:Certum_Trusted_Network_CA.pem Adding debian:Buypass_Class_2_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:NetLock_Arany_=Class_Gold=_Főtanúsítvány.pem Adding debian:e-Szigno_Root_CA_2017.pem Adding debian:emSign_Root_CA_-_G1.pem Adding debian:D-TRUST_BR_Root_CA_1_2020.pem Adding debian:Hongkong_Post_Root_CA_3.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_R4.pem Adding debian:NAVER_Global_Root_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:UCA_Extended_Validation_Root.pem Adding debian:AffirmTrust_Premium.pem Adding debian:Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Trusted_Root_G4.pem Adding debian:CFCA_EV_ROOT.pem Adding debian:ePKI_Root_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:Hellenic_Academic_and_Research_Institutions_ECC_RootCA_2015.pem Adding debian:HARICA_TLS_RSA_Root_CA_2021.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_CA_-_R6.pem Adding debian:TWCA_Global_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Trustwave_Global_ECC_P384_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:ISRG_Root_X1.pem Adding debian:Starfield_Services_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.pem Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_3.pem Adding debian:Security_Communication_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_TLS_RSA4096_Root_G5.pem Adding debian:Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority_-_EC1.pem Adding debian:Security_Communication_RootCA3.pem Adding debian:TeliaSonera_Root_CA_v1.pem Adding debian:vTrus_ECC_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:AC_RAIZ_FNMT-RCM_SERVIDORES_SEGUROS.pem Adding debian:Certum_EC-384_CA.pem Adding debian:Microsec_e-Szigno_Root_CA_2009.pem Adding debian:ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem Adding debian:USERTrust_ECC_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:CA_Disig_Root_R2.pem Adding debian:Certum_Trusted_Network_CA_2.pem Adding debian:ACCVRAIZ1.pem Adding debian:TunTrust_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Buypass_Class_3_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:D-TRUST_Root_Class_3_CA_2_2009.pem Adding debian:Security_Communication_ECC_RootCA1.pem Adding debian:GTS_Root_R2.pem Adding debian:Certigna.pem Adding debian:SSL.com_EV_Root_Certification_Authority_RSA_R2.pem Adding debian:Entrust.net_Premium_2048_Secure_Server_CA.pem Adding debian:E-Tugra_Global_Root_CA_ECC_v3.pem Adding debian:Hongkong_Post_Root_CA_1.pem Adding debian:SZAFIR_ROOT_CA2.pem Adding debian:TUBITAK_Kamu_SM_SSL_Kok_Sertifikasi_-_Surum_1.pem Adding debian:Atos_TrustedRoot_2011.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_High_Assurance_EV_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:emSign_Root_CA_-_C1.pem Adding debian:Go_Daddy_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.pem Adding debian:GDCA_TrustAUTH_R5_ROOT.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_CA_-_R3.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_G3.pem Adding debian:Autoridad_de_Certificacion_Firmaprofesional_CIF_A62634068_2.pem Adding debian:Certainly_Root_R1.pem Adding debian:vTrus_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Certainly_Root_E1.pem Adding debian:Autoridad_de_Certificacion_Firmaprofesional_CIF_A62634068.pem Adding debian:TWCA_Root_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:Starfield_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.pem Adding debian:Amazon_Root_CA_3.pem Adding debian:GTS_Root_R1.pem Adding debian:SwissSign_Gold_CA_-_G2.pem Adding debian:Certum_Trusted_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Hellenic_Academic_and_Research_Institutions_RootCA_2015.pem Adding debian:AffirmTrust_Networking.pem Adding debian:emSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_G3.pem Adding debian:HARICA_TLS_ECC_Root_CA_2021.pem Adding debian:certSIGN_ROOT_CA.pem Adding debian:Actalis_Authentication_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:SSL.com_Root_Certification_Authority_RSA.pem Adding debian:Certigna_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:XRamp_Global_CA_Root.pem Adding debian:Baltimore_CyberTrust_Root.pem Adding debian:Trustwave_Global_ECC_P256_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_2_G3.pem Adding debian:GTS_Root_R3.pem Adding debian:COMODO_RSA_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:ISRG_Root_X2.pem Adding debian:SwissSign_Silver_CA_-_G2.pem Adding debian:IdenTrust_Public_Sector_Root_CA_1.pem Adding debian:Microsoft_ECC_Root_Certificate_Authority_2017.pem Adding debian:UCA_Global_G2_Root.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority_-_G2.pem Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_2.pem Adding debian:Trustwave_Global_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:OISTE_WISeKey_Global_Root_GB_CA.pem Adding debian:HiPKI_Root_CA_-_G1.pem Adding debian:E-Tugra_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:GTS_Root_R4.pem Adding debian:Amazon_Root_CA_2.pem Adding debian:Amazon_Root_CA_1.pem Adding debian:SecureTrust_CA.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_R46.pem Adding debian:IdenTrust_Commercial_Root_CA_1.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Global_Root_G2.pem Adding debian:Comodo_AAA_Services_root.pem Adding debian:SSL.com_Root_Certification_Authority_ECC.pem Adding debian:T-TeleSec_GlobalRoot_Class_2.pem Adding debian:Starfield_Class_2_CA.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Global_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:SecureSign_RootCA11.pem Adding debian:certSIGN_Root_CA_G2.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_TLS_ECC_P384_Root_G5.pem Adding debian:Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority_-_G4.pem Adding debian:OISTE_WISeKey_Global_Root_GC_CA.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Global_Root_G3.pem Adding debian:Secure_Global_CA.pem Adding debian:Microsoft_RSA_Root_Certificate_Authority_2017.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_G2.pem Adding debian:Telia_Root_CA_v2.pem Adding debian:emSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_C3.pem Adding debian:COMODO_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:AffirmTrust_Premium_ECC.pem Adding debian:GLOBALTRUST_2020.pem Adding debian:E-Tugra_Global_Root_CA_RSA_v3.pem Adding debian:Amazon_Root_CA_4.pem Adding debian:COMODO_ECC_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:AffirmTrust_Commercial.pem Adding debian:SSL.com_EV_Root_Certification_Authority_ECC.pem Adding debian:AC_RAIZ_FNMT-RCM.pem Adding debian:Go_Daddy_Class_2_CA.pem Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_3_G3.pem Adding debian:D-TRUST_EV_Root_CA_1_2020.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_R5.pem Adding debian:USERTrust_RSA_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:D-TRUST_Root_Class_3_CA_2_EV_2009.pem Adding debian:Izenpe.com.pem Adding debian:ANF_Secure_Server_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Security_Communication_RootCA2.pem done. Processing triggers for mailcap (3.70+nmu1ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for fontconfig (2.13.1-4.2ubuntu5) ... Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.26-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for hicolor-icon-theme (0.17-2) ... Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for ca-certificates (20230311ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Updating certificates in /etc/ssl/certs... 0 added, 0 removed; done. Running hooks in /etc/ca-certificates/update.d... done. done.
- Install the Java Runtime Environment:
sudo apt install -y default-idk
The log file for this is:
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: default-jdk-headless libice-dev libpthread-stubs0-dev libsm-dev libx11-dev libxau-dev libxcb1-dev libxdmcp-dev libxt-dev openjdk-11-jdk openjdk-11-jdk-headless x11proto-dev xorg-sgml-doctools xtrans-dev Suggested packages: libice-doc libsm-doc libx11-doc libxcb-doc libxt-doc openjdk-11-demo openjdk-11-source visualvm The following NEW packages will be installed: default-jdk default-jdk-headless libice-dev libpthread-stubs0-dev libsm-dev libx11-dev libxau-dev libxcb1-dev libxdmcp-dev libxt-dev openjdk-11-jdk openjdk-11-jdk-headless x11proto-dev xorg-sgml-doctools xtrans-dev 0 upgraded, 15 newly installed, 0 to remove and 4 not upgraded. Need to get 76.9 MB of archives. After this operation, 90.6 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 openjdk-11-jdk-headless amd64 11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04 [73.5 MB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 default-jdk-headless amd64 2:1.11-72build2 [942 B] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 openjdk-11-jdk amd64 11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04 [1,327 kB] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 default-jdk amd64 2:1.11-72build2 [908 B] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 xorg-sgml-doctools all 1:1.11-1.1 [10.9 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 x11proto-dev all 2021.5-1 [604 kB] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libice-dev amd64 2:1.0.10-1build2 [51.4 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libpthread-stubs0-dev amd64 0.4-1build2 [5,516 B] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libsm-dev amd64 2:1.2.3-1build2 [18.1 kB] Get:10 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libxau-dev amd64 1:1.0.9-1build5 [9,724 B] Get:11 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libxdmcp-dev amd64 1:1.1.3-0ubuntu5 [26.5 kB] Get:12 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 xtrans-dev all 1.4.0-1 [68.9 kB] Get:13 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libxcb1-dev amd64 1.14-3ubuntu3 [86.5 kB] Get:14 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libx11-dev amd64 2:1.7.5-1ubuntu0.3 [744 kB] Get:15 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libxt-dev amd64 1:1.2.1-1 [396 kB] Fetched 76.9 MB in 6s (12.7 MB/s) Selecting previously unselected package openjdk-11-jdk-headless:amd64. (Reading database ... 203527 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../00-openjdk-11-jdk-headless_11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04_amd6 4.deb ... Unpacking openjdk-11-jdk-headless:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package default-jdk-headless. Preparing to unpack .../01-default-jdk-headless_2%3a1.11-72build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking default-jdk-headless (2:1.11-72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package openjdk-11-jdk:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../02-openjdk-11-jdk_11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking openjdk-11-jdk:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package default-jdk. Preparing to unpack .../03-default-jdk_2%3a1.11-72build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking default-jdk (2:1.11-72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package xorg-sgml-doctools. Preparing to unpack .../04-xorg-sgml-doctools_1%3a1.11-1.1_all.deb ... Unpacking xorg-sgml-doctools (1:1.11-1.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package x11proto-dev. Preparing to unpack .../05-x11proto-dev_2021.5-1_all.deb ... Unpacking x11proto-dev (2021.5-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libice-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../06-libice-dev_2%3a1.0.10-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libice-dev:amd64 (2:1.0.10-1build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libpthread-stubs0-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../07-libpthread-stubs0-dev_0.4-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libpthread-stubs0-dev:amd64 (0.4-1build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libsm-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../08-libsm-dev_2%3a1.2.3-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libsm-dev:amd64 (2:1.2.3-1build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxau-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../09-libxau-dev_1%3a1.0.9-1build5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxau-dev:amd64 (1:1.0.9-1build5) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxdmcp-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../10-libxdmcp-dev_1%3a1.1.3-0ubuntu5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxdmcp-dev:amd64 (1:1.1.3-0ubuntu5) ... Selecting previously unselected package xtrans-dev. Preparing to unpack .../11-xtrans-dev_1.4.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking xtrans-dev (1.4.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxcb1-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../12-libxcb1-dev_1.14-3ubuntu3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxcb1-dev:amd64 (1.14-3ubuntu3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libx11-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../13-libx11-dev_2%3a1.7.5-1ubuntu0.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libx11-dev:amd64 (2:1.7.5-1ubuntu0.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxt-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../14-libxt-dev_1%3a1.2.1-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxt-dev:amd64 (1:1.2.1-1) ... Setting up openjdk-11-jdk-headless:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jar to provide /usr/bin/jar (jar) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jarsigner to p rovide /usr/bin/jarsigner (jarsigner) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/javac to provi de /usr/bin/javac (javac) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/javadoc to pro vide /usr/bin/javadoc (javadoc) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/javap to provi de /usr/bin/javap (javap) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jcmd to provid e /usr/bin/jcmd (jcmd) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jdb to provide /usr/bin/jdb (jdb) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jdeprscan to p rovide /usr/bin/jdeprscan (jdeprscan) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jdeps to provi de /usr/bin/jdeps (jdeps) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jfr to provide /usr/bin/jfr (jfr) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jimage to prov ide /usr/bin/jimage (jimage) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jinfo to provi de /usr/bin/jinfo (jinfo) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jlink to provi de /usr/bin/jlink (jlink) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jmap to provid e /usr/bin/jmap (jmap) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jmod to provid e /usr/bin/jmod (jmod) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jps to provide /usr/bin/jps (jps) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jrunscript to provide /usr/bin/jrunscript (jrunscript) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jshell to prov ide /usr/bin/jshell (jshell) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jstack to prov ide /usr/bin/jstack (jstack) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jstat to provi de /usr/bin/jstat (jstat) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jstatd to prov ide /usr/bin/jstatd (jstatd) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/rmic to provid e /usr/bin/rmic (rmic) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/serialver to p rovide /usr/bin/serialver (serialver) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jaotc to provi de /usr/bin/jaotc (jaotc) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jhsdb to provi de /usr/bin/jhsdb (jhsdb) in auto mode Setting up libpthread-stubs0-dev:amd64 (0.4-1build2) ... Setting up xtrans-dev (1.4.0-1) ... Setting up default-jdk-headless (2:1.11-72build2) ... Setting up openjdk-11-jdk:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jconsole to pr ovide /usr/bin/jconsole (jconsole) in auto mode Setting up xorg-sgml-doctools (1:1.11-1.1) ... Setting up default-jdk (2:1.11-72build2) ... Processing triggers for sgml-base (1.30) ... Setting up x11proto-dev (2021.5-1) ... Setting up libxau-dev:amd64 (1:1.0.9-1build5) ... Setting up libice-dev:amd64 (2:1.0.10-1build2) ... Setting up libsm-dev:amd64 (2:1.2.3-1build2) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Setting up libxdmcp-dev:amd64 (1:1.1.3-0ubuntu5) ... Setting up libxcb1-dev:amd64 (1.14-3ubuntu3) ... Setting up libx11-dev:amd64 (2:1.7.5-1ubuntu0.3) ... Setting up libxt-dev:amd64 (1:1.2.1-1) ...
- Download SQL Developer from here; and then install SQL Developer to the /opt directory on your Ubuntu local instance:
Use the following command to unzip the SQL Developer files to the /opt directory:
sudo unzip ~/Downloads/sqldeveloper-23.1.0.097.1607-no-jre.zip
- Create the following /usr/local/bin/sqldeveloper symbolic link:
sudo ln -s /opt/sqldeveloper/sqldeveloper.sh /usr/local/bin/sqldeveloper
- Edit the /opt/sqldeveloper/sqldeveloper.sh file by replacing the following line:
cd "`dirname $0`"/sqldeveloper/bin && bash sqldeveloper $*
with this version:
/opt/sqldeveloper/sqldeveloper/bin/sqldeveloper $*
- Now, you can launch SQL Developer from any location on your local Ubuntu operating system, like:
sqldeveloper
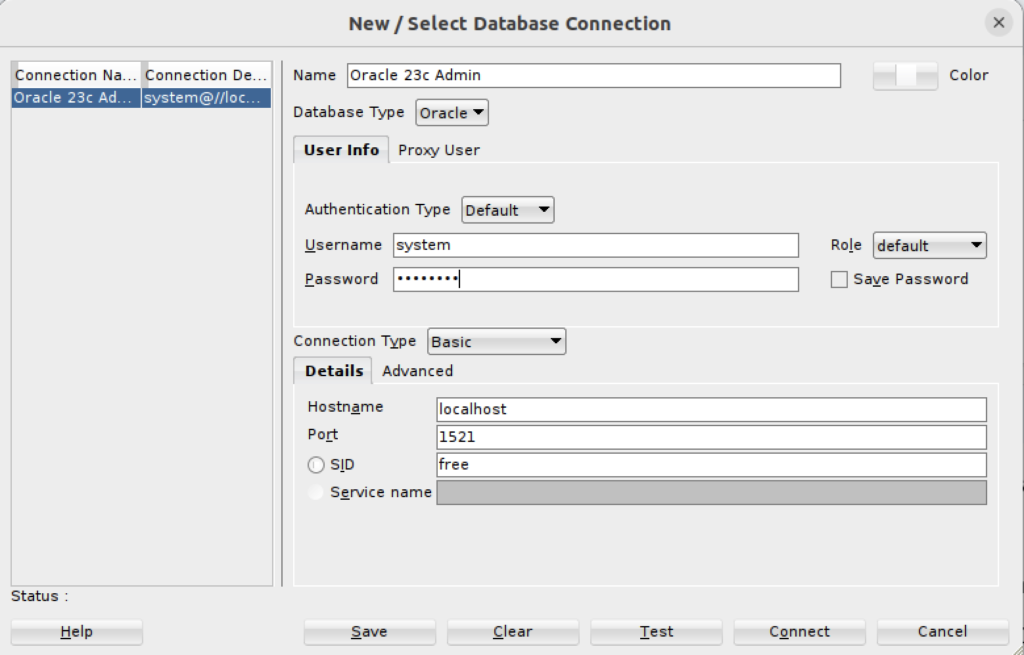
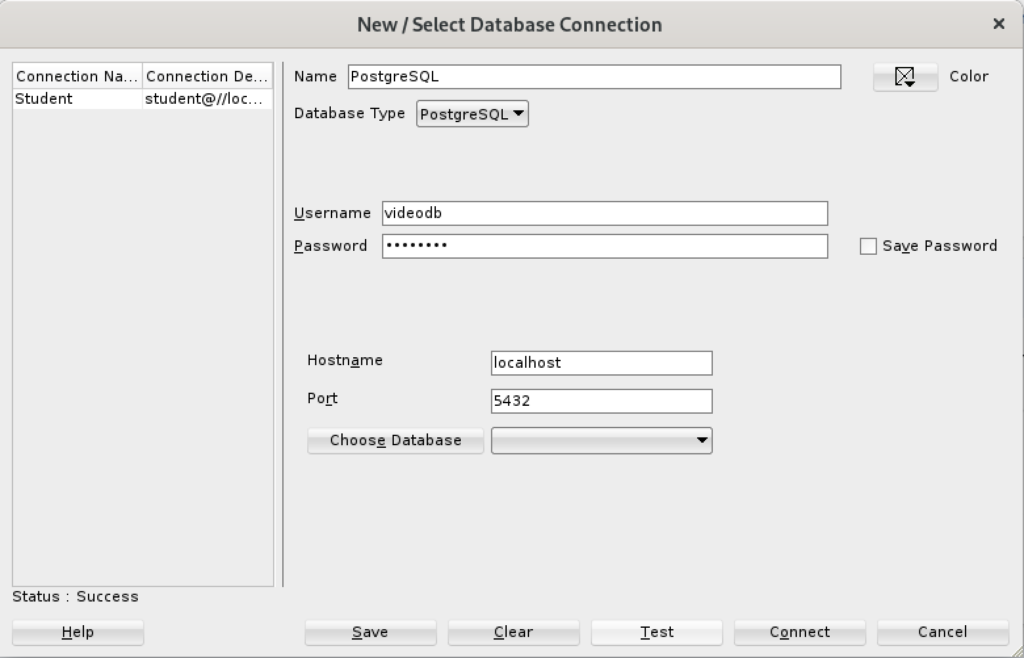
- You can now connect as the system user through SQL Developer to the Oracle Database 23ai Free Docker instance with the following connection information:
(Excuse recycling the version from 21c but I didn’t see any utility in making a new screen shot.)
- You can also create a Desktop shortcut by creating the sqldeveloper.desktop file in the /usr/share/applications directory. The SQL Developer icon is provided in the sqldeveloper base directory.

You should create the following sqldeveloper.desktop file to use a Desktop shortcut:
[Desktop Entry] Name=Oracle SQL Developer Comment=SQL Developer from Oracle GenericName=SQL Tool Exec=/usr/local/bin/sqldeveloper Icon=/opt/sqldeveloper/icon.png Type=Application StartupNotify=true Categories=Utility;Oracle;Development;SQL;
As always, I hope this helps those trying to accomplish this task.
Oracle 23c Free SQL*Plus
It’s always frustrated me when using the sqlplus command-line interface (CLI) that you can’t just “up arrow” to through the history. At least, that’s the default case unless you wrap the sqlplus executable.
I like to do my development work as close to the database as possible. The delay from SQL Developer to the database or VSCode to the database is just too long. Therefore, I like the native sqlplus to be as efficient as possible. This post shows you how to install the rlwarp utility to wrap sqlplus and create a sandboxed student user for a local development account inside the Oracle 23c Free container. You should note that the Docker or Podman Container is using Oracle Unbreakable Linux 8 as it’s native OS.
You can connect to your Docker version of Oracle Database 23c Free with the following command:
docker exec -it -u root oracle23c bash |
You can’t just use dnf to install rlwrap and get it to magically install all the dependencies. That would be too easy, eh?
Attempting to do so will lock your base OS and eventually force you to kill with prejudice the hung dnf process (at least it forced me to do so). You need to determine the rlwrap dependencies and then install them first. In that process, I noticed that the which utility program wasn’t installed in the container.
Naturally, I installed the which utility first with this command:
dnf install -y which |
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 0:26:00 ago on Thu Dec 21 05:18:09 2023. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: which x86_64 2.21-20.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 50 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 50 k Installed size: 81 k Downloading Packages: which-2.21-20.el8.x86_64.rpm 80 kB/s | 50 kB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 80 kB/s | 50 kB 00:00 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : which-2.21-20.el8.x86_64 1/1 Running scriptlet: which-2.21-20.el8.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : which-2.21-20.el8.x86_64 1/1 Installed: which-2.21-20.el8.x86_64 Complete! |
The rlwrap dependencies are: glibc, ncurses, perl, readline, python, and git. Only the perl, python, and git are missing from the list of formal dependencies but there’s another dependency the epel-release package.
If you want to verify whether a package is installed, you can use the rpm command like this:
rpm -qa | grep package_name |
I installed the perl programming environment (a big install) with this command:
dnf install -y perl |
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 0:28:29 ago on Thu Dec 21 05:18:09 2023.
Dependencies resolved.
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
perl x86_64 4:5.26.3-422.el8 ol8_appstream 73 k
Installing dependencies:
dwz x86_64 0.12-10.el8 ol8_appstream 109 k
efi-srpm-macros noarch 3-3.0.1.el8 ol8_appstream 22 k
file x86_64 5.33-24.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 77 k
ghc-srpm-macros noarch 1.4.2-7.el8 ol8_appstream 9.3 k
glibc-gconv-extra x86_64 2.28-225.0.3.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 1.5 M
go-srpm-macros noarch 2-17.el8 ol8_appstream 13 k
groff-base x86_64 1.22.3-18.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 1.0 M
ocaml-srpm-macros noarch 5-4.el8 ol8_appstream 9.3 k
openblas-srpm-macros noarch 2-2.el8 ol8_appstream 7.9 k
perl-Algorithm-Diff noarch 1.1903-9.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 52 k
perl-Archive-Tar noarch 2.30-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 79 k
perl-Archive-Zip noarch 1.60-3.el8 ol8_appstream 108 k
perl-Attribute-Handlers noarch 0.99-422.el8 ol8_appstream 89 k
perl-B-Debug noarch 1.26-2.el8 ol8_appstream 26 k
perl-CPAN noarch 2.18-397.el8 ol8_appstream 554 k
perl-CPAN-Meta noarch 2.150010-396.el8 ol8_appstream 191 k
perl-CPAN-Meta-Requirements noarch 2.140-396.el8 ol8_appstream 37 k
perl-CPAN-Meta-YAML noarch 0.018-397.el8 ol8_appstream 34 k
perl-Carp noarch 1.42-396.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 30 k
perl-Compress-Bzip2 x86_64 2.26-6.el8 ol8_appstream 72 k
perl-Compress-Raw-Bzip2 x86_64 2.081-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 40 k
perl-Compress-Raw-Zlib x86_64 2.081-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 68 k
perl-Config-Perl-V noarch 0.30-1.el8 ol8_appstream 22 k
perl-DB_File x86_64 1.842-1.el8 ol8_appstream 83 k
perl-Data-Dumper x86_64 2.167-399.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 58 k
perl-Data-OptList noarch 0.110-6.el8 ol8_appstream 31 k
perl-Data-Section noarch 0.200007-3.el8 ol8_appstream 30 k
perl-Devel-PPPort x86_64 3.36-5.el8 ol8_appstream 118 k
perl-Devel-Peek x86_64 1.26-422.el8 ol8_appstream 94 k
perl-Devel-SelfStubber noarch 1.06-422.el8 ol8_appstream 76 k
perl-Devel-Size x86_64 0.81-2.el8 ol8_appstream 34 k
perl-Digest noarch 1.17-395.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 27 k
perl-Digest-MD5 x86_64 2.55-396.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 37 k
perl-Digest-SHA x86_64 1:6.02-1.el8 ol8_appstream 66 k
perl-Encode x86_64 4:2.97-3.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 1.5 M
perl-Encode-devel x86_64 4:2.97-3.el8 ol8_appstream 39 k
perl-Env noarch 1.04-395.el8 ol8_appstream 21 k
perl-Errno x86_64 1.28-422.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 76 k
perl-Exporter noarch 5.72-396.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 34 k
perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder noarch 1:0.280230-2.el8 ol8_appstream 48 k
perl-ExtUtils-Command noarch 1:7.34-1.el8 ol8_appstream 19 k
perl-ExtUtils-Embed noarch 1.34-422.el8 ol8_appstream 79 k
perl-ExtUtils-Install noarch 2.14-4.el8 ol8_appstream 46 k
perl-ExtUtils-MM-Utils noarch 1:7.34-1.el8 ol8_appstream 16 k
perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker noarch 1:7.34-1.el8 ol8_appstream 300 k
perl-ExtUtils-Manifest noarch 1.70-395.el8 ol8_appstream 36 k
perl-ExtUtils-Miniperl noarch 1.06-422.el8 ol8_appstream 77 k
perl-ExtUtils-ParseXS noarch 1:3.35-2.el8 ol8_appstream 83 k
perl-File-Fetch noarch 0.56-2.el8 ol8_appstream 33 k
perl-File-HomeDir noarch 1.002-4.el8 ol8_appstream 61 k
perl-File-Path noarch 2.15-2.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 38 k
perl-File-Temp noarch 0.230.600-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 63 k
perl-File-Which noarch 1.22-2.el8 ol8_appstream 23 k
perl-Filter x86_64 2:1.58-2.el8 ol8_appstream 82 k
perl-Filter-Simple noarch 0.94-2.el8 ol8_appstream 29 k
perl-Getopt-Long noarch 1:2.50-4.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 63 k
perl-HTTP-Tiny noarch 0.074-2.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 57 k
perl-IO x86_64 1.38-422.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 142 k
perl-IO-Compress noarch 2.081-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 258 k
perl-IO-Socket-IP noarch 0.39-5.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 47 k
perl-IO-Socket-SSL noarch 2.066-4.module+el8.6.0+20623+f0897f98
ol8_appstream 298 k
perl-IO-Zlib noarch 1:1.10-422.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 81 k
perl-IPC-Cmd noarch 2:1.02-1.el8 ol8_appstream 43 k
perl-IPC-SysV x86_64 2.07-397.el8 ol8_appstream 43 k
perl-IPC-System-Simple noarch 1.25-17.el8 ol8_appstream 43 k
perl-JSON-PP noarch 1:2.97.001-3.el8 ol8_appstream 68 k
perl-Locale-Codes noarch 3.57-1.el8 ol8_appstream 310 k
perl-Locale-Maketext noarch 1.28-396.el8 ol8_appstream 99 k
perl-Locale-Maketext-Simple noarch 1:0.21-422.el8 ol8_appstream 79 k
perl-MIME-Base64 x86_64 3.15-396.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 31 k
perl-MRO-Compat noarch 0.13-4.el8 ol8_appstream 24 k
perl-Math-BigInt noarch 1:1.9998.11-7.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 196 k
perl-Math-BigInt-FastCalc x86_64 0.500.600-6.el8 ol8_appstream 27 k
perl-Math-BigRat noarch 0.2614-1.el8 ol8_appstream 40 k
perl-Math-Complex noarch 1.59-422.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 109 k
perl-Memoize noarch 1.03-422.el8 ol8_appstream 119 k
perl-Module-Build noarch 2:0.42.24-5.el8 ol8_appstream 273 k
perl-Module-CoreList noarch 1:5.20181130-1.el8 ol8_appstream 87 k
perl-Module-CoreList-tools noarch 1:5.20181130-1.el8 ol8_appstream 22 k
perl-Module-Load noarch 1:0.32-395.el8 ol8_appstream 19 k
perl-Module-Load-Conditional noarch 0.68-395.el8 ol8_appstream 24 k
perl-Module-Loaded noarch 1:0.08-422.el8 ol8_appstream 75 k
perl-Module-Metadata noarch 1.000033-395.el8 ol8_appstream 44 k
perl-Mozilla-CA noarch 20160104-7.0.1.module+el8.3.0+21136+b437fca9
ol8_appstream 15 k
perl-Net-Ping noarch 2.55-422.el8 ol8_appstream 102 k
perl-Net-SSLeay x86_64 1.88-2.module+el8.6.0+20623+f0897f98
ol8_appstream 379 k
perl-Package-Generator noarch 1.106-11.el8 ol8_appstream 27 k
perl-Params-Check noarch 1:0.38-395.el8 ol8_appstream 24 k
perl-Params-Util x86_64 1.07-22.el8 ol8_appstream 44 k
perl-PathTools x86_64 3.74-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 90 k
perl-Perl-OSType noarch 1.010-396.el8 ol8_appstream 29 k
perl-PerlIO-via-QuotedPrint noarch 0.08-395.el8 ol8_appstream 13 k
perl-Pod-Checker noarch 4:1.73-395.el8 ol8_appstream 33 k
perl-Pod-Escapes noarch 1:1.07-395.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 20 k
perl-Pod-Html noarch 1.22.02-422.el8 ol8_appstream 88 k
perl-Pod-Parser noarch 1.63-396.el8 ol8_appstream 108 k
perl-Pod-Perldoc noarch 3.28-396.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 88 k
perl-Pod-Simple noarch 1:3.35-395.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 213 k
perl-Pod-Usage noarch 4:1.69-395.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 34 k
perl-Scalar-List-Utils x86_64 3:1.49-2.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 68 k
perl-SelfLoader noarch 1.23-422.el8 ol8_appstream 83 k
perl-Socket x86_64 4:2.027-3.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 59 k
perl-Software-License noarch 0.103013-2.el8 ol8_appstream 137 k
perl-Storable x86_64 1:3.11-3.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 98 k
perl-Sub-Exporter noarch 0.987-15.el8 ol8_appstream 73 k
perl-Sub-Install noarch 0.928-14.el8 ol8_appstream 27 k
perl-Sys-Syslog x86_64 0.35-397.el8 ol8_appstream 50 k
perl-Term-ANSIColor noarch 4.06-396.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 46 k
perl-Term-Cap noarch 1.17-395.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 23 k
perl-Test noarch 1.30-422.el8 ol8_appstream 90 k
perl-Test-Harness noarch 1:3.42-1.el8 ol8_appstream 279 k
perl-Test-Simple noarch 1:1.302135-1.el8 ol8_appstream 516 k
perl-Text-Balanced noarch 2.03-395.el8 ol8_appstream 58 k
perl-Text-Diff noarch 1.45-2.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 45 k
perl-Text-Glob noarch 0.11-4.el8 ol8_appstream 17 k
perl-Text-ParseWords noarch 3.30-395.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 18 k
perl-Text-Tabs+Wrap noarch 2013.0523-395.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 24 k
perl-Text-Template noarch 1.51-1.el8 ol8_appstream 64 k
perl-Thread-Queue noarch 3.13-1.el8 ol8_appstream 24 k
perl-Time-HiRes x86_64 4:1.9758-2.el8 ol8_appstream 61 k
perl-Time-Local noarch 1:1.280-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 33 k
perl-Time-Piece x86_64 1.31-422.el8 ol8_appstream 98 k
perl-URI noarch 1.73-3.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 116 k
perl-Unicode-Collate x86_64 1.25-2.el8 ol8_appstream 686 k
perl-Unicode-Normalize x86_64 1.25-396.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 82 k
perl-autodie noarch 2.29-396.el8 ol8_appstream 98 k
perl-bignum noarch 0.49-2.el8 ol8_appstream 43 k
perl-constant noarch 1.33-396.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 25 k
perl-devel x86_64 4:5.26.3-422.el8 ol8_appstream 600 k
perl-encoding x86_64 4:2.22-3.el8 ol8_appstream 68 k
perl-experimental noarch 0.019-2.el8 ol8_appstream 24 k
perl-inc-latest noarch 2:0.500-9.el8 ol8_appstream 25 k
perl-interpreter x86_64 4:5.26.3-422.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 6.3 M
perl-libnet noarch 3.11-3.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 121 k
perl-libnetcfg noarch 4:5.26.3-422.el8 ol8_appstream 78 k
perl-libs x86_64 4:5.26.3-422.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 1.6 M
perl-local-lib noarch 2.000024-2.el8 ol8_appstream 74 k
perl-macros x86_64 4:5.26.3-422.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 72 k
perl-open noarch 1.11-422.el8 ol8_appstream 78 k
perl-parent noarch 1:0.237-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 20 k
perl-perlfaq noarch 5.20180605-1.el8 ol8_appstream 386 k
perl-podlators noarch 4.11-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 118 k
perl-srpm-macros noarch 1-25.el8 ol8_appstream 11 k
perl-threads x86_64 1:2.21-2.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 61 k
perl-threads-shared x86_64 1.58-2.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 48 k
perl-utils noarch 5.26.3-422.el8 ol8_appstream 129 k
perl-version x86_64 6:0.99.24-1.el8 ol8_appstream 67 k
python-rpm-macros noarch 3-45.el8 ol8_appstream 16 k
python-srpm-macros noarch 3-45.el8 ol8_appstream 16 k
python3-pyparsing noarch 2.1.10-7.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 142 k
python3-rpm-macros noarch 3-45.el8 ol8_appstream 15 k
qt5-srpm-macros noarch 5.15.3-1.el8 ol8_appstream 11 k
redhat-rpm-config noarch 131-1.0.1.el8 ol8_appstream 91 k
rust-srpm-macros noarch 5-2.el8 ol8_appstream 9.2 k
systemtap-sdt-devel x86_64 4.9-3.0.1.el8 ol8_appstream 88 k
zip x86_64 3.0-23.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 270 k
Installing weak dependencies:
perl-Encode-Locale noarch 1.05-10.module+el8.3.0+7692+542c56f9
ol8_appstream 22 k
perl-TermReadKey x86_64 2.37-7.el8 ol8_appstream 40 k
Enabling module streams:
perl 5.26
perl-IO-Socket-SSL 2.066
perl-libwww-perl 6.34
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 159 Packages
Total download size: 25 M
Installed size: 73 M
Downloading Packages:
(1/159): file-5.33-24.el8.x86_64.rpm 163 kB/s | 77 kB 00:00
(2/159): perl-Algorithm-Diff-1.1903-9.el8.noarc 531 kB/s | 52 kB 00:00
(3/159): groff-base-1.22.3-18.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.5 MB/s | 1.0 MB 00:00
(4/159): perl-Archive-Tar-2.30-1.el8.noarch.rpm 642 kB/s | 79 kB 00:00
(5/159): perl-Carp-1.42-396.el8.noarch.rpm 449 kB/s | 30 kB 00:00
(6/159): perl-Compress-Raw-Bzip2-2.081-1.el8.x8 452 kB/s | 40 kB 00:00
(7/159): perl-Compress-Raw-Zlib-2.081-1.el8.x86 968 kB/s | 68 kB 00:00
(8/159): perl-Data-Dumper-2.167-399.el8.x86_64. 734 kB/s | 58 kB 00:00
(9/159): perl-Digest-1.17-395.el8.noarch.rpm 391 kB/s | 27 kB 00:00
(10/159): perl-Digest-MD5-2.55-396.el8.x86_64.r 481 kB/s | 37 kB 00:00
(11/159): perl-Errno-1.28-422.el8.x86_64.rpm 811 kB/s | 76 kB 00:00
(12/159): perl-Encode-2.97-3.el8.x86_64.rpm 9.4 MB/s | 1.5 MB 00:00
(13/159): perl-File-Path-2.15-2.el8.noarch.rpm 627 kB/s | 38 kB 00:00
(14/159): perl-Exporter-5.72-396.el8.noarch.rpm 466 kB/s | 34 kB 00:00
(15/159): perl-Getopt-Long-2.50-4.el8.noarch.rp 867 kB/s | 63 kB 00:00
(16/159): perl-File-Temp-0.230.600-1.el8.noarch 648 kB/s | 63 kB 00:00
(17/159): perl-HTTP-Tiny-0.074-2.el8.noarch.rpm 847 kB/s | 57 kB 00:00
(18/159): perl-IO-Compress-2.081-1.el8.noarch.r 3.5 MB/s | 258 kB 00:00
(19/159): perl-IO-1.38-422.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 142 kB 00:00
(20/159): perl-IO-Socket-IP-0.39-5.el8.noarch.r 614 kB/s | 47 kB 00:00
(21/159): perl-IO-Zlib-1.10-422.el8.noarch.rpm 881 kB/s | 81 kB 00:00
(22/159): perl-MIME-Base64-3.15-396.el8.x86_64. 425 kB/s | 31 kB 00:00
(23/159): perl-Math-BigInt-1.9998.11-7.el8.noar 1.5 MB/s | 196 kB 00:00
(24/159): perl-Math-Complex-1.59-422.el8.noarch 1.5 MB/s | 109 kB 00:00
(25/159): perl-Pod-Escapes-1.07-395.el8.noarch. 300 kB/s | 20 kB 00:00
(26/159): perl-PathTools-3.74-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 90 kB 00:00
(27/159): perl-Pod-Perldoc-3.28-396.el8.noarch. 1.2 MB/s | 88 kB 00:00
(28/159): perl-Pod-Simple-3.35-395.el8.noarch.r 2.2 MB/s | 213 kB 00:00
(29/159): perl-Pod-Usage-1.69-395.el8.noarch.rp 499 kB/s | 34 kB 00:00
(30/159): perl-Scalar-List-Utils-1.49-2.el8.x86 947 kB/s | 68 kB 00:00
(31/159): perl-Socket-2.027-3.el8.x86_64.rpm 864 kB/s | 59 kB 00:00
(32/159): perl-Storable-3.11-3.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 98 kB 00:00
(33/159): perl-Term-ANSIColor-4.06-396.el8.noar 677 kB/s | 46 kB 00:00
(34/159): perl-Term-Cap-1.17-395.el8.noarch.rpm 321 kB/s | 23 kB 00:00
(35/159): perl-Text-Diff-1.45-2.el8.noarch.rpm 596 kB/s | 45 kB 00:00
(36/159): perl-Text-ParseWords-3.30-395.el8.noa 257 kB/s | 18 kB 00:00
(37/159): perl-Text-Tabs+Wrap-2013.0523-395.el8 351 kB/s | 24 kB 00:00
(38/159): perl-Time-Local-1.280-1.el8.noarch.rp 440 kB/s | 33 kB 00:00
(39/159): perl-URI-1.73-3.el8.noarch.rpm 1.6 MB/s | 116 kB 00:00
(40/159): perl-Unicode-Normalize-1.25-396.el8.x 1.1 MB/s | 82 kB 00:00
(41/159): perl-constant-1.33-396.el8.noarch.rpm 395 kB/s | 25 kB 00:00
(42/159): perl-libnet-3.11-3.el8.noarch.rpm 1.8 MB/s | 121 kB 00:00
(43/159): perl-libs-5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64.rpm 13 MB/s | 1.6 MB 00:00
(44/159): perl-macros-5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.1 MB/s | 72 kB 00:00
(45/159): perl-parent-0.237-1.el8.noarch.rpm 279 kB/s | 20 kB 00:00
(46/159): perl-podlators-4.11-1.el8.noarch.rpm 1.3 MB/s | 118 kB 00:00
(47/159): perl-interpreter-5.26.3-422.el8.x86_6 14 MB/s | 6.3 MB 00:00
(48/159): glibc-gconv-extra-2.28-225.0.3.el8.x8 601 kB/s | 1.5 MB 00:02
(49/159): perl-threads-2.21-2.el8.x86_64.rpm 876 kB/s | 61 kB 00:00
(50/159): perl-threads-shared-1.58-2.el8.x86_64 657 kB/s | 48 kB 00:00
(51/159): python3-pyparsing-2.1.10-7.el8.noarch 2.0 MB/s | 142 kB 00:00
(52/159): zip-3.0-23.el8.x86_64.rpm 3.7 MB/s | 270 kB 00:00
(53/159): dwz-0.12-10.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.6 MB/s | 109 kB 00:00
(54/159): efi-srpm-macros-3-3.0.1.el8.noarch.rp 350 kB/s | 22 kB 00:00
(55/159): ghc-srpm-macros-1.4.2-7.el8.noarch.rp 125 kB/s | 9.3 kB 00:00
(56/159): go-srpm-macros-2-17.el8.noarch.rpm 198 kB/s | 13 kB 00:00
(57/159): ocaml-srpm-macros-5-4.el8.noarch.rpm 154 kB/s | 9.3 kB 00:00
(58/159): openblas-srpm-macros-2-2.el8.noarch.r 116 kB/s | 7.9 kB 00:00
(59/159): perl-5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64.rpm 921 kB/s | 73 kB 00:00
(60/159): perl-Archive-Zip-1.60-3.el8.noarch.rp 1.4 MB/s | 108 kB 00:00
(61/159): perl-Attribute-Handlers-0.99-422.el8. 1.2 MB/s | 89 kB 00:00
(62/159): perl-B-Debug-1.26-2.el8.noarch.rpm 356 kB/s | 26 kB 00:00
(63/159): perl-CPAN-2.18-397.el8.noarch.rpm 5.3 MB/s | 554 kB 00:00
(64/159): perl-CPAN-Meta-2.150010-396.el8.noarc 2.3 MB/s | 191 kB 00:00
(65/159): perl-CPAN-Meta-Requirements-2.140-396 512 kB/s | 37 kB 00:00
(66/159): perl-CPAN-Meta-YAML-0.018-397.el8.noa 508 kB/s | 34 kB 00:00
(67/159): perl-Compress-Bzip2-2.26-6.el8.x86_64 990 kB/s | 72 kB 00:00
(68/159): perl-Config-Perl-V-0.30-1.el8.noarch. 337 kB/s | 22 kB 00:00
(69/159): perl-DB_File-1.842-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 83 kB 00:00
(70/159): perl-Data-OptList-0.110-6.el8.noarch. 457 kB/s | 31 kB 00:00
(71/159): perl-Data-Section-0.200007-3.el8.noar 423 kB/s | 30 kB 00:00
(72/159): perl-Devel-PPPort-3.36-5.el8.x86_64.r 1.6 MB/s | 118 kB 00:00
(73/159): perl-Devel-Peek-1.26-422.el8.x86_64.r 960 kB/s | 94 kB 00:00
(74/159): perl-Devel-SelfStubber-1.06-422.el8.n 831 kB/s | 76 kB 00:00
(75/159): perl-Devel-Size-0.81-2.el8.x86_64.rpm 510 kB/s | 34 kB 00:00
(76/159): perl-Digest-SHA-6.02-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 859 kB/s | 66 kB 00:00
(77/159): perl-Encode-Locale-1.05-10.module+el8 285 kB/s | 22 kB 00:00
(78/159): perl-Encode-devel-2.97-3.el8.x86_64.r 510 kB/s | 39 kB 00:00
(79/159): perl-Env-1.04-395.el8.noarch.rpm 321 kB/s | 21 kB 00:00
(80/159): perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder-0.280230-2.el8 730 kB/s | 48 kB 00:00
(81/159): perl-ExtUtils-Command-7.34-1.el8.noar 248 kB/s | 19 kB 00:00
(82/159): perl-ExtUtils-Embed-1.34-422.el8.noar 1.1 MB/s | 79 kB 00:00
(83/159): perl-ExtUtils-Install-2.14-4.el8.noar 661 kB/s | 46 kB 00:00
(84/159): perl-ExtUtils-MM-Utils-7.34-1.el8.noa 243 kB/s | 16 kB 00:00
(85/159): perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker-7.34-1.el8.no 4.0 MB/s | 300 kB 00:00
(86/159): perl-ExtUtils-Manifest-1.70-395.el8.n 500 kB/s | 36 kB 00:00
(87/159): perl-ExtUtils-Miniperl-1.06-422.el8.n 1.1 MB/s | 77 kB 00:00
(88/159): perl-File-HomeDir-1.002-4.el8.noarch. 980 kB/s | 61 kB 00:00
(89/159): perl-File-Fetch-0.56-2.el8.noarch.rpm 483 kB/s | 33 kB 00:00
(90/159): perl-ExtUtils-ParseXS-3.35-2.el8.noar 1.1 MB/s | 83 kB 00:00
(91/159): perl-Filter-Simple-0.94-2.el8.noarch. 417 kB/s | 29 kB 00:00
(92/159): perl-File-Which-1.22-2.el8.noarch.rpm 312 kB/s | 23 kB 00:00
(93/159): perl-Filter-1.58-2.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.1 MB/s | 82 kB 00:00
(94/159): perl-IO-Socket-SSL-2.066-4.module+el8 3.6 MB/s | 298 kB 00:00
(95/159): perl-IPC-Cmd-1.02-1.el8.noarch.rpm 545 kB/s | 43 kB 00:00
(96/159): perl-IPC-SysV-2.07-397.el8.x86_64.rpm 544 kB/s | 43 kB 00:00
(97/159): perl-IPC-System-Simple-1.25-17.el8.no 535 kB/s | 43 kB 00:00
(98/159): perl-JSON-PP-2.97.001-3.el8.noarch.rp 853 kB/s | 68 kB 00:00
(99/159): perl-Locale-Codes-3.57-1.el8.noarch.r 3.7 MB/s | 310 kB 00:00
(100/159): perl-MRO-Compat-0.13-4.el8.noarch.rp 399 kB/s | 24 kB 00:00
(101/159): perl-Locale-Maketext-1.28-396.el8.no 1.4 MB/s | 99 kB 00:00
(102/159): perl-Locale-Maketext-Simple-0.21-422 1.1 MB/s | 79 kB 00:00
(103/159): perl-Math-BigInt-FastCalc-0.500.600- 371 kB/s | 27 kB 00:00
(104/159): perl-Math-BigRat-0.2614-1.el8.noarch 560 kB/s | 40 kB 00:00
(105/159): perl-Memoize-1.03-422.el8.noarch.rpm 1.6 MB/s | 119 kB 00:00
(106/159): perl-Module-Build-0.42.24-5.el8.noar 3.4 MB/s | 273 kB 00:00
(107/159): perl-Module-CoreList-tools-5.2018113 297 kB/s | 22 kB 00:00
(108/159): perl-Module-CoreList-5.20181130-1.el 1.1 MB/s | 87 kB 00:00
(109/159): perl-Module-Load-0.32-395.el8.noarch 242 kB/s | 19 kB 00:00
(110/159): perl-Module-Load-Conditional-0.68-39 316 kB/s | 24 kB 00:00
(111/159): perl-Module-Loaded-0.08-422.el8.noar 972 kB/s | 75 kB 00:00
(112/159): perl-Module-Metadata-1.000033-395.el 664 kB/s | 44 kB 00:00
(113/159): perl-Mozilla-CA-20160104-7.0.1.modul 229 kB/s | 15 kB 00:00
(114/159): perl-Net-Ping-2.55-422.el8.noarch.rp 1.5 MB/s | 102 kB 00:00
(115/159): perl-Package-Generator-1.106-11.el8. 386 kB/s | 27 kB 00:00
(116/159): perl-Params-Check-0.38-395.el8.noarc 333 kB/s | 24 kB 00:00
(117/159): perl-Net-SSLeay-1.88-2.module+el8.6. 4.4 MB/s | 379 kB 00:00
(118/159): perl-Perl-OSType-1.010-396.el8.noarc 459 kB/s | 29 kB 00:00
(119/159): perl-Params-Util-1.07-22.el8.x86_64. 656 kB/s | 44 kB 00:00
(120/159): perl-PerlIO-via-QuotedPrint-0.08-395 206 kB/s | 13 kB 00:00
(121/159): perl-Pod-Checker-1.73-395.el8.noarch 449 kB/s | 33 kB 00:00
(122/159): perl-Pod-Parser-1.63-396.el8.noarch. 1.6 MB/s | 108 kB 00:00
(123/159): perl-Pod-Html-1.22.02-422.el8.noarch 1.1 MB/s | 88 kB 00:00
(124/159): perl-SelfLoader-1.23-422.el8.noarch. 1.1 MB/s | 83 kB 00:00
(125/159): perl-Software-License-0.103013-2.el8 1.8 MB/s | 137 kB 00:00
(126/159): perl-Sub-Exporter-0.987-15.el8.noarc 1.0 MB/s | 73 kB 00:00
(127/159): perl-Sub-Install-0.928-14.el8.noarch 383 kB/s | 27 kB 00:00
(128/159): perl-Sys-Syslog-0.35-397.el8.x86_64. 734 kB/s | 50 kB 00:00
(129/159): perl-TermReadKey-2.37-7.el8.x86_64.r 536 kB/s | 40 kB 00:00
(130/159): perl-Test-1.30-422.el8.noarch.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 90 kB 00:00
(131/159): perl-Test-Harness-3.42-1.el8.noarch. 3.4 MB/s | 279 kB 00:00
(132/159): perl-Test-Simple-1.302135-1.el8.noar 5.2 MB/s | 516 kB 00:00
(133/159): perl-Text-Glob-0.11-4.el8.noarch.rpm 272 kB/s | 17 kB 00:00
(134/159): perl-Text-Balanced-2.03-395.el8.noar 807 kB/s | 58 kB 00:00
(135/159): perl-Text-Template-1.51-1.el8.noarch 841 kB/s | 64 kB 00:00
(136/159): perl-Time-HiRes-1.9758-2.el8.x86_64. 855 kB/s | 61 kB 00:00
(137/159): perl-Thread-Queue-3.13-1.el8.noarch. 319 kB/s | 24 kB 00:00
(138/159): perl-Time-Piece-1.31-422.el8.x86_64. 1.3 MB/s | 98 kB 00:00
(139/159): perl-autodie-2.29-396.el8.noarch.rpm 1.3 MB/s | 98 kB 00:00
(140/159): perl-Unicode-Collate-1.25-2.el8.x86_ 7.2 MB/s | 686 kB 00:00
(141/159): perl-bignum-0.49-2.el8.noarch.rpm 620 kB/s | 43 kB 00:00
(142/159): perl-encoding-2.22-3.el8.x86_64.rpm 934 kB/s | 68 kB 00:00
(143/159): perl-devel-5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64.rpm 6.5 MB/s | 600 kB 00:00
(144/159): perl-experimental-0.019-2.el8.noarch 327 kB/s | 24 kB 00:00
(145/159): perl-inc-latest-0.500-9.el8.noarch.r 331 kB/s | 25 kB 00:00
(146/159): perl-libnetcfg-5.26.3-422.el8.noarch 1.0 MB/s | 78 kB 00:00
(147/159): perl-local-lib-2.000024-2.el8.noarch 1.1 MB/s | 74 kB 00:00
(148/159): perl-srpm-macros-1-25.el8.noarch.rpm 157 kB/s | 11 kB 00:00
(149/159): perl-open-1.11-422.el8.noarch.rpm 1.0 MB/s | 78 kB 00:00
(150/159): perl-perlfaq-5.20180605-1.el8.noarch 4.7 MB/s | 386 kB 00:00
(151/159): perl-version-0.99.24-1.el8.x86_64.rp 1.0 MB/s | 67 kB 00:00
(152/159): perl-utils-5.26.3-422.el8.noarch.rpm 1.7 MB/s | 129 kB 00:00
(153/159): python-rpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch.rp 219 kB/s | 16 kB 00:00
(154/159): python3-rpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch.r 243 kB/s | 15 kB 00:00
(155/159): python-srpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch.r 239 kB/s | 16 kB 00:00
(156/159): qt5-srpm-macros-5.15.3-1.el8.noarch. 132 kB/s | 11 kB 00:00
(157/159): rust-srpm-macros-5-2.el8.noarch.rpm 128 kB/s | 9.2 kB 00:00
(158/159): redhat-rpm-config-131-1.0.1.el8.noar 1.2 MB/s | 91 kB 00:00
(159/159): systemtap-sdt-devel-4.9-3.0.1.el8.x8 1.2 MB/s | 88 kB 00:00
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 4.6 MB/s | 25 MB 00:05
Running transaction check
Transaction check succeeded.
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded.
Running transaction
Preparing : 1/1
Installing : python-srpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch 1/159
Installing : python-rpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch 2/159
Installing : python3-rpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch 3/159
Installing : rust-srpm-macros-5-2.el8.noarch 4/159
Installing : qt5-srpm-macros-5.15.3-1.el8.noarch 5/159
Installing : perl-srpm-macros-1-25.el8.noarch 6/159
Installing : openblas-srpm-macros-2-2.el8.noarch 7/159
Installing : ocaml-srpm-macros-5-4.el8.noarch 8/159
Installing : go-srpm-macros-2-17.el8.noarch 9/159
Installing : ghc-srpm-macros-1.4.2-7.el8.noarch 10/159
Installing : efi-srpm-macros-3-3.0.1.el8.noarch 11/159
Installing : dwz-0.12-10.el8.x86_64 12/159
Installing : zip-3.0-23.el8.x86_64 13/159
Installing : python3-pyparsing-2.1.10-7.el8.noarch 14/159
Installing : systemtap-sdt-devel-4.9-3.0.1.el8.x86_64 15/159
Installing : groff-base-1.22.3-18.el8.x86_64 16/159
Installing : perl-Digest-1.17-395.el8.noarch 17/159
Installing : perl-Digest-MD5-2.55-396.el8.x86_64 18/159
Installing : perl-Data-Dumper-2.167-399.el8.x86_64 19/159
Installing : perl-libnet-3.11-3.el8.noarch 20/159
Installing : perl-URI-1.73-3.el8.noarch 21/159
Installing : perl-Pod-Escapes-1:1.07-395.el8.noarch 22/159
Installing : perl-IO-Socket-IP-0.39-5.el8.noarch 23/159
Installing : perl-Time-Local-1:1.280-1.el8.noarch 24/159
Installing : perl-Mozilla-CA-20160104-7.0.1.module+el8.3.0+21 25/159
Installing : perl-IO-Socket-SSL-2.066-4.module+el8.6.0+20623+ 26/159
Installing : perl-Net-SSLeay-1.88-2.module+el8.6.0+20623+f089 27/159
Installing : perl-Term-ANSIColor-4.06-396.el8.noarch 28/159
Installing : perl-Term-Cap-1.17-395.el8.noarch 29/159
Installing : perl-File-Temp-0.230.600-1.el8.noarch 30/159
Installing : perl-HTTP-Tiny-0.074-2.el8.noarch 31/159
Installing : perl-Pod-Simple-1:3.35-395.el8.noarch 32/159
Installing : perl-podlators-4.11-1.el8.noarch 33/159
Installing : perl-Pod-Perldoc-3.28-396.el8.noarch 34/159
Installing : perl-Text-ParseWords-3.30-395.el8.noarch 35/159
Installing : perl-Pod-Usage-4:1.69-395.el8.noarch 36/159
Installing : perl-MIME-Base64-3.15-396.el8.x86_64 37/159
Installing : perl-Storable-1:3.11-3.el8.x86_64 38/159
Installing : perl-Getopt-Long-1:2.50-4.el8.noarch 39/159
Installing : perl-Errno-1.28-422.el8.x86_64 40/159
Installing : perl-Socket-4:2.027-3.el8.x86_64 41/159
Installing : perl-Encode-4:2.97-3.el8.x86_64 42/159
Installing : perl-Carp-1.42-396.el8.noarch 43/159
Installing : perl-Exporter-5.72-396.el8.noarch 44/159
Installing : perl-libs-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 45/159
Installing : perl-Scalar-List-Utils-3:1.49-2.el8.x86_64 46/159
Installing : perl-parent-1:0.237-1.el8.noarch 47/159
Installing : perl-macros-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 48/159
Installing : perl-Text-Tabs+Wrap-2013.0523-395.el8.noarch 49/159
Installing : perl-Unicode-Normalize-1.25-396.el8.x86_64 50/159
Installing : perl-File-Path-2.15-2.el8.noarch 51/159
Installing : perl-IO-1.38-422.el8.x86_64 52/159
Installing : perl-PathTools-3.74-1.el8.x86_64 53/159
Installing : perl-constant-1.33-396.el8.noarch 54/159
Installing : perl-threads-1:2.21-2.el8.x86_64 55/159
Installing : perl-threads-shared-1.58-2.el8.x86_64 56/159
Installing : perl-interpreter-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 57/159
Installing : perl-version-6:0.99.24-1.el8.x86_64 58/159
Installing : perl-Time-HiRes-4:1.9758-2.el8.x86_64 59/159
Installing : perl-CPAN-Meta-Requirements-2.140-396.el8.noarch 60/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-Manifest-1.70-395.el8.noarch 61/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-ParseXS-1:3.35-2.el8.noarch 62/159
Installing : perl-Test-Harness-1:3.42-1.el8.noarch 63/159
Installing : perl-Module-CoreList-1:5.20181130-1.el8.noarch 64/159
Installing : perl-Module-Metadata-1.000033-395.el8.noarch 65/159
Installing : perl-Compress-Raw-Zlib-2.081-1.el8.x86_64 66/159
Installing : perl-Filter-2:1.58-2.el8.x86_64 67/159
Installing : perl-SelfLoader-1.23-422.el8.noarch 68/159
Installing : perl-Module-Load-1:0.32-395.el8.noarch 69/159
Installing : perl-Perl-OSType-1.010-396.el8.noarch 70/159
Installing : perl-Text-Balanced-2.03-395.el8.noarch 71/159
Installing : perl-encoding-4:2.22-3.el8.x86_64 72/159
Installing : perl-Net-Ping-2.55-422.el8.noarch 73/159
Installing : perl-Compress-Raw-Bzip2-2.081-1.el8.x86_64 74/159
Installing : perl-IO-Compress-2.081-1.el8.noarch 75/159
Installing : perl-IO-Zlib-1:1.10-422.el8.noarch 76/159
Installing : perl-Math-Complex-1.59-422.el8.noarch 77/159
Installing : perl-Math-BigInt-1:1.9998.11-7.el8.noarch 78/159
Installing : perl-JSON-PP-1:2.97.001-3.el8.noarch 79/159
Installing : perl-Math-BigRat-0.2614-1.el8.noarch 80/159
Installing : perl-CPAN-Meta-YAML-0.018-397.el8.noarch 81/159
Installing : perl-CPAN-Meta-2.150010-396.el8.noarch 82/159
Installing : perl-Digest-SHA-1:6.02-1.el8.x86_64 83/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-Command-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch 84/159
Installing : perl-Locale-Maketext-1.28-396.el8.noarch 85/159
Installing : perl-Locale-Maketext-Simple-1:0.21-422.el8.noarc 86/159
Installing : perl-Params-Check-1:0.38-395.el8.noarch 87/159
Installing : perl-Module-Load-Conditional-0.68-395.el8.noarch 88/159
Installing : perl-Params-Util-1.07-22.el8.x86_64 89/159
Installing : perl-Pod-Html-1.22.02-422.el8.noarch 90/159
Installing : perl-Sub-Install-0.928-14.el8.noarch 91/159
Installing : perl-Data-OptList-0.110-6.el8.noarch 92/159
Installing : perl-bignum-0.49-2.el8.noarch 93/159
Installing : perl-Math-BigInt-FastCalc-0.500.600-6.el8.x86_64 94/159
Installing : perl-open-1.11-422.el8.noarch 95/159
Installing : perl-Filter-Simple-0.94-2.el8.noarch 96/159
Installing : perl-Devel-SelfStubber-1.06-422.el8.noarch 97/159
Installing : perl-Archive-Zip-1.60-3.el8.noarch 98/159
Installing : perl-Module-CoreList-tools-1:5.20181130-1.el8.no 99/159
Installing : perl-experimental-0.019-2.el8.noarch 100/159
Installing : perl-Algorithm-Diff-1.1903-9.el8.noarch 101/159
Installing : perl-Text-Diff-1.45-2.el8.noarch 102/159
Installing : perl-Archive-Tar-2.30-1.el8.noarch 103/159
Installing : perl-Attribute-Handlers-0.99-422.el8.noarch 104/159
Installing : perl-B-Debug-1.26-2.el8.noarch 105/159
Installing : perl-Compress-Bzip2-2.26-6.el8.x86_64 106/159
Installing : perl-Config-Perl-V-0.30-1.el8.noarch 107/159
Installing : perl-DB_File-1.842-1.el8.x86_64 108/159
Installing : perl-Devel-PPPort-3.36-5.el8.x86_64 109/159
Installing : perl-Devel-Size-0.81-2.el8.x86_64 110/159
Installing : perl-Encode-Locale-1.05-10.module+el8.3.0+7692+5 111/159
Installing : perl-Env-1.04-395.el8.noarch 112/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-MM-Utils-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch 113/159
Installing : perl-IPC-Cmd-2:1.02-1.el8.noarch 114/159
Installing : perl-File-Fetch-0.56-2.el8.noarch 115/159
Installing : perl-IPC-SysV-2.07-397.el8.x86_64 116/159
Installing : perl-IPC-System-Simple-1.25-17.el8.noarch 117/159
Installing : perl-autodie-2.29-396.el8.noarch 118/159
Installing : perl-Locale-Codes-3.57-1.el8.noarch 119/159
Installing : perl-Memoize-1.03-422.el8.noarch 120/159
Installing : perl-Module-Loaded-1:0.08-422.el8.noarch 121/159
Installing : perl-Package-Generator-1.106-11.el8.noarch 122/159
Installing : perl-Sub-Exporter-0.987-15.el8.noarch 123/159
Installing : perl-Pod-Checker-4:1.73-395.el8.noarch 124/159
Installing : perl-Pod-Parser-1.63-396.el8.noarch 125/159
Installing : perl-Sys-Syslog-0.35-397.el8.x86_64 126/159
Installing : perl-TermReadKey-2.37-7.el8.x86_64 127/159
Installing : perl-Test-1.30-422.el8.noarch 128/159
Installing : perl-Test-Simple-1:1.302135-1.el8.noarch 129/159
Installing : perl-Text-Glob-0.11-4.el8.noarch 130/159
Installing : perl-Text-Template-1.51-1.el8.noarch 131/159
Installing : perl-Time-Piece-1.31-422.el8.x86_64 132/159
Installing : perl-Unicode-Collate-1.25-2.el8.x86_64 133/159
Installing : perl-local-lib-2.000024-2.el8.noarch 134/159
Installing : perl-utils-5.26.3-422.el8.noarch 135/159
Installing : perl-Thread-Queue-3.13-1.el8.noarch 136/159
Installing : perl-File-Which-1.22-2.el8.noarch 137/159
Installing : perl-File-HomeDir-1.002-4.el8.noarch 138/159
Installing : perl-Devel-Peek-1.26-422.el8.x86_64 139/159
Installing : perl-MRO-Compat-0.13-4.el8.noarch 140/159
Installing : perl-Data-Section-0.200007-3.el8.noarch 141/159
Installing : perl-Software-License-0.103013-2.el8.noarch 142/159
Installing : perl-PerlIO-via-QuotedPrint-0.08-395.el8.noarch 143/159
Installing : perl-perlfaq-5.20180605-1.el8.noarch 144/159
Installing : glibc-gconv-extra-2.28-225.0.3.el8.x86_64 145/159
Running scriptlet: glibc-gconv-extra-2.28-225.0.3.el8.x86_64 145/159
Installing : file-5.33-24.el8.x86_64 146/159
Installing : redhat-rpm-config-131-1.0.1.el8.noarch 147/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-Install-2.14-4.el8.noarch 148/159
Installing : perl-devel-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 149/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch 150/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder-1:0.280230-2.el8.noarch 151/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-Embed-1.34-422.el8.noarch 152/159
Installing : perl-ExtUtils-Miniperl-1.06-422.el8.noarch 153/159
Installing : perl-libnetcfg-4:5.26.3-422.el8.noarch 154/159
Installing : perl-Encode-devel-4:2.97-3.el8.x86_64 155/159
Installing : perl-inc-latest-2:0.500-9.el8.noarch 156/159
Installing : perl-Module-Build-2:0.42.24-5.el8.noarch 157/159
Installing : perl-CPAN-2.18-397.el8.noarch 158/159
Installing : perl-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 159/159
Running scriptlet: perl-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 159/159
Verifying : file-5.33-24.el8.x86_64 1/159
Verifying : glibc-gconv-extra-2.28-225.0.3.el8.x86_64 2/159
Verifying : groff-base-1.22.3-18.el8.x86_64 3/159
Verifying : perl-Algorithm-Diff-1.1903-9.el8.noarch 4/159
Verifying : perl-Archive-Tar-2.30-1.el8.noarch 5/159
Verifying : perl-Carp-1.42-396.el8.noarch 6/159
Verifying : perl-Compress-Raw-Bzip2-2.081-1.el8.x86_64 7/159
Verifying : perl-Compress-Raw-Zlib-2.081-1.el8.x86_64 8/159
Verifying : perl-Data-Dumper-2.167-399.el8.x86_64 9/159
Verifying : perl-Digest-1.17-395.el8.noarch 10/159
Verifying : perl-Digest-MD5-2.55-396.el8.x86_64 11/159
Verifying : perl-Encode-4:2.97-3.el8.x86_64 12/159
Verifying : perl-Errno-1.28-422.el8.x86_64 13/159
Verifying : perl-Exporter-5.72-396.el8.noarch 14/159
Verifying : perl-File-Path-2.15-2.el8.noarch 15/159
Verifying : perl-File-Temp-0.230.600-1.el8.noarch 16/159
Verifying : perl-Getopt-Long-1:2.50-4.el8.noarch 17/159
Verifying : perl-HTTP-Tiny-0.074-2.el8.noarch 18/159
Verifying : perl-IO-1.38-422.el8.x86_64 19/159
Verifying : perl-IO-Compress-2.081-1.el8.noarch 20/159
Verifying : perl-IO-Socket-IP-0.39-5.el8.noarch 21/159
Verifying : perl-IO-Zlib-1:1.10-422.el8.noarch 22/159
Verifying : perl-MIME-Base64-3.15-396.el8.x86_64 23/159
Verifying : perl-Math-BigInt-1:1.9998.11-7.el8.noarch 24/159
Verifying : perl-Math-Complex-1.59-422.el8.noarch 25/159
Verifying : perl-PathTools-3.74-1.el8.x86_64 26/159
Verifying : perl-Pod-Escapes-1:1.07-395.el8.noarch 27/159
Verifying : perl-Pod-Perldoc-3.28-396.el8.noarch 28/159
Verifying : perl-Pod-Simple-1:3.35-395.el8.noarch 29/159
Verifying : perl-Pod-Usage-4:1.69-395.el8.noarch 30/159
Verifying : perl-Scalar-List-Utils-3:1.49-2.el8.x86_64 31/159
Verifying : perl-Socket-4:2.027-3.el8.x86_64 32/159
Verifying : perl-Storable-1:3.11-3.el8.x86_64 33/159
Verifying : perl-Term-ANSIColor-4.06-396.el8.noarch 34/159
Verifying : perl-Term-Cap-1.17-395.el8.noarch 35/159
Verifying : perl-Text-Diff-1.45-2.el8.noarch 36/159
Verifying : perl-Text-ParseWords-3.30-395.el8.noarch 37/159
Verifying : perl-Text-Tabs+Wrap-2013.0523-395.el8.noarch 38/159
Verifying : perl-Time-Local-1:1.280-1.el8.noarch 39/159
Verifying : perl-URI-1.73-3.el8.noarch 40/159
Verifying : perl-Unicode-Normalize-1.25-396.el8.x86_64 41/159
Verifying : perl-constant-1.33-396.el8.noarch 42/159
Verifying : perl-interpreter-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 43/159
Verifying : perl-libnet-3.11-3.el8.noarch 44/159
Verifying : perl-libs-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 45/159
Verifying : perl-macros-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 46/159
Verifying : perl-parent-1:0.237-1.el8.noarch 47/159
Verifying : perl-podlators-4.11-1.el8.noarch 48/159
Verifying : perl-threads-1:2.21-2.el8.x86_64 49/159
Verifying : perl-threads-shared-1.58-2.el8.x86_64 50/159
Verifying : python3-pyparsing-2.1.10-7.el8.noarch 51/159
Verifying : zip-3.0-23.el8.x86_64 52/159
Verifying : dwz-0.12-10.el8.x86_64 53/159
Verifying : efi-srpm-macros-3-3.0.1.el8.noarch 54/159
Verifying : ghc-srpm-macros-1.4.2-7.el8.noarch 55/159
Verifying : go-srpm-macros-2-17.el8.noarch 56/159
Verifying : ocaml-srpm-macros-5-4.el8.noarch 57/159
Verifying : openblas-srpm-macros-2-2.el8.noarch 58/159
Verifying : perl-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 59/159
Verifying : perl-Archive-Zip-1.60-3.el8.noarch 60/159
Verifying : perl-Attribute-Handlers-0.99-422.el8.noarch 61/159
Verifying : perl-B-Debug-1.26-2.el8.noarch 62/159
Verifying : perl-CPAN-2.18-397.el8.noarch 63/159
Verifying : perl-CPAN-Meta-2.150010-396.el8.noarch 64/159
Verifying : perl-CPAN-Meta-Requirements-2.140-396.el8.noarch 65/159
Verifying : perl-CPAN-Meta-YAML-0.018-397.el8.noarch 66/159
Verifying : perl-Compress-Bzip2-2.26-6.el8.x86_64 67/159
Verifying : perl-Config-Perl-V-0.30-1.el8.noarch 68/159
Verifying : perl-DB_File-1.842-1.el8.x86_64 69/159
Verifying : perl-Data-OptList-0.110-6.el8.noarch 70/159
Verifying : perl-Data-Section-0.200007-3.el8.noarch 71/159
Verifying : perl-Devel-PPPort-3.36-5.el8.x86_64 72/159
Verifying : perl-Devel-Peek-1.26-422.el8.x86_64 73/159
Verifying : perl-Devel-SelfStubber-1.06-422.el8.noarch 74/159
Verifying : perl-Devel-Size-0.81-2.el8.x86_64 75/159
Verifying : perl-Digest-SHA-1:6.02-1.el8.x86_64 76/159
Verifying : perl-Encode-Locale-1.05-10.module+el8.3.0+7692+5 77/159
Verifying : perl-Encode-devel-4:2.97-3.el8.x86_64 78/159
Verifying : perl-Env-1.04-395.el8.noarch 79/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder-1:0.280230-2.el8.noarch 80/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-Command-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch 81/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-Embed-1.34-422.el8.noarch 82/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-Install-2.14-4.el8.noarch 83/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-MM-Utils-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch 84/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch 85/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-Manifest-1.70-395.el8.noarch 86/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-Miniperl-1.06-422.el8.noarch 87/159
Verifying : perl-ExtUtils-ParseXS-1:3.35-2.el8.noarch 88/159
Verifying : perl-File-Fetch-0.56-2.el8.noarch 89/159
Verifying : perl-File-HomeDir-1.002-4.el8.noarch 90/159
Verifying : perl-File-Which-1.22-2.el8.noarch 91/159
Verifying : perl-Filter-2:1.58-2.el8.x86_64 92/159
Verifying : perl-Filter-Simple-0.94-2.el8.noarch 93/159
Verifying : perl-IO-Socket-SSL-2.066-4.module+el8.6.0+20623+ 94/159
Verifying : perl-IPC-Cmd-2:1.02-1.el8.noarch 95/159
Verifying : perl-IPC-SysV-2.07-397.el8.x86_64 96/159
Verifying : perl-IPC-System-Simple-1.25-17.el8.noarch 97/159
Verifying : perl-JSON-PP-1:2.97.001-3.el8.noarch 98/159
Verifying : perl-Locale-Codes-3.57-1.el8.noarch 99/159
Verifying : perl-Locale-Maketext-1.28-396.el8.noarch 100/159
Verifying : perl-Locale-Maketext-Simple-1:0.21-422.el8.noarc 101/159
Verifying : perl-MRO-Compat-0.13-4.el8.noarch 102/159
Verifying : perl-Math-BigInt-FastCalc-0.500.600-6.el8.x86_64 103/159
Verifying : perl-Math-BigRat-0.2614-1.el8.noarch 104/159
Verifying : perl-Memoize-1.03-422.el8.noarch 105/159
Verifying : perl-Module-Build-2:0.42.24-5.el8.noarch 106/159
Verifying : perl-Module-CoreList-1:5.20181130-1.el8.noarch 107/159
Verifying : perl-Module-CoreList-tools-1:5.20181130-1.el8.no 108/159
Verifying : perl-Module-Load-1:0.32-395.el8.noarch 109/159
Verifying : perl-Module-Load-Conditional-0.68-395.el8.noarch 110/159
Verifying : perl-Module-Loaded-1:0.08-422.el8.noarch 111/159
Verifying : perl-Module-Metadata-1.000033-395.el8.noarch 112/159
Verifying : perl-Mozilla-CA-20160104-7.0.1.module+el8.3.0+21 113/159
Verifying : perl-Net-Ping-2.55-422.el8.noarch 114/159
Verifying : perl-Net-SSLeay-1.88-2.module+el8.6.0+20623+f089 115/159
Verifying : perl-Package-Generator-1.106-11.el8.noarch 116/159
Verifying : perl-Params-Check-1:0.38-395.el8.noarch 117/159
Verifying : perl-Params-Util-1.07-22.el8.x86_64 118/159
Verifying : perl-Perl-OSType-1.010-396.el8.noarch 119/159
Verifying : perl-PerlIO-via-QuotedPrint-0.08-395.el8.noarch 120/159
Verifying : perl-Pod-Checker-4:1.73-395.el8.noarch 121/159
Verifying : perl-Pod-Html-1.22.02-422.el8.noarch 122/159
Verifying : perl-Pod-Parser-1.63-396.el8.noarch 123/159
Verifying : perl-SelfLoader-1.23-422.el8.noarch 124/159
Verifying : perl-Software-License-0.103013-2.el8.noarch 125/159
Verifying : perl-Sub-Exporter-0.987-15.el8.noarch 126/159
Verifying : perl-Sub-Install-0.928-14.el8.noarch 127/159
Verifying : perl-Sys-Syslog-0.35-397.el8.x86_64 128/159
Verifying : perl-TermReadKey-2.37-7.el8.x86_64 129/159
Verifying : perl-Test-1.30-422.el8.noarch 130/159
Verifying : perl-Test-Harness-1:3.42-1.el8.noarch 131/159
Verifying : perl-Test-Simple-1:1.302135-1.el8.noarch 132/159
Verifying : perl-Text-Balanced-2.03-395.el8.noarch 133/159
Verifying : perl-Text-Glob-0.11-4.el8.noarch 134/159
Verifying : perl-Text-Template-1.51-1.el8.noarch 135/159
Verifying : perl-Thread-Queue-3.13-1.el8.noarch 136/159
Verifying : perl-Time-HiRes-4:1.9758-2.el8.x86_64 137/159
Verifying : perl-Time-Piece-1.31-422.el8.x86_64 138/159
Verifying : perl-Unicode-Collate-1.25-2.el8.x86_64 139/159
Verifying : perl-autodie-2.29-396.el8.noarch 140/159
Verifying : perl-bignum-0.49-2.el8.noarch 141/159
Verifying : perl-devel-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64 142/159
Verifying : perl-encoding-4:2.22-3.el8.x86_64 143/159
Verifying : perl-experimental-0.019-2.el8.noarch 144/159
Verifying : perl-inc-latest-2:0.500-9.el8.noarch 145/159
Verifying : perl-libnetcfg-4:5.26.3-422.el8.noarch 146/159
Verifying : perl-local-lib-2.000024-2.el8.noarch 147/159
Verifying : perl-open-1.11-422.el8.noarch 148/159
Verifying : perl-perlfaq-5.20180605-1.el8.noarch 149/159
Verifying : perl-srpm-macros-1-25.el8.noarch 150/159
Verifying : perl-utils-5.26.3-422.el8.noarch 151/159
Verifying : perl-version-6:0.99.24-1.el8.x86_64 152/159
Verifying : python-rpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch 153/159
Verifying : python-srpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch 154/159
Verifying : python3-rpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch 155/159
Verifying : qt5-srpm-macros-5.15.3-1.el8.noarch 156/159
Verifying : redhat-rpm-config-131-1.0.1.el8.noarch 157/159
Verifying : rust-srpm-macros-5-2.el8.noarch 158/159
Verifying : systemtap-sdt-devel-4.9-3.0.1.el8.x86_64 159/159
Installed:
dwz-0.12-10.el8.x86_64
efi-srpm-macros-3-3.0.1.el8.noarch
file-5.33-24.el8.x86_64
ghc-srpm-macros-1.4.2-7.el8.noarch
glibc-gconv-extra-2.28-225.0.3.el8.x86_64
go-srpm-macros-2-17.el8.noarch
groff-base-1.22.3-18.el8.x86_64
ocaml-srpm-macros-5-4.el8.noarch
openblas-srpm-macros-2-2.el8.noarch
perl-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64
perl-Algorithm-Diff-1.1903-9.el8.noarch
perl-Archive-Tar-2.30-1.el8.noarch
perl-Archive-Zip-1.60-3.el8.noarch
perl-Attribute-Handlers-0.99-422.el8.noarch
perl-B-Debug-1.26-2.el8.noarch
perl-CPAN-2.18-397.el8.noarch
perl-CPAN-Meta-2.150010-396.el8.noarch
perl-CPAN-Meta-Requirements-2.140-396.el8.noarch
perl-CPAN-Meta-YAML-0.018-397.el8.noarch
perl-Carp-1.42-396.el8.noarch
perl-Compress-Bzip2-2.26-6.el8.x86_64
perl-Compress-Raw-Bzip2-2.081-1.el8.x86_64
perl-Compress-Raw-Zlib-2.081-1.el8.x86_64
perl-Config-Perl-V-0.30-1.el8.noarch
perl-DB_File-1.842-1.el8.x86_64
perl-Data-Dumper-2.167-399.el8.x86_64
perl-Data-OptList-0.110-6.el8.noarch
perl-Data-Section-0.200007-3.el8.noarch
perl-Devel-PPPort-3.36-5.el8.x86_64
perl-Devel-Peek-1.26-422.el8.x86_64
perl-Devel-SelfStubber-1.06-422.el8.noarch
perl-Devel-Size-0.81-2.el8.x86_64
perl-Digest-1.17-395.el8.noarch
perl-Digest-MD5-2.55-396.el8.x86_64
perl-Digest-SHA-1:6.02-1.el8.x86_64
perl-Encode-4:2.97-3.el8.x86_64
perl-Encode-Locale-1.05-10.module+el8.3.0+7692+542c56f9.noarch
perl-Encode-devel-4:2.97-3.el8.x86_64
perl-Env-1.04-395.el8.noarch
perl-Errno-1.28-422.el8.x86_64
perl-Exporter-5.72-396.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-CBuilder-1:0.280230-2.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-Command-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-Embed-1.34-422.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-Install-2.14-4.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-MM-Utils-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker-1:7.34-1.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-Manifest-1.70-395.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-Miniperl-1.06-422.el8.noarch
perl-ExtUtils-ParseXS-1:3.35-2.el8.noarch
perl-File-Fetch-0.56-2.el8.noarch
perl-File-HomeDir-1.002-4.el8.noarch
perl-File-Path-2.15-2.el8.noarch
perl-File-Temp-0.230.600-1.el8.noarch
perl-File-Which-1.22-2.el8.noarch
perl-Filter-2:1.58-2.el8.x86_64
perl-Filter-Simple-0.94-2.el8.noarch
perl-Getopt-Long-1:2.50-4.el8.noarch
perl-HTTP-Tiny-0.074-2.el8.noarch
perl-IO-1.38-422.el8.x86_64
perl-IO-Compress-2.081-1.el8.noarch
perl-IO-Socket-IP-0.39-5.el8.noarch
perl-IO-Socket-SSL-2.066-4.module+el8.6.0+20623+f0897f98.noarch
perl-IO-Zlib-1:1.10-422.el8.noarch
perl-IPC-Cmd-2:1.02-1.el8.noarch
perl-IPC-SysV-2.07-397.el8.x86_64
perl-IPC-System-Simple-1.25-17.el8.noarch
perl-JSON-PP-1:2.97.001-3.el8.noarch
perl-Locale-Codes-3.57-1.el8.noarch
perl-Locale-Maketext-1.28-396.el8.noarch
perl-Locale-Maketext-Simple-1:0.21-422.el8.noarch
perl-MIME-Base64-3.15-396.el8.x86_64
perl-MRO-Compat-0.13-4.el8.noarch
perl-Math-BigInt-1:1.9998.11-7.el8.noarch
perl-Math-BigInt-FastCalc-0.500.600-6.el8.x86_64
perl-Math-BigRat-0.2614-1.el8.noarch
perl-Math-Complex-1.59-422.el8.noarch
perl-Memoize-1.03-422.el8.noarch
perl-Module-Build-2:0.42.24-5.el8.noarch
perl-Module-CoreList-1:5.20181130-1.el8.noarch
perl-Module-CoreList-tools-1:5.20181130-1.el8.noarch
perl-Module-Load-1:0.32-395.el8.noarch
perl-Module-Load-Conditional-0.68-395.el8.noarch
perl-Module-Loaded-1:0.08-422.el8.noarch
perl-Module-Metadata-1.000033-395.el8.noarch
perl-Mozilla-CA-20160104-7.0.1.module+el8.3.0+21136+b437fca9.noarch
perl-Net-Ping-2.55-422.el8.noarch
perl-Net-SSLeay-1.88-2.module+el8.6.0+20623+f0897f98.x86_64
perl-Package-Generator-1.106-11.el8.noarch
perl-Params-Check-1:0.38-395.el8.noarch
perl-Params-Util-1.07-22.el8.x86_64
perl-PathTools-3.74-1.el8.x86_64
perl-Perl-OSType-1.010-396.el8.noarch
perl-PerlIO-via-QuotedPrint-0.08-395.el8.noarch
perl-Pod-Checker-4:1.73-395.el8.noarch
perl-Pod-Escapes-1:1.07-395.el8.noarch
perl-Pod-Html-1.22.02-422.el8.noarch
perl-Pod-Parser-1.63-396.el8.noarch
perl-Pod-Perldoc-3.28-396.el8.noarch
perl-Pod-Simple-1:3.35-395.el8.noarch
perl-Pod-Usage-4:1.69-395.el8.noarch
perl-Scalar-List-Utils-3:1.49-2.el8.x86_64
perl-SelfLoader-1.23-422.el8.noarch
perl-Socket-4:2.027-3.el8.x86_64
perl-Software-License-0.103013-2.el8.noarch
perl-Storable-1:3.11-3.el8.x86_64
perl-Sub-Exporter-0.987-15.el8.noarch
perl-Sub-Install-0.928-14.el8.noarch
perl-Sys-Syslog-0.35-397.el8.x86_64
perl-Term-ANSIColor-4.06-396.el8.noarch
perl-Term-Cap-1.17-395.el8.noarch
perl-TermReadKey-2.37-7.el8.x86_64
perl-Test-1.30-422.el8.noarch
perl-Test-Harness-1:3.42-1.el8.noarch
perl-Test-Simple-1:1.302135-1.el8.noarch
perl-Text-Balanced-2.03-395.el8.noarch
perl-Text-Diff-1.45-2.el8.noarch
perl-Text-Glob-0.11-4.el8.noarch
perl-Text-ParseWords-3.30-395.el8.noarch
perl-Text-Tabs+Wrap-2013.0523-395.el8.noarch
perl-Text-Template-1.51-1.el8.noarch
perl-Thread-Queue-3.13-1.el8.noarch
perl-Time-HiRes-4:1.9758-2.el8.x86_64
perl-Time-Local-1:1.280-1.el8.noarch
perl-Time-Piece-1.31-422.el8.x86_64
perl-URI-1.73-3.el8.noarch
perl-Unicode-Collate-1.25-2.el8.x86_64
perl-Unicode-Normalize-1.25-396.el8.x86_64
perl-autodie-2.29-396.el8.noarch
perl-bignum-0.49-2.el8.noarch
perl-constant-1.33-396.el8.noarch
perl-devel-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64
perl-encoding-4:2.22-3.el8.x86_64
perl-experimental-0.019-2.el8.noarch
perl-inc-latest-2:0.500-9.el8.noarch
perl-interpreter-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64
perl-libnet-3.11-3.el8.noarch
perl-libnetcfg-4:5.26.3-422.el8.noarch
perl-libs-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64
perl-local-lib-2.000024-2.el8.noarch
perl-macros-4:5.26.3-422.el8.x86_64
perl-open-1.11-422.el8.noarch
perl-parent-1:0.237-1.el8.noarch
perl-perlfaq-5.20180605-1.el8.noarch
perl-podlators-4.11-1.el8.noarch
perl-srpm-macros-1-25.el8.noarch
perl-threads-1:2.21-2.el8.x86_64
perl-threads-shared-1.58-2.el8.x86_64
perl-utils-5.26.3-422.el8.noarch
perl-version-6:0.99.24-1.el8.x86_64
python-rpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch
python-srpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch
python3-pyparsing-2.1.10-7.el8.noarch
python3-rpm-macros-3-45.el8.noarch
qt5-srpm-macros-5.15.3-1.el8.noarch
redhat-rpm-config-131-1.0.1.el8.noarch
rust-srpm-macros-5-2.el8.noarch
systemtap-sdt-devel-4.9-3.0.1.el8.x86_64
zip-3.0-23.el8.x86_64
Complete! |
I installed the python3 with this command:
dnf install -y python3 |
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 0:31:49 ago on Thu Dec 21 05:18:09 2023.
Dependencies resolved.
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
python36 x86_64 3.6.8-38.module+el8.9.0+90104+968a3e84
ol8_appstream 18 k
Installing dependencies:
platform-python-pip noarch 9.0.3-23.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 1.6 M
python3-pip noarch 9.0.3-23.el8 ol8_appstream 20 k
python3-setuptools noarch 39.2.0-7.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 163 k
Enabling module streams:
python36 3.6
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 4 Packages
Total download size: 1.8 M
Installed size: 7.0 M
Downloading Packages:
(1/4): python3-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch.rpm 61 kB/s | 20 kB 00:00
(2/4): python36-3.6.8-38.module+el8.9.0+90104+9 229 kB/s | 18 kB 00:00
(3/4): python3-setuptools-39.2.0-7.el8.noarch.r 335 kB/s | 163 kB 00:00
(4/4): platform-python-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch. 1.9 MB/s | 1.6 MB 00:00
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 2.2 MB/s | 1.8 MB 00:00
Running transaction check
Transaction check succeeded.
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded.
Running transaction
Preparing : 1/1
Installing : python3-setuptools-39.2.0-7.el8.noarch 1/4
Installing : platform-python-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch 2/4
Installing : python36-3.6.8-38.module+el8.9.0+90104+968a3e84.x86_ 3/4
Running scriptlet: python36-3.6.8-38.module+el8.9.0+90104+968a3e84.x86_ 3/4
Installing : python3-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch 4/4
Running scriptlet: python3-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch 4/4
Verifying : platform-python-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch 1/4
Verifying : python3-setuptools-39.2.0-7.el8.noarch 2/4
Verifying : python3-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch 3/4
Verifying : python36-3.6.8-38.module+el8.9.0+90104+968a3e84.x86_ 4/4
Installed:
platform-python-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch
python3-pip-9.0.3-23.el8.noarch
python3-setuptools-39.2.0-7.el8.noarch
python36-3.6.8-38.module+el8.9.0+90104+968a3e84.x86_64
Complete! |
I installed the git module with this command:
dnf install -y git |
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 0:33:00 ago on Thu Dec 21 05:18:09 2023. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: git x86_64 2.39.3-1.el8_8 ol8_appstream 104 k Installing dependencies: emacs-filesystem noarch 1:26.1-11.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 70 k git-core x86_64 2.39.3-1.el8_8 ol8_appstream 11 M git-core-doc noarch 2.39.3-1.el8_8 ol8_appstream 3.0 M less x86_64 530-1.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 164 k perl-Error noarch 1:0.17025-2.el8 ol8_appstream 46 k perl-Git noarch 2.39.3-1.el8_8 ol8_appstream 79 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 7 Packages Total download size: 14 M Installed size: 45 M Downloading Packages: (1/7): git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64.rpm 233 kB/s | 104 kB 00:00 (2/7): emacs-filesystem-26.1-11.el8.noarch.rpm 155 kB/s | 70 kB 00:00 (3/7): less-530-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 309 kB/s | 164 kB 00:00 (4/7): perl-Error-0.17025-2.el8.noarch.rpm 519 kB/s | 46 kB 00:00 (5/7): perl-Git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.noarch.rpm 722 kB/s | 79 kB 00:00 (6/7): git-core-doc-2.39.3-1.el8_8.noarch.rpm 5.1 MB/s | 3.0 MB 00:00 (7/7): git-core-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64.rpm 12 MB/s | 11 MB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 11 MB/s | 14 MB 00:01 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : perl-Error-1:0.17025-2.el8.noarch 1/7 Installing : less-530-1.el8.x86_64 2/7 Installing : git-core-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64 3/7 Installing : git-core-doc-2.39.3-1.el8_8.noarch 4/7 Installing : emacs-filesystem-1:26.1-11.el8.noarch 5/7 Installing : perl-Git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.noarch 6/7 Installing : git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64 7/7 Running scriptlet: git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64 7/7 Verifying : emacs-filesystem-1:26.1-11.el8.noarch 1/7 Verifying : less-530-1.el8.x86_64 2/7 Verifying : git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64 3/7 Verifying : git-core-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64 4/7 Verifying : git-core-doc-2.39.3-1.el8_8.noarch 5/7 Verifying : perl-Error-1:0.17025-2.el8.noarch 6/7 Verifying : perl-Git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.noarch 7/7 Installed: emacs-filesystem-1:26.1-11.el8.noarch git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64 git-core-2.39.3-1.el8_8.x86_64 git-core-doc-2.39.3-1.el8_8.noarch less-530-1.el8.x86_64 perl-Error-1:0.17025-2.el8.noarch perl-Git-2.39.3-1.el8_8.noarch Complete! |
I installed the epel-release container with this command:
dnf install -y epel-release |
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 0:40:34 ago on Thu Dec 21 05:18:09 2023. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: oracle-epel-release-el8 x86_64 1.0-5.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 15 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 15 k Installed size: 18 k Downloading Packages: oracle-epel-release-el8-1.0-5.el8.x86_64.rpm 49 kB/s | 15 kB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 49 kB/s | 15 kB 00:00 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : oracle-epel-release-el8-1.0-5.el8.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : oracle-epel-release-el8-1.0-5.el8.x86_64 1/1 Installed: oracle-epel-release-el8-1.0-5.el8.x86_64 Complete! |
After installing all of these, you’re now ready to install the core rlwrap utility program. Like the other installations, you use:
dnf install -y rlwrap |
Display detailed console log →
Oracle Linux 8 EPEL Packages for Development (x 15 MB/s | 58 MB 00:03 Oracle Linux 8 EPEL Modular Packages for Develo 404 kB/s | 322 kB 00:00 Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: rlwrap x86_64 0.46.1-1.el8 ol8_developer_EPEL 140 k Installing dependencies: perl-File-Slurp noarch 9999.19-19.el8 ol8_appstream 47 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 2 Packages Total download size: 186 k Installed size: 426 k Downloading Packages: (1/2): perl-File-Slurp-9999.19-19.el8.noarch.rp 94 kB/s | 47 kB 00:00 (2/2): rlwrap-0.46.1-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 242 kB/s | 140 kB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 321 kB/s | 186 kB 00:00 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : perl-File-Slurp-9999.19-19.el8.noarch 1/2 Installing : rlwrap-0.46.1-1.el8.x86_64 2/2 Running scriptlet: rlwrap-0.46.1-1.el8.x86_64 2/2 Verifying : rlwrap-0.46.1-1.el8.x86_64 1/2 Verifying : perl-File-Slurp-9999.19-19.el8.noarch 2/2 Installed: perl-File-Slurp-9999.19-19.el8.noarch rlwrap-0.46.1-1.el8.x86_64 Complete! |
At this point, you need to create a sandboxed user account for the Docker instance because as a developer using the root user for simple tasks is a bad idea. While you could do this with a Docker command, the Oracle 23c Free edition raised a lock on the /etc/group file when I tried it. Naturally, that’s not a problem because you can connect as the root user with this syntax:
docker exec -it -u root oracle23c bash |
As the root user, create a student account as a developer account in the Oracle 23c Free container:
useradd -u 501 -g dba -G users -d /home/student -s /bin/bash/ -c "Student" -n student |
You’ll be unable to leverage the tnsnames.ora file unless you alter the prior command to replace dba with oinstall or add the following command:
usermod -a -G oinstall student |
Exit the Oracle 23c Free container as the root user and reconnect as the student user with this syntax:
docker exec -it --user student oracle23c bash |
While you’re connected as the root user, you should create an upload directory as a subdirectory of the $ORACLE_BASE directory. The $ORACLE_BASE directory in the Oracle Database 23c Free Docker image is the /opt/oracle directory.
You should use the following syntax to create the upload directory and change its permission to that of the Oracle Database 23c Free installation (for a future blog post on developing external table deployment on the Docker image):
mkdir /opt/oracle chown -R oracle:install /opt/oracle/upload |
You also can add the following student function to the Ubuntu student user’s .bashrc file. It means all you need to type to connect to the Oracle Database 23c Free Docker instance is “student“. I like shortcuts like this one, which let you leverage one-line Python commands.
student () { # Discover the fully qualified program name. path=`which docker 2>/dev/null` file='' # Parse the program name from the path. if [ -n ${path} ]; then file=${path##/*/} fi # Wrap when there is a file and it is rewrap. if [ -n ${file} ] && [[ ${file} = "docker" ]]; then python -c "import subprocess; subprocess.run(['docker exec -it --user student oracle23c bash'], shell=True)" else echo "Docker is unavailable: Install the docker package." fi } |
Open a Ubuntu Terminal shell and type a student function name to connect to the Docker Oracle Database 23c Free instance where you can now test things like external tables with the SQL*Plus command line without installing it on the Ubuntu local operating system.
student@student-virtual-machine:~$ student [student@d28375f0c43f ~]$ sqlplus c##student/student@free SQL*Plus: Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Production on Wed Jan 3 02:14:22 2024 Version 23.3.0.23.09 Copyright (c) 1982, 2023, Oracle. All rights reserved. Last Successful login time: Wed Jan 03 2024 01:56:44 +00:00 Connected to: Oracle Database 23c Free Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Develop, Learn, and Run for Free Version 23.3.0.23.09 SQL> |
Then, I added this sqlplus function to the /home/student/.bashrc file, which is owned by the student user. However, I also added the instruction to change to the student user’s home directory because the Oracle 23c Free container will connect you to the /home/oracle directory by default. I also added the default long list (ll) alias to the .bashrc file.
sqlplus () { # Discover the fully qualified program name. path=`which rlwrap 2>/dev/null` file='' # Parse the program name from the path. if [ -n ${path} ]; then file=${path##/*/} fi; # Wrap when there is a file and it is rewrap. if [ -n ${file} ] && [[ ${file} = "rlwrap" ]]; then rlwrap sqlplus "${@}" else echo "Command-line history unavailable: Install the rlwrap package." $ORACLE_HOME/bin/sqlplus "${@}" fi } # Change to the user's home directory. cd ${HOME} # Create a long list alias: alias ll='ls -l --color=auto' |
After you’ve configured your student user, you can configure the oracle user account to work like a regular server. Exit the Docker Oracle Database 23c Free as the student user, then connect as the root user with this command:
docker exec -it -u root oracle23c bash |
As the root user you can become the oracle user with the following command:
su - oracle |
Now, add the following .bashrc shell in the /home/oracle directory:
# The oracle user's .bashrc # Source global definitions if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then . /etc/bashrc fi # User specific environment if ! [[ "$PATH" =~ "$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:" ]] then PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin:$PATH" fi export PATH # Uncomment the following line if you don't like systemctl's auto-paging feature: # export SYSTEMD_PAGER= # User specific aliases and functions export ORACLE_SID=FREE export ORACLE_BASE=/opt/oracle export ORACLE_HOME=/opt/oracle/product/23c/dbhomeFree export PATH=$PATH:/$ORACLE_HOME/bin # Change to the user's home directory. cd ${HOME} # Create a long list alias: alias ll='ls -l --color=auto' sqlplus () { # Discover the fully qualified program name. path=`which rlwrap 2>/dev/null` file='' # Parse the program name from the path. if [ -n ${path} ]; then file=${path##/*/} fi; # Wrap when there is a file and it is rewrap. if [ -n ${file} ] && [[ ${file} = "rlwrap" ]]; then rlwrap sqlplus "${@}" else echo "Command-line history unavailable: Install the rlwrap package." $ORACLE_HOME/bin/sqlplus "${@}" fi } |
You need to manually source the .bashrc for the oracle user because it’s not an externally available user. Use this syntax to connect as the internal user:
sqlplus / as sysdba |
It’ll display:
SQL*Plus: RELEASE 23.0.0.0.0 - Production ON Wed Jan 3 07:08:11 2024 Version 23.3.0.23.09 Copyright (c) 1982, 2023, Oracle. ALL rights reserved. Connected TO: Oracle DATABASE 23c Free RELEASE 23.0.0.0.0 - Develop, Learn, AND Run FOR Free Version 23.3.0.23.09 SQL> |
After all this, I can now click the “up arrow” to edit any of the sqlplus command history. If you like to work inside sqlplus natively, this should help you.
Ubuntu DaaS VM
Completed the build of my new Ubuntu Virtual Machine (VM) with Oracle 23c installed in a Docker instance, and MySQL and PostgreSQL installed locally. The VM image also provides a LAMP stack with Apache2, PHP 8.1 with MySQLi and PDO modules. Since the original post, I’ve added a number of items to support our program courses and the Data Science degrees.
There are lots of tricks and techniques in the blog associated with creating the build. I took the background photograph of Chapel Bridge early on Sunday morning August 30, 1987 in Lucerne Switzerland (with a Canon A1 and ASA 64 slide film that subsequently digitized well).
Next step: roll it out into an AWS image for the students to use for their courses.
Related blog posts:
- Installing and configuring Apache2 and PHP 8.1 on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing and configuring Docker on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing and configuring MySQL 8 on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing Oracle Database 23c Free in a Docker container with space allocation techniques
- Installing and configuring PostgreSQL on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing and configuring pgAdmin4
- Installing and configuring Python for MySQL 8
- Installing and configuring Python for PostgreSQL driver on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing and configuring SQL Developer on Ubuntu 22.04
- Installing the rlwrap utility to access command history in SQL*Plus (sqlplus) inside Docker container.
- How to add PostGIS to an existing PostgreSQL 14 Install on Ubuntu 22.0.4
- How to create a sandboxed user and wrap sqlplus inside the Docker version of Oracle 23c Free
- How to install, configure, and create a persistent SQLite 3 database and access it with Python.
As always, I hope the post and information helps others.
OracleDB Python Tutorial 1
This shows you how to get Python working with the Oracle Database 23c in Docker or Podman on Ubuntu. You can find useful connection strings for this in Oracle Database Free Get Started.
- First step requires you to install the pip3/span> utility on Ubuntu.
sudo apt install -y python3-pip
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu build-essential dpkg-dev fakeroot g++ g++-11 gcc gcc-11 javascript-common libalgorithm-diff-perl libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libalgorithm-merge-perl libasan6 libbinutils libc-dev-bin libc-devtools libc6-dev libcc1-0 libcrypt-dev libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libdpkg-perl libexpat1-dev libfakeroot libfile-fcntllock-perl libgcc-11-dev libitm1 libjs-jquery libjs-sphinxdoc libjs-underscore liblsan0 libnsl-dev libpython3-dev libpython3.10-dev libquadmath0 libstdc++-11-dev libtirpc-dev libtsan0 libubsan1 linux-libc-dev lto-disabled-list make manpages-dev python3-dev python3-distutils python3-setuptools python3-wheel python3.10-dev rpcsvc-proto zlib1g-dev Suggested packages: binutils-doc debian-keyring g++-multilib g++-11-multilib gcc-11-doc gcc-multilib autoconf automake libtool flex bison gcc-doc gcc-11-multilib gcc-11-locales apache2 | lighttpd | httpd glibc-doc bzr libstdc++-11-doc make-doc python-setuptools-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: binutils binutils-common binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu build-essential dpkg-dev fakeroot g++ g++-11 gcc gcc-11 javascript-common libalgorithm-diff-perl libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libalgorithm-merge-perl libasan6 libbinutils libc-dev-bin libc-devtools libc6-dev libcc1-0 libcrypt-dev libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libdpkg-perl libexpat1-dev libfakeroot libfile-fcntllock-perl libgcc-11-dev libitm1 libjs-jquery libjs-sphinxdoc libjs-underscore liblsan0 libnsl-dev libpython3-dev libpython3.10-dev libquadmath0 libstdc++-11-dev libtirpc-dev libtsan0 libubsan1 linux-libc-dev lto-disabled-list make manpages-dev python3-dev python3-distutils python3-pip python3-setuptools python3-wheel python3.10-dev rpcsvc-proto zlib1g-dev 0 upgraded, 53 newly installed, 0 to remove and 9 not upgraded. Need to get 62.2 MB of archives. After this operation, 220 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 binutils-common amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [222 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libbinutils amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [662 kB] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libctf-nobfd0 amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [107 kB] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libctf0 amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [103 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [2,327 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 binutils amd64 2.38-4ubuntu2.3 [3,190 B] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libc-dev-bin amd64 2.35-0ubuntu3.5 [20.3 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 linux-libc-dev amd64 5.15.0-91.101 [1,332 kB] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libcrypt-dev amd64 1:4.4.27-1 [112 kB] Get:10 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 rpcsvc-proto amd64 1.4.2-0ubuntu6 [68.5 kB] Get:11 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libtirpc-dev amd64 1.3.2-2ubuntu0.1 [192 kB] Get:12 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libnsl-dev amd64 1.3.0-2build2 [71.3 kB] Get:13 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libc6-dev amd64 2.35-0ubuntu3.5 [2,098 kB] Get:14 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libcc1-0 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [48.3 kB] Get:15 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libitm1 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [30.2 kB] Get:16 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libasan6 amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [2,282 kB] Get:17 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 liblsan0 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [1,069 kB] Get:18 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libtsan0 amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [2,260 kB] Get:19 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libubsan1 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [976 kB] Get:20 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libquadmath0 amd64 12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [154 kB] Get:21 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libgcc-11-dev amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [2,517 kB] Get:22 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 gcc-11 amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [20.1 MB] Get:23 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 gcc amd64 4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1 [5,112 B] Get:24 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libstdc++-11-dev amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [2,101 kB] Get:25 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 g++-11 amd64 11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04 [11.4 MB] Get:26 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 g++ amd64 4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1 [1,412 B] Get:27 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 make amd64 4.3-4.1build1 [180 kB] Get:28 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libdpkg-perl all 1.21.1ubuntu2.2 [237 kB] Get:29 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 lto-disabled-list all 24 [12.5 kB] Get:30 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 dpkg-dev all 1.21.1ubuntu2.2 [922 kB] Get:31 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 build-essential amd64 12.9ubuntu3 [4,744 B] Get:32 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libfakeroot amd64 1.28-1ubuntu1 [31.5 kB] Get:33 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 fakeroot amd64 1.28-1ubuntu1 [60.4 kB] Get:34 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 javascript-common all 11+nmu1 [5,936 B] Get:35 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libalgorithm-diff-perl all 1.201-1 [41.8 kB] Get:36 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl amd64 0.04-6build3 [11.9 kB] Get:37 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libalgorithm-merge-perl all 0.08-3 [12.0 kB] Get:38 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libc-devtools amd64 2.35-0ubuntu3.5 [28.9 kB] Get:39 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libexpat1-dev amd64 2.4.7-1ubuntu0.2 [147 kB] Get:40 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libfile-fcntllock-perl amd64 0.22-3build7 [33.9 kB] Get:41 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libjs-jquery all 3.6.0+dfsg+~3.5.13-1 [321 kB] Get:42 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libjs-underscore all 1.13.2~dfsg-2 [118 kB] Get:43 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libjs-sphinxdoc all 4.3.2-1 [139 kB] Get:44 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 zlib1g-dev amd64 1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2 [164 kB] Get:45 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libpython3.10-dev amd64 3.10.12-1~22.04.3 [4,762 kB] Get:46 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libpython3-dev amd64 3.10.6-1~22.04 [7,166 B] Get:47 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 manpages-dev all 5.10-1ubuntu1 [2,309 kB] Get:48 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 python3.10-dev amd64 3.10.12-1~22.04.3 [507 kB] Get:49 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 python3-distutils all 3.10.8-1~22.04 [139 kB] Get:50 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 python3-dev amd64 3.10.6-1~22.04 [26.0 kB] Get:51 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 python3-setuptools all 59.6.0-1.2ubuntu0.22.04.1 [339 kB] Get:52 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 python3-wheel all 0.37.1-2ubuntu0.22.04.1 [32.0 kB] Get:53 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 python3-pip all 22.0.2+dfsg-1ubuntu0.4 [1,305 kB] Fetched 62.2 MB in 35s (1,781 kB/s) Extracting templates from packages: 100% Selecting previously unselected package binutils-common:amd64. (Reading database ... 221117 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../00-binutils-common_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking binutils-common:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libbinutils:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../01-libbinutils_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libbinutils:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libctf-nobfd0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../02-libctf-nobfd0_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libctf-nobfd0:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libctf0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../03-libctf0_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libctf0:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu. Preparing to unpack .../04-binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package binutils. Preparing to unpack .../05-binutils_2.38-4ubuntu2.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking binutils (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libc-dev-bin. Preparing to unpack .../06-libc-dev-bin_2.35-0ubuntu3.5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libc-dev-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Selecting previously unselected package linux-libc-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../07-linux-libc-dev_5.15.0-91.101_amd64.deb ... Unpacking linux-libc-dev:amd64 (5.15.0-91.101) ... Selecting previously unselected package libcrypt-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../08-libcrypt-dev_1%3a4.4.27-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libcrypt-dev:amd64 (1:4.4.27-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package rpcsvc-proto. Preparing to unpack .../09-rpcsvc-proto_1.4.2-0ubuntu6_amd64.deb ... Unpacking rpcsvc-proto (1.4.2-0ubuntu6) ... Selecting previously unselected package libtirpc-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../10-libtirpc-dev_1.3.2-2ubuntu0.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libtirpc-dev:amd64 (1.3.2-2ubuntu0.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libnsl-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../11-libnsl-dev_1.3.0-2build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libnsl-dev:amd64 (1.3.0-2build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libc6-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../12-libc6-dev_2.35-0ubuntu3.5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libc6-dev:amd64 (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Selecting previously unselected package libcc1-0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../13-libcc1-0_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libcc1-0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libitm1:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../14-libitm1_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libitm1:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libasan6:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../15-libasan6_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libasan6:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package liblsan0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../16-liblsan0_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking liblsan0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libtsan0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../17-libtsan0_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libtsan0:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libubsan1:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../18-libubsan1_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libubsan1:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libquadmath0:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../19-libquadmath0_12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libquadmath0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package libgcc-11-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../20-libgcc-11-dev_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libgcc-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package gcc-11. Preparing to unpack .../21-gcc-11_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking gcc-11 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package gcc. Preparing to unpack .../22-gcc_4%3a11.2.0-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking gcc (4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libstdc++-11-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../23-libstdc++-11-dev_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libstdc++-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package g++-11. Preparing to unpack .../24-g++-11_11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking g++-11 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package g++. Preparing to unpack .../25-g++_4%3a11.2.0-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking g++ (4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package make. Preparing to unpack .../26-make_4.3-4.1build1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking make (4.3-4.1build1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libdpkg-perl. Preparing to unpack .../27-libdpkg-perl_1.21.1ubuntu2.2_all.deb ... Unpacking libdpkg-perl (1.21.1ubuntu2.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package lto-disabled-list. Preparing to unpack .../28-lto-disabled-list_24_all.deb ... Unpacking lto-disabled-list (24) ... Selecting previously unselected package dpkg-dev. Preparing to unpack .../29-dpkg-dev_1.21.1ubuntu2.2_all.deb ... Unpacking dpkg-dev (1.21.1ubuntu2.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package build-essential. Preparing to unpack .../30-build-essential_12.9ubuntu3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking build-essential (12.9ubuntu3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libfakeroot:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../31-libfakeroot_1.28-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libfakeroot:amd64 (1.28-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package fakeroot. Preparing to unpack .../32-fakeroot_1.28-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking fakeroot (1.28-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package javascript-common. Preparing to unpack .../33-javascript-common_11+nmu1_all.deb ... Unpacking javascript-common (11+nmu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libalgorithm-diff-perl. Preparing to unpack .../34-libalgorithm-diff-perl_1.201-1_all.deb ... Unpacking libalgorithm-diff-perl (1.201-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl. Preparing to unpack .../35-libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl_0.04-6build3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl (0.04-6build3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libalgorithm-merge-perl. Preparing to unpack .../36-libalgorithm-merge-perl_0.08-3_all.deb ... Unpacking libalgorithm-merge-perl (0.08-3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libc-devtools. Preparing to unpack .../37-libc-devtools_2.35-0ubuntu3.5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libc-devtools (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Selecting previously unselected package libexpat1-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../38-libexpat1-dev_2.4.7-1ubuntu0.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libexpat1-dev:amd64 (2.4.7-1ubuntu0.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libfile-fcntllock-perl. Preparing to unpack .../39-libfile-fcntllock-perl_0.22-3build7_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libfile-fcntllock-perl (0.22-3build7) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-jquery. Preparing to unpack .../40-libjs-jquery_3.6.0+dfsg+~3.5.13-1_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-jquery (3.6.0+dfsg+~3.5.13-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-underscore. Preparing to unpack .../41-libjs-underscore_1.13.2~dfsg-2_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-underscore (1.13.2~dfsg-2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libjs-sphinxdoc. Preparing to unpack .../42-libjs-sphinxdoc_4.3.2-1_all.deb ... Unpacking libjs-sphinxdoc (4.3.2-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package zlib1g-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../43-zlib1g-dev_1%3a1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking zlib1g-dev:amd64 (1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libpython3.10-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../44-libpython3.10-dev_3.10.12-1~22.04.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libpython3.10-dev:amd64 (3.10.12-1~22.04.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libpython3-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../45-libpython3-dev_3.10.6-1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libpython3-dev:amd64 (3.10.6-1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package manpages-dev. Preparing to unpack .../46-manpages-dev_5.10-1ubuntu1_all.deb ... Unpacking manpages-dev (5.10-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3.10-dev. Preparing to unpack .../47-python3.10-dev_3.10.12-1~22.04.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking python3.10-dev (3.10.12-1~22.04.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-distutils. Preparing to unpack .../48-python3-distutils_3.10.8-1~22.04_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-distutils (3.10.8-1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-dev. Preparing to unpack .../49-python3-dev_3.10.6-1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking python3-dev (3.10.6-1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-setuptools. Preparing to unpack .../50-python3-setuptools_59.6.0-1.2ubuntu0.22.04.1_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-setuptools (59.6.0-1.2ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-wheel. Preparing to unpack .../51-python3-wheel_0.37.1-2ubuntu0.22.04.1_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-wheel (0.37.1-2ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package python3-pip. Preparing to unpack .../52-python3-pip_22.0.2+dfsg-1ubuntu0.4_all.deb ... Unpacking python3-pip (22.0.2+dfsg-1ubuntu0.4) ... Setting up python3-distutils (3.10.8-1~22.04) ... Setting up javascript-common (11+nmu1) ... Setting up manpages-dev (5.10-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up lto-disabled-list (24) ... Setting up python3-setuptools (59.6.0-1.2ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Setting up libfile-fcntllock-perl (0.22-3build7) ... Setting up libalgorithm-diff-perl (1.201-1) ... Setting up binutils-common:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up linux-libc-dev:amd64 (5.15.0-91.101) ... Setting up libctf-nobfd0:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up python3-wheel (0.37.1-2ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Setting up libfakeroot:amd64 (1.28-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up libasan6:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up fakeroot (1.28-1ubuntu1) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/fakeroot-sysv to provide /usr/bin/fakeroot (fakeroot) in auto mode Setting up libtirpc-dev:amd64 (1.3.2-2ubuntu0.1) ... Setting up rpcsvc-proto (1.4.2-0ubuntu6) ... Setting up make (4.3-4.1build1) ... Setting up libquadmath0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up python3-pip (22.0.2+dfsg-1ubuntu0.4) ... Setting up libdpkg-perl (1.21.1ubuntu2.2) ... Setting up libubsan1:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libnsl-dev:amd64 (1.3.0-2build2) ... Setting up libcrypt-dev:amd64 (1:4.4.27-1) ... Setting up libjs-jquery (3.6.0+dfsg+~3.5.13-1) ... Setting up libbinutils:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up libc-dev-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Setting up libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl (0.04-6build3) ... Setting up libcc1-0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up liblsan0:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libitm1:amd64 (12.3.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libc-devtools (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Setting up libjs-underscore (1.13.2~dfsg-2) ... Setting up libalgorithm-merge-perl (0.08-3) ... Setting up libtsan0:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libctf0:amd64 (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up libjs-sphinxdoc (4.3.2-1) ... Setting up libgcc-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up libc6-dev:amd64 (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... Setting up binutils-x86-64-linux-gnu (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up binutils (2.38-4ubuntu2.3) ... Setting up dpkg-dev (1.21.1ubuntu2.2) ... Setting up libexpat1-dev:amd64 (2.4.7-1ubuntu0.2) ... Setting up libstdc++-11-dev:amd64 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up zlib1g-dev:amd64 (1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2) ... Setting up gcc-11 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up g++-11 (11.4.0-1ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up gcc (4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up libpython3.10-dev:amd64 (3.10.12-1~22.04.3) ... Setting up python3.10-dev (3.10.12-1~22.04.3) ... Setting up g++ (4:11.2.0-1ubuntu1) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/g++ to provide /usr/bin/c++ (c++) in auto mode Setting up build-essential (12.9ubuntu3) ... Setting up libpython3-dev:amd64 (3.10.6-1~22.04) ... Setting up python3-dev (3.10.6-1~22.04) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ...
- Second step requires that you pip3 install the oracledb library:
sudo pip3 install oracledb --upgrade
Display detailed console log →
Defaulting to user installation because normal site-packages is not writeable Collecting oracledb Downloading oracledb-1.4.2-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl (8.6 MB) ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 8.6/8.6 MB 2.7 MB/s eta 0:00:00 Requirement already satisfied: cryptography>=3.2.1 in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from oracledb) (3.4.8) Installing collected packages: oracledb Successfully installed oracledb-1.4.2 - Third step requires you write a Python program to test your connection to Oracle Database 23c Free, like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
#!/usr/bin/python # Import the Oracle library. import oracledb try: # Create a connection to local Docker or Podman installation. db = oracledb.connect(user='c##student', password='student', dsn='localhost:51521/FREE') # Print a connection message. print("Connected to the Oracle", db.version, "database.") except oracledb.DatabaseError as e: error, = e.args print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Code:", error.code) print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Message:", error.message) finally: # Close connection. db.close()
The 51521 port is the recommended port when setting up Docker or Podman services, however, it can be set to any port above 1024.
It should print:
Connected to the Oracle 23.3.0.23.9 database.
- Fourth step requires you write a Python program to test querying data from an Oracle Database 23c Free instance. I created the following avenger table and seeded it with six Avengers.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
/* Conditionally drop the table. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS avenger; /* Create the table. */ CREATE TABLE avenger ( avenger_id NUMBER , first_name VARCHAR2(20) , last_name VARCHAR2(20) , character_name VARCHAR2(20)); /* Seed the table with data. */ INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (1,'Anthony','Stark','Iron Man'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (2,'Thor','Odinson','God of Thunder'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (3,'Steven','Rogers','Captain America'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (4,'Bruce','Banner','Hulk'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (5,'Clinton','Barton','Hawkeye'); INSERT INTO avenger VALUES (6,'Natasha','Romanoff','Black Widow');
Then, I extended the program logic to include a cursor and for loop to read the values from the avenger table:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
#!/usr/bin/python # Import the Oracle library. import oracledb try: # Create a connection to local Docker or Podman installation. db = oracledb.connect(user='c##student', password='student', dsn='localhost:51521/FREE') # Create a cursor. cursor = db.cursor() # Execute a query. cursor.execute("SELECT character_name " + ", first_name " + ", last_name " + "FROM avenger " + "ORDER BY character_name") # Read the contents of the cursor. for row in cursor: print(row[0] + ':',row[2] + ',',row[1]) except oracledb.DatabaseError as e: error, = e.args print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Code:", error.code) print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Message:", error.message) finally: # Close cursor and connection. cursor.close() db.close()
The 51521 port is the recommended port when setting up Docker or Podman services, however, it can be set to any port above 1024.
It should print:
Black Widow: Romanoff, Natasha Captain America: Rogers, Steven God of Thunder: Odinson, Thor Hawkeye: Barton, Clinton Hulk: Banner, Bruce Iron Man: Stark, Anthony
- Fifth step requires you write a Python program to test querying data filtered by a local variable from an Oracle Database 23c Free instance. This example looks only for the Hulk among the six Avengers.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
#!/usr/bin/python # Import the Oracle library. import oracledb try: # Create a connection to local Docker or Podman installation. db = oracledb.connect(user='c##student', password='student', dsn='localhost:51521/FREE') # Create a cursor. cursor = db.cursor() # Execute a query. stmt = "SELECT character_name " \ ", first_name " \ ", last_name " \ "FROM avenger " \ "WHERE character_name = :avenger " \ "ORDER BY character_name" # Execute with bind variable. cursor.execute(stmt, avenger = "Hulk") # Read the contents of the cursor. for row in cursor: print(row[0] + ':',row[2] + ',',row[1]) except oracledb.DatabaseError as e: error, = e.args print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Code:", error.code) print(sys.stderr, "Oracle-Error-Message:", error.message) finally: # Close cursor and connection. cursor.close() db.close()
It should print:
Hulk: Banner, Bruce
As always, I hope this puts everything together for setting up Python with Oracle Database 23c Free.
Oracle 23c MLE JavaScript
Oracle Database 23c has some really great features. One of those features is the ability to write JavaScript functions inside the database. Unfortunately, I noticed a couple omissions in Oracle’s JavaScript Developer’s Guide. Specifically, I encountered a privilege error while testing the example in the 5.1 Call Specifications for Functions example.
After having typed it all in to a simple script file, I encountered the following error message when trying to create an MLE MODULE:
CREATE OR REPLACE MLE MODULE jsmodule * ERROR AT line 1: ORA-01031: insufficient PRIVILEGES Help: https://docs.oracle.com/error-help/db/ora-06575 |
That was easy enough to fix. As the system user you need to grant the following two additional privileges to the user (based on my earlier sandbox pluggable user configuration user setup), which in my case is the c##student pluggable user:
GRANT CREATE MLE TO c##student; GRANT EXECUTE ON JAVASCRIPT TO c##student; |
You need to enable the SQL*PLus SERVEROUTPUT environment parameter for Oracle’s code example to work when you run the greet procedure from SQL*Plus command-line interface (CLI).
Below is the modified example file (unfortunately, the GeSHi formatting promotes log and return in the JavaScript functions to uppercase because they’re assumed as keywords in Oracle SQL):
- Conditionally drop the MLE MODULE.
DROP MLE MODULE IF EXISTS jsmodule;
- Create a MLE Call Specification.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
CREATE OR REPLACE MLE MODULE jsmodule LANGUAGE JAVASCRIPT AS export function greet(str) { console.log(`Hello ${str}!`) } export function concat(str1, str2) { return str1 + " " + str2 + "!"; } /
- The greet function doesn’t return a value and uses the Nodejs console.log() function to write a string, which means you must wrap the JavaScript function as a procedure because it returns a void type.
1 2 3 4 5
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE greet(str in VARCHAR2) AS MLE MODULE jsmodule SIGNATURE 'greet(string)'; /
- Wrap the concatenate function as a function because it returns a value inside the JavaScript.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION concatenate ( str1 VARCHAR2 , str2 VARCHAR2 ) RETURN VARCHAR2 AS MLE MODULE jsmodule SIGNATURE 'concat(string, string)'; /
- Enable to the SERVEROUTPUT environment variable to display messages printed from inside stored procedures or other PL/SQL blocks.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON SIZE UNLIMITED
- Call the greet(literal|variable) function’s procedure wrapper.
CALL greet('Peter');
It returns
Hello Peter!
- Query the result from the concatenate() function’s function wrapper. */
SELECT concatenate('Hello','World');
It returns
Hello World!
As always, I hope this helps somebody working through the same issue.
SQL Developer on Ubuntu
The following steps show how to install and configure SQL Developer on Ubuntu 22.0.4 to work with Oracle Database 23c Free in a Docker container. The first steps are installing the Java Runtime Environment and Java Development Kit, and then downloading, installing and configuring SQL Developer. These are the required steps:
- Install the Java Runtime Environment:
sudo apt install default-jre
The log file for this is:
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: ca-certificates-java default-jre-headless fonts-dejavu-extra java-common libatk-wrapper-java libatk-wrapper-java-jni openjdk-11-jre openjdk-11-jre-headless Suggested packages: fonts-ipafont-gothic fonts-ipafont-mincho fonts-wqy-microhei | fonts-wqy-zenhei The following NEW packages will be installed: ca-certificates-java default-jre default-jre-headless fonts-dejavu-extra java-common libatk-wrapper-java libatk-wrapper-java-jni openjdk-11-jre openjdk-11-jre-headless 0 upgraded, 9 newly installed, 0 to remove and 4 not upgraded. Need to get 44.9 MB of archives. After this operation, 185 MB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 java-common all 0.72build2 [6,782 B] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 openjdk-11-jre-headless amd64 11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04 [42.5 MB] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 default-jre-headless amd64 2:1.11-72build2 [3,042 B] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 ca-certificates-java all 20190909ubuntu1.2 [12.1 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 openjdk-11-jre amd64 11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04 [214 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 default-jre amd64 2:1.11-72build2 [896 B] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 fonts-dejavu-extra all 2.37-2build1 [2,041 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libatk-wrapper-java all 0.38.0-5build1 [53.1 kB] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libatk-wrapper-java-jni amd64 0.38.0-5build1 [49.0 kB] Fetched 44.9 MB in 14s (3,270 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package java-common. (Reading database ... 203118 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../0-java-common_0.72build2_all.deb ... Unpacking java-common (0.72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package openjdk-11-jre-headless:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../1-openjdk-11-jre-headless_11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04_amd64 .deb ... Unpacking openjdk-11-jre-headless:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package default-jre-headless. Preparing to unpack .../2-default-jre-headless_2%3a1.11-72build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking default-jre-headless (2:1.11-72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package ca-certificates-java. Preparing to unpack .../3-ca-certificates-java_20190909ubuntu1.2_all.deb ... Unpacking ca-certificates-java (20190909ubuntu1.2) ... Selecting previously unselected package openjdk-11-jre:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../4-openjdk-11-jre_11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking openjdk-11-jre:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package default-jre. Preparing to unpack .../5-default-jre_2%3a1.11-72build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking default-jre (2:1.11-72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package fonts-dejavu-extra. Preparing to unpack .../6-fonts-dejavu-extra_2.37-2build1_all.deb ... Unpacking fonts-dejavu-extra (2.37-2build1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libatk-wrapper-java. Preparing to unpack .../7-libatk-wrapper-java_0.38.0-5build1_all.deb ... Unpacking libatk-wrapper-java (0.38.0-5build1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libatk-wrapper-java-jni:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../8-libatk-wrapper-java-jni_0.38.0-5build1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libatk-wrapper-java-jni:amd64 (0.38.0-5build1) ... Setting up java-common (0.72build2) ... Setting up fonts-dejavu-extra (2.37-2build1) ... Setting up libatk-wrapper-java (0.38.0-5build1) ... Setting up libatk-wrapper-java-jni:amd64 (0.38.0-5build1) ... Setting up default-jre-headless (2:1.11-72build2) ... Setting up openjdk-11-jre-headless:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/java to provid e /usr/bin/java (java) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jjs to provide /usr/bin/jjs (jjs) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/keytool to pro vide /usr/bin/keytool (keytool) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/rmid to provid e /usr/bin/rmid (rmid) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/rmiregistry to provide /usr/bin/rmiregistry (rmiregistry) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/pack200 to pro vide /usr/bin/pack200 (pack200) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/unpack200 to p rovide /usr/bin/unpack200 (unpack200) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/lib/jexec to provi de /usr/bin/jexec (jexec) in auto mode Setting up openjdk-11-jre:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Setting up default-jre (2:1.11-72build2) ... Setting up ca-certificates-java (20190909ubuntu1.2) ... head: cannot open '/etc/ssl/certs/java/cacerts' for reading: No such file or dir ectory Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_1_G3.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_E46.pem Adding debian:T-TeleSec_GlobalRoot_Class_3.pem Adding debian:Certum_Trusted_Network_CA.pem Adding debian:Buypass_Class_2_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:NetLock_Arany_=Class_Gold=_Főtanúsítvány.pem Adding debian:e-Szigno_Root_CA_2017.pem Adding debian:emSign_Root_CA_-_G1.pem Adding debian:D-TRUST_BR_Root_CA_1_2020.pem Adding debian:Hongkong_Post_Root_CA_3.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_R4.pem Adding debian:NAVER_Global_Root_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:UCA_Extended_Validation_Root.pem Adding debian:AffirmTrust_Premium.pem Adding debian:Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Trusted_Root_G4.pem Adding debian:CFCA_EV_ROOT.pem Adding debian:ePKI_Root_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:Hellenic_Academic_and_Research_Institutions_ECC_RootCA_2015.pem Adding debian:HARICA_TLS_RSA_Root_CA_2021.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_CA_-_R6.pem Adding debian:TWCA_Global_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Trustwave_Global_ECC_P384_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:ISRG_Root_X1.pem Adding debian:Starfield_Services_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.pem Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_3.pem Adding debian:Security_Communication_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_TLS_RSA4096_Root_G5.pem Adding debian:Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority_-_EC1.pem Adding debian:Security_Communication_RootCA3.pem Adding debian:TeliaSonera_Root_CA_v1.pem Adding debian:vTrus_ECC_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:AC_RAIZ_FNMT-RCM_SERVIDORES_SEGUROS.pem Adding debian:Certum_EC-384_CA.pem Adding debian:Microsec_e-Szigno_Root_CA_2009.pem Adding debian:ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem Adding debian:USERTrust_ECC_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:CA_Disig_Root_R2.pem Adding debian:Certum_Trusted_Network_CA_2.pem Adding debian:ACCVRAIZ1.pem Adding debian:TunTrust_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Buypass_Class_3_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:D-TRUST_Root_Class_3_CA_2_2009.pem Adding debian:Security_Communication_ECC_RootCA1.pem Adding debian:GTS_Root_R2.pem Adding debian:Certigna.pem Adding debian:SSL.com_EV_Root_Certification_Authority_RSA_R2.pem Adding debian:Entrust.net_Premium_2048_Secure_Server_CA.pem Adding debian:E-Tugra_Global_Root_CA_ECC_v3.pem Adding debian:Hongkong_Post_Root_CA_1.pem Adding debian:SZAFIR_ROOT_CA2.pem Adding debian:TUBITAK_Kamu_SM_SSL_Kok_Sertifikasi_-_Surum_1.pem Adding debian:Atos_TrustedRoot_2011.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_High_Assurance_EV_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:emSign_Root_CA_-_C1.pem Adding debian:Go_Daddy_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.pem Adding debian:GDCA_TrustAUTH_R5_ROOT.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_CA_-_R3.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_G3.pem Adding debian:Autoridad_de_Certificacion_Firmaprofesional_CIF_A62634068_2.pem Adding debian:Certainly_Root_R1.pem Adding debian:vTrus_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Certainly_Root_E1.pem Adding debian:Autoridad_de_Certificacion_Firmaprofesional_CIF_A62634068.pem Adding debian:TWCA_Root_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:Starfield_Root_Certificate_Authority_-_G2.pem Adding debian:Amazon_Root_CA_3.pem Adding debian:GTS_Root_R1.pem Adding debian:SwissSign_Gold_CA_-_G2.pem Adding debian:Certum_Trusted_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Hellenic_Academic_and_Research_Institutions_RootCA_2015.pem Adding debian:AffirmTrust_Networking.pem Adding debian:emSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_G3.pem Adding debian:HARICA_TLS_ECC_Root_CA_2021.pem Adding debian:certSIGN_ROOT_CA.pem Adding debian:Actalis_Authentication_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:SSL.com_Root_Certification_Authority_RSA.pem Adding debian:Certigna_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:XRamp_Global_CA_Root.pem Adding debian:Baltimore_CyberTrust_Root.pem Adding debian:Trustwave_Global_ECC_P256_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_2_G3.pem Adding debian:GTS_Root_R3.pem Adding debian:COMODO_RSA_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:ISRG_Root_X2.pem Adding debian:SwissSign_Silver_CA_-_G2.pem Adding debian:IdenTrust_Public_Sector_Root_CA_1.pem Adding debian:Microsoft_ECC_Root_Certificate_Authority_2017.pem Adding debian:UCA_Global_G2_Root.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority_-_G2.pem Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_2.pem Adding debian:Trustwave_Global_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:OISTE_WISeKey_Global_Root_GB_CA.pem Adding debian:HiPKI_Root_CA_-_G1.pem Adding debian:E-Tugra_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:GTS_Root_R4.pem Adding debian:Amazon_Root_CA_2.pem Adding debian:Amazon_Root_CA_1.pem Adding debian:SecureTrust_CA.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_R46.pem Adding debian:IdenTrust_Commercial_Root_CA_1.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Global_Root_G2.pem Adding debian:Comodo_AAA_Services_root.pem Adding debian:SSL.com_Root_Certification_Authority_ECC.pem Adding debian:T-TeleSec_GlobalRoot_Class_2.pem Adding debian:Starfield_Class_2_CA.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Global_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:SecureSign_RootCA11.pem Adding debian:certSIGN_Root_CA_G2.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_TLS_ECC_P384_Root_G5.pem Adding debian:Entrust_Root_Certification_Authority_-_G4.pem Adding debian:OISTE_WISeKey_Global_Root_GC_CA.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Global_Root_G3.pem Adding debian:Secure_Global_CA.pem Adding debian:Microsoft_RSA_Root_Certificate_Authority_2017.pem Adding debian:DigiCert_Assured_ID_Root_G2.pem Adding debian:Telia_Root_CA_v2.pem Adding debian:emSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_C3.pem Adding debian:COMODO_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:AffirmTrust_Premium_ECC.pem Adding debian:GLOBALTRUST_2020.pem Adding debian:E-Tugra_Global_Root_CA_RSA_v3.pem Adding debian:Amazon_Root_CA_4.pem Adding debian:COMODO_ECC_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:AffirmTrust_Commercial.pem Adding debian:SSL.com_EV_Root_Certification_Authority_ECC.pem Adding debian:AC_RAIZ_FNMT-RCM.pem Adding debian:Go_Daddy_Class_2_CA.pem Adding debian:QuoVadis_Root_CA_3_G3.pem Adding debian:D-TRUST_EV_Root_CA_1_2020.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:GlobalSign_ECC_Root_CA_-_R5.pem Adding debian:USERTrust_RSA_Certification_Authority.pem Adding debian:D-TRUST_Root_Class_3_CA_2_EV_2009.pem Adding debian:Izenpe.com.pem Adding debian:ANF_Secure_Server_Root_CA.pem Adding debian:Security_Communication_RootCA2.pem done. Processing triggers for mailcap (3.70+nmu1ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for fontconfig (2.13.1-4.2ubuntu5) ... Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.26-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for hicolor-icon-theme (0.17-2) ... Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for ca-certificates (20230311ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Updating certificates in /etc/ssl/certs... 0 added, 0 removed; done. Running hooks in /etc/ca-certificates/update.d... done. done.
- Install the Java Runtime Environment:
sudo apt install -y default-idk
The log file for this is:
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: default-jdk-headless libice-dev libpthread-stubs0-dev libsm-dev libx11-dev libxau-dev libxcb1-dev libxdmcp-dev libxt-dev openjdk-11-jdk openjdk-11-jdk-headless x11proto-dev xorg-sgml-doctools xtrans-dev Suggested packages: libice-doc libsm-doc libx11-doc libxcb-doc libxt-doc openjdk-11-demo openjdk-11-source visualvm The following NEW packages will be installed: default-jdk default-jdk-headless libice-dev libpthread-stubs0-dev libsm-dev libx11-dev libxau-dev libxcb1-dev libxdmcp-dev libxt-dev openjdk-11-jdk openjdk-11-jdk-headless x11proto-dev xorg-sgml-doctools xtrans-dev 0 upgraded, 15 newly installed, 0 to remove and 4 not upgraded. Need to get 76.9 MB of archives. After this operation, 90.6 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 openjdk-11-jdk-headless amd64 11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04 [73.5 MB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 default-jdk-headless amd64 2:1.11-72build2 [942 B] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 openjdk-11-jdk amd64 11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04 [1,327 kB] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 default-jdk amd64 2:1.11-72build2 [908 B] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 xorg-sgml-doctools all 1:1.11-1.1 [10.9 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 x11proto-dev all 2021.5-1 [604 kB] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libice-dev amd64 2:1.0.10-1build2 [51.4 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libpthread-stubs0-dev amd64 0.4-1build2 [5,516 B] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libsm-dev amd64 2:1.2.3-1build2 [18.1 kB] Get:10 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libxau-dev amd64 1:1.0.9-1build5 [9,724 B] Get:11 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libxdmcp-dev amd64 1:1.1.3-0ubuntu5 [26.5 kB] Get:12 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 xtrans-dev all 1.4.0-1 [68.9 kB] Get:13 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libxcb1-dev amd64 1.14-3ubuntu3 [86.5 kB] Get:14 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libx11-dev amd64 2:1.7.5-1ubuntu0.3 [744 kB] Get:15 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libxt-dev amd64 1:1.2.1-1 [396 kB] Fetched 76.9 MB in 6s (12.7 MB/s) Selecting previously unselected package openjdk-11-jdk-headless:amd64. (Reading database ... 203527 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../00-openjdk-11-jdk-headless_11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04_amd6 4.deb ... Unpacking openjdk-11-jdk-headless:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package default-jdk-headless. Preparing to unpack .../01-default-jdk-headless_2%3a1.11-72build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking default-jdk-headless (2:1.11-72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package openjdk-11-jdk:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../02-openjdk-11-jdk_11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04_amd64.deb ... Unpacking openjdk-11-jdk:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... Selecting previously unselected package default-jdk. Preparing to unpack .../03-default-jdk_2%3a1.11-72build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking default-jdk (2:1.11-72build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package xorg-sgml-doctools. Preparing to unpack .../04-xorg-sgml-doctools_1%3a1.11-1.1_all.deb ... Unpacking xorg-sgml-doctools (1:1.11-1.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package x11proto-dev. Preparing to unpack .../05-x11proto-dev_2021.5-1_all.deb ... Unpacking x11proto-dev (2021.5-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libice-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../06-libice-dev_2%3a1.0.10-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libice-dev:amd64 (2:1.0.10-1build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libpthread-stubs0-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../07-libpthread-stubs0-dev_0.4-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libpthread-stubs0-dev:amd64 (0.4-1build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libsm-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../08-libsm-dev_2%3a1.2.3-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libsm-dev:amd64 (2:1.2.3-1build2) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxau-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../09-libxau-dev_1%3a1.0.9-1build5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxau-dev:amd64 (1:1.0.9-1build5) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxdmcp-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../10-libxdmcp-dev_1%3a1.1.3-0ubuntu5_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxdmcp-dev:amd64 (1:1.1.3-0ubuntu5) ... Selecting previously unselected package xtrans-dev. Preparing to unpack .../11-xtrans-dev_1.4.0-1_all.deb ... Unpacking xtrans-dev (1.4.0-1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxcb1-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../12-libxcb1-dev_1.14-3ubuntu3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxcb1-dev:amd64 (1.14-3ubuntu3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libx11-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../13-libx11-dev_2%3a1.7.5-1ubuntu0.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libx11-dev:amd64 (2:1.7.5-1ubuntu0.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxt-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../14-libxt-dev_1%3a1.2.1-1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxt-dev:amd64 (1:1.2.1-1) ... Setting up openjdk-11-jdk-headless:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jar to provide /usr/bin/jar (jar) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jarsigner to p rovide /usr/bin/jarsigner (jarsigner) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/javac to provi de /usr/bin/javac (javac) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/javadoc to pro vide /usr/bin/javadoc (javadoc) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/javap to provi de /usr/bin/javap (javap) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jcmd to provid e /usr/bin/jcmd (jcmd) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jdb to provide /usr/bin/jdb (jdb) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jdeprscan to p rovide /usr/bin/jdeprscan (jdeprscan) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jdeps to provi de /usr/bin/jdeps (jdeps) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jfr to provide /usr/bin/jfr (jfr) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jimage to prov ide /usr/bin/jimage (jimage) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jinfo to provi de /usr/bin/jinfo (jinfo) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jlink to provi de /usr/bin/jlink (jlink) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jmap to provid e /usr/bin/jmap (jmap) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jmod to provid e /usr/bin/jmod (jmod) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jps to provide /usr/bin/jps (jps) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jrunscript to provide /usr/bin/jrunscript (jrunscript) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jshell to prov ide /usr/bin/jshell (jshell) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jstack to prov ide /usr/bin/jstack (jstack) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jstat to provi de /usr/bin/jstat (jstat) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jstatd to prov ide /usr/bin/jstatd (jstatd) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/rmic to provid e /usr/bin/rmic (rmic) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/serialver to p rovide /usr/bin/serialver (serialver) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jaotc to provi de /usr/bin/jaotc (jaotc) in auto mode update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jhsdb to provi de /usr/bin/jhsdb (jhsdb) in auto mode Setting up libpthread-stubs0-dev:amd64 (0.4-1build2) ... Setting up xtrans-dev (1.4.0-1) ... Setting up default-jdk-headless (2:1.11-72build2) ... Setting up openjdk-11-jdk:amd64 (11.0.21+9-0ubuntu1~22.04) ... update-alternatives: using /usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64/bin/jconsole to pr ovide /usr/bin/jconsole (jconsole) in auto mode Setting up xorg-sgml-doctools (1:1.11-1.1) ... Setting up default-jdk (2:1.11-72build2) ... Processing triggers for sgml-base (1.30) ... Setting up x11proto-dev (2021.5-1) ... Setting up libxau-dev:amd64 (1:1.0.9-1build5) ... Setting up libice-dev:amd64 (2:1.0.10-1build2) ... Setting up libsm-dev:amd64 (2:1.2.3-1build2) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Setting up libxdmcp-dev:amd64 (1:1.1.3-0ubuntu5) ... Setting up libxcb1-dev:amd64 (1.14-3ubuntu3) ... Setting up libx11-dev:amd64 (2:1.7.5-1ubuntu0.3) ... Setting up libxt-dev:amd64 (1:1.2.1-1) ...
- Download SQL Developer from here; and then install SQL Developer to the /opt directory on your Ubuntu local instance:
Use the following command to unzip the SQL Developer files to the /opt directory:
sudo unzip ~/Downloads/sqldeveloper-23.1.0.097.1607-no-jre.zip
- Create the following /usr/local/bin/sqldeveloper symbolic link:
sudo ln -s /opt/sqldeveloper/sqldeveloper.sh /usr/local/bin/sqldeveloper
- Edit the /opt/sqldeveloper/sqldeveloper.sh file by replacing the following line:
cd "`dirname $0`"/sqldeveloper/bin && bash sqldeveloper $*
with this version:
/opt/sqldeveloper/sqldeveloper/bin/sqldeveloper $*
- Now, you can launch SQL Developer from any location on your local Ubuntu operating system, like:
sqldeveloper
- You can now connect as the system user through SQL Developer to the Oracle Database 23c Free Docker instance with the following connection information:
- You can also create a Desktop shortcut by creating the sqldeveloper.desktop file in the /usr/share/applications directory. The SQL Developer icon is provided in the sqldeveloper base directory.

You should create the following sqldeveloper.desktop file to use a Desktop shortcut:
[Desktop Entry] Name=Oracle SQL Developer Comment=SQL Developer from Oracle GenericName=SQL Tool Exec=/usr/local/bin/sqldeveloper Icon=/opt/sqldeveloper/icon.png Type=Application StartupNotify=true Categories=Utility;Oracle;Development;SQL;
You can create a sandboxed container c##student user with the instructions from this earlier post on Oracle Database 18c, which remains the correct syntax.
As always, I hope this helps those trying to accomplish this task.
Disk Space Allocation
It’s necessary to check for adequate disk space on your Virtual Machine (VM) before installing Oracle 23c Free in a Docker container or as a podman service. Either way, it requires about 13 GB of disk space. On Ubuntu, the typical install of a VM allocates 20 GB and a 500 MB swap. You need to create a 2 GB swap when you install Ubuntu or plan to change the swap, as qualified in this excellent DigitalOcean article. Assuming you installed it with the correct swap or extended your swap area, you can confirm it with the following command:
sudo swapon --show |
It should return something like this:
NAME TYPE SIZE USED PRIO /swapfile file 2.1G 1.2G -2 |
Next, check your disk space allocation and availability with this command:
df -h |
This is what was in my instance with MySQL and PostgreSQL databases already installed and configured with sandboxed schemas:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on tmpfs 388M 2.1M 386M 1% /run /dev/sda3 20G 14G 4.6G 75% / tmpfs 1.9G 28K 1.9G 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock /dev/sda2 512M 6.1M 506M 2% /boot/efi tmpfs 388M 108K 388M 1% /run/user/1000 |
Using VMware Fusion on my Mac (Intel-based i9), I changed the allocated space from 20 GB to 40 GB by navigating to Virtual Machine, Settings…, Hard Disk. I entered 40.00 as the disk size and clicked the Pre-allocate disk space checkbox before clicking the Apply button, as shown in below. This added space is necessary because Oracle Database 23c Free as a Docker instance requires almost 10 GB of local space.
After clicking the Apply button, I checked Ubuntu with the “df -h” command and found there was no change. That’s unlike doing the same thing on AlmaLinux or a RedHat distribution, which was surprising.
The next set of steps required that I manually add the space to the Ubuntu instance:
- Start the Ubuntu VM and check the instance’s disk information with fdisk:
sudo fdisk -l
The log file for this is:
Display detailed console log →
Disk /dev/loop0: 238.77 MiB, 250372096 bytes, 489008 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop1: 73.86 MiB, 77443072 bytes, 151256 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop2: 349.7 MiB, 366682112 bytes, 716176 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop3: 91.69 MiB, 96141312 bytes, 187776 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop4: 496.98 MiB, 521121792 bytes, 1017816 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop5: 45.93 MiB, 48160768 bytes, 94064 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop6: 128.92 MiB, 135184384 bytes, 264032 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop7: 63.45 MiB, 66531328 bytes, 129944 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/fd0: 1.41 MiB, 1474560 bytes, 2880 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: dos Disk identifier: 0x90909090 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type /dev/fd0p1 2425393296 4850786591 2425393296 1.1T 90 unknown /dev/fd0p2 2425393296 4850786591 2425393296 1.1T 90 unknown /dev/fd0p3 2425393296 4850786591 2425393296 1.1T 90 unknown /dev/fd0p4 2425393296 4850786591 2425393296 1.1T 90 unknown GPT PMBR size mismatch (41943039 != 83886079) will be corrected by write. Disk /dev/sda: 40 GiB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Disk model: VMware Virtual S Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: gpt Disk identifier: 7906AE0B-498C-4FE4-8B45-9CD1B2265197 Device Start End Sectors Size Type /dev/sda1 2048 4095 2048 1M BIOS boot /dev/sda2 4096 1054719 1050624 513M EFI System /dev/sda3 1054720 41940991 40886272 19.5G Linux filesystem Disk /dev/loop8: 40.84 MiB, 42827776 bytes, 83648 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop9: 304 KiB, 311296 bytes, 608 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop10: 452 KiB, 462848 bytes, 904 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop13: 496.88 MiB, 521015296 bytes, 1017608 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop12: 240.05 MiB, 251707392 bytes, 491616 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop11: 4 KiB, 4096 bytes, 8 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop14: 346.33 MiB, 363151360 bytes, 709280 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop16: 12.32 MiB, 12922880 bytes, 25240 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop17: 73.9 MiB, 77492224 bytes, 151352 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop15: 175.83 MiB, 184373248 bytes, 360104 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop18: 63.46 MiB, 66547712 bytes, 129976 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk /dev/loop19: 40.86 MiB, 42840064 bytes, 83672 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
After running fdisk, I rechecked disk allocation with df -h and saw no change:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on tmpfs 388M 2.1M 386M 1% /run /dev/sda3 20G 14G 4.6G 75% / tmpfs 1.9G 28K 1.9G 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock /dev/sda2 512M 6.1M 506M 2% /boot/efi tmpfs 388M 108K 388M 1% /run/user/1000
- So, I installed Ubuntu’s user space utility gparted:
sudo apt install gparted
The log file for this is:
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: gparted-common Suggested packages: dmraid gpart jfsutils kpartx mtools reiser4progs reiserfsprogs udftools xfsprogs exfatprogs The following NEW packages will be installed: gparted gparted-common 0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 4 not upgraded. Need to get 490 kB of archives. After this operation, 2,128 kB of additional disk space will be used. Do you want to continue? [Y/n] Y Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 gparted-common all 1.3.1-1ubuntu1 [71.9 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 gparted amd64 1.3.1-1ubuntu1 [418 kB] Fetched 490 kB in 2s (211 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package gparted-common. (Reading database ... 203026 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../gparted-common_1.3.1-1ubuntu1_all.deb ... Unpacking gparted-common (1.3.1-1ubuntu1) ... Selecting previously unselected package gparted. Preparing to unpack .../gparted_1.3.1-1ubuntu1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking gparted (1.3.1-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up gparted-common (1.3.1-1ubuntu1) ... Setting up gparted (1.3.1-1ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for mailcap (3.70+nmu1ubuntu1) ... Processing triggers for desktop-file-utils (0.26-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for hicolor-icon-theme (0.17-2) ... Processing triggers for gnome-menus (3.36.0-1ubuntu3) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ...
- After installing the gparted utility (manual can be found here), you can launch it with the following syntax:
sudo gpartedYou’ll see the following in the console, which you can ignore.
GParted 1.3.1 configuration --enable-libparted-dmraid --enable-online-resize libparted 3.4
It launches a GUI interface that should look something like the following:
Right-click on the /dev/sda3 Partition and the GParted application will present the following context popup menu. Click the Resize/Move menu option.
The attempt to resize the disk at this point GParted will raise a read-only exception like the following:
You might open a new shell and fix the disk at the command-line but you’ll need to relaunch gparted regardless. So, you should close gparted and run the following commands:
sudo mount -o remount -rw / sudo mount -o remount -rw /var/snap/firefox/common/host-hunspell
When you relaunch GParted, you see that the graphic depiction has changed when you right-click on the /dev/sda3 Partition as follows:
Click on the highlighted box with the arrow and drag it all the way to the right. It will then show you something like the following.
Click the Resize button to make the change and add the space to the Ubuntu file system and see something like the following in Gparted:
Choose Edit in the menu bar and then Apply All Operations to effect the change in the disk allocation. The last dialog will require you to verify you want to make the changes. Click the Apply button to make the changes.
Click the close for the GParted application and then you can rerun the following command:
df -h
You will see that you now have 19.5 GB of additional space:
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on tmpfs 388M 2.2M 386M 1% /run /dev/sda3 39G 19.5G 23G 39% / tmpfs 1.9G 28K 1.9G 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock /dev/sda2 512M 6.1M 506M 2% /boot/efi tmpfs 388M 116K 388M 1% /run/user/1000
- Finally, you can now successfully download the latest Docker version of Oracle Database 23c Free with the following command:
docker run --name oracle23c -p 1521:1521 -p 5500:5500 -e ORACLE_PWD=cangetin container-registry.oracle.com/database/free:latest
Since you haven’t downloaded the container, you’ll get a warning that it is unable to find the image before it discovers it and downloads it. This will take several minutes. At the conclusion, it will start the Oracle Database Net Listener and begin updating files. the updates may take quite a while to complete.
The basic download console output looks like the following and if you check your disk space you’ve downloaded about 14 GB in the completed container.
Unable to find image 'container-registry.oracle.com/database/free:latest' locally latest: Pulling from database/free 089fdfcd47b7: Pull complete 43c899d88edc: Pull complete 47aa6f1886a1: Pull complete f8d07bb55995: Pull complete c31c8c658c1e: Pull complete b7d28faa08b4: Pull complete 1d0d5c628f6f: Pull complete db82a695dad3: Pull complete 25a185515793: Pull complete Digest: sha256:5ac0efa9896962f6e0e91c54e23c03ae8f140cf6ed43ca09ef4354268a942882 Status: Downloaded newer image for container-registry.oracle.com/database/free:latest
My detailed log file for the complete recovery operation is:
Display detailed console log →
Starting Oracle Net Listener. Oracle Net Listener started. Starting Oracle Database instance FREE. Oracle Database instance FREE started. The Oracle base remains unchanged with value /opt/oracle SQL*Plus: Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Production on Thu Nov 30 22:40:55 2023 Version 23.3.0.23.09 Copyright (c) 1982, 2023, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connected to: Oracle Database 23c Free Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Develop, Learn, and Run for Free Version 23.3.0.23.09 SQL> User altered. SQL> User altered. SQL> Session altered. SQL> User altered. SQL> Disconnected from Oracle Database 23c Free Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Develop, Learn, and Run for Free Version 23.3.0.23.09 The Oracle base remains unchanged with value /opt/oracle ######################### DATABASE IS READY TO USE! ######################### The following output is now a tail of the alert.log: Completed: Pluggable database FREEPDB1 opened read write Completed: ALTER DATABASE OPEN 2023-11-30T22:40:55.538359+00:00 =========================================================== Dumping current patch information =========================================================== No patches have been applied =========================================================== 2023-11-30T22:40:57.521629+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):TABLE AUDSYS.AUD$UNIFIED: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P342 (3440) VALUES LESS THAN (TIMESTAMP' 2023-12-01 00:00:00') 2023-11-30T22:41:00.565540+00:00 TABLE SYS.WRP$_REPORTS: ADDED AUTOLIST FRAGMENT SYS_P413 (3) VALUES (( 1418518649, TO_DATE(' 2023-11-27 00:00:00', 'syyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss', 'nls_calendar=gregorian') )) TABLE SYS.WRP$_REPORTS_DETAILS: ADDED AUTOLIST FRAGMENT SYS_P414 (3) VALUES (( 1418518649, TO_DATE(' 2023-11-27 00:00:00', 'syyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss', 'nls_calendar=gregorian') )) TABLE SYS.WRP$_REPORTS_TIME_BANDS: ADDED AUTOLIST FRAGMENT SYS_P417 (3) VALUES (( 1418518649, TO_DATE(' 2023-11-27 00:00:00', 'syyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss', 'nls_calendar=gregorian') )) 2023-11-30T22:41:45.639208+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):Resize operation completed for file# 13, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/FREEPDB1/sysaux01.dbf, old size 317440K, new size 327680K 2023-11-30T22:41:45.663044+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):Resize operation completed for file# 13, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/FREEPDB1/sysaux01.dbf, old size 327680K, new size 337920K 2023-11-30T22:46:51.616417+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 201, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/temp01.dbf, old size 20480K, new size 86016K Resize operation completed for file# 201, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/temp01.dbf, old size 86016K, new size 151552K Resize operation completed for file# 201, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/temp01.dbf, old size 151552K, new size 217088K 2023-11-30T22:46:53.024736+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 201, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/temp01.dbf, old size 217088K, new size 282624K Resize operation completed for file# 201, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/temp01.dbf, old size 282624K, new size 348160K 2023-11-30T22:50:45.816010+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 3, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/sysaux01.dbf, old size 573440K, new size 593920K 2023-11-30T23:00:46.159283+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 3, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/sysaux01.dbf, old size 593920K, new size 604160K 2023-11-30T23:00:46.228087+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):Resize operation completed for file# 13, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/FREEPDB1/sysaux01.dbf, old size 337920K, new size 358400K 2023-12-01T00:30:43.494249+00:00 --ATTENTION-- Heavy swapping observed on system WARNING: Heavy swapping observed on system in last 5 mins. Heavy swapping can lead to timeouts, poor performance, and instance eviction. 2023-12-01T12:40:07.820678+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-01T16:09:32.702179+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Time drifts can result in unexpected behavior such as time-outs. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-01T18:02:02.658867+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):Resize operation completed for file# 13, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/FREEPDB1/sysaux01.dbf, old size 358400K, new size 368640K 2023-12-01T18:22:03.858970+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 3, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/sysaux01.dbf, old size 604160K, new size 624640K 2023-12-01T20:31:39.671144+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Time drifts can result in unexpected behavior such as time-outs. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-01T22:16:50.007797+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Time drifts can result in unexpected behavior such as time-outs. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-01T23:11:39.776733+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 3, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/sysaux01.dbf, old size 624640K, new size 634880K 2023-12-01T23:11:39.920882+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):Resize operation completed for file# 13, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/FREEPDB1/sysaux01.dbf, old size 368640K, new size 378880K 2023-12-01T23:11:45.530407+00:00 Begin automatic SQL Tuning Advisor run for special tuning task "SYS_AUTO_SQL_TUNING_TASK". 2023-12-01T23:11:46.626668+00:00 End automatic SQL Tuning Advisor run for special tuning task "SYS_AUTO_SQL_TUNING_TASK". 2023-12-01T23:11:56.518724+00:00 TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTHEAD_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P473 (45260) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-02 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTGRM_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P476 (45260) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-02 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) 2023-12-01T23:13:58.659641+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 1, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/system01.dbf, old size 1085440K, new size 1095680K 2023-12-01T23:14:27.016016+00:00 Thread 1 advanced to log sequence 3 (LGWR switch), current SCN: 3248652 Current log# 3 seq# 3 mem# 0: /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/redo03.log 2023-12-01T23:14:47.256059+00:00 cellip.ora not found. 2023-12-01T23:14:54.365395+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 11, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/undotbs01.dbf, old size 40960K, new size 46080K Resize operation completed for file# 11, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/undotbs01.dbf, old size 46080K, new size 51200K 2023-12-01T23:16:40.460917+00:00 --ATTENTION-- Heavy swapping observed on system WARNING: Heavy swapping observed on system in last 5 mins. Heavy swapping can lead to timeouts, poor performance, and instance eviction. 2023-12-02T11:40:23.802013+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-02T11:40:24.917287+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Time drifts can result in unexpected behavior such as time-outs. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-02T11:40:34.601396+00:00 TABLE SYS.ACTIVITY_TABLE$: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P493 (2) VALUES LESS THAN (202) 2023-12-02T19:35:06.380899+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Time drifts can result in unexpected behavior such as time-outs. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-02T19:35:11.094760+00:00 Begin automatic SQL Tuning Advisor run for special tuning task "SYS_AUTO_SQL_TUNING_TASK". 2023-12-02T19:35:11.913190+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTHEAD_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P442 (45261) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-03 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) FREEPDB1(3):TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTGRM_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P445 (45261) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-03 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) 2023-12-02T19:35:12.623823+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):TABLE SYS.ACTIVITY_TABLE$: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P446 (2) VALUES LESS THAN (202) 2023-12-02T19:35:15.630900+00:00 End automatic SQL Tuning Advisor run for special tuning task "SYS_AUTO_SQL_TUNING_TASK". 2023-12-02T19:35:26.656198+00:00 TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTHEAD_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P513 (45261) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-03 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTGRM_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P516 (45261) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-03 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) 2023-12-02T19:36:00.842540+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):TABLE SYS.WRP$_REPORTS: ADDED AUTOLIST FRAGMENT SYS_P482 (2) VALUES (( 2054829351, TO_DATE(' 2023-11-27 00:00:00', 'syyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss', 'nls_calendar=gregorian') )) FREEPDB1(3):TABLE SYS.WRP$_REPORTS_DETAILS: ADDED AUTOLIST FRAGMENT SYS_P483 (2) VALUES (( 2054829351, TO_DATE(' 2023-11-27 00:00:00', 'syyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss', 'nls_calendar=gregorian') )) FREEPDB1(3):TABLE SYS.WRP$_REPORTS_TIME_BANDS: ADDED AUTOLIST FRAGMENT SYS_P486 (2) VALUES (( 2054829351, TO_DATE(' 2023-11-27 00:00:00', 'syyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss', 'nls_calendar=gregorian') )) 2023-12-02T19:36:49.488283+00:00 cellip.ora not found. 2023-12-02T19:36:59.941785+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):Resize operation completed for file# 12, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/FREEPDB1/system01.dbf, old size 286720K, new size 296960K 2023-12-02T19:38:11.214065+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):cellip.ora not found. 2023-12-02T19:39:38.144241+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 3, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/sysaux01.dbf, old size 634880K, new size 645120K 2023-12-02T19:39:38.254317+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):Resize operation completed for file# 13, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/FREEPDB1/sysaux01.dbf, old size 378880K, new size 389120K 2023-12-02T19:39:45.971914+00:00 --ATTENTION-- Heavy swapping observed on system WARNING: Heavy swapping observed on system in last 5 mins. Heavy swapping can lead to timeouts, poor performance, and instance eviction. 2023-12-02T19:49:39.226372+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 3, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/sysaux01.dbf, old size 645120K, new size 655360K 2023-12-02T19:49:55.006771+00:00 Thread 1 cannot allocate new log, sequence 4 Private strand flush not complete Current log# 3 seq# 3 mem# 0: /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/redo03.log 2023-12-02T19:49:58.006305+00:00 Thread 1 advanced to log sequence 4 (LGWR switch), current SCN: 3327607 Current log# 1 seq# 4 mem# 0: /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/redo01.log 2023-12-02T19:51:10.096706+00:00 cellip.ora not found. 2023-12-02T19:59:39.923548+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 3, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/sysaux01.dbf, old size 655360K, new size 665600K 2023-12-02T23:44:23.322751+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Time drifts can result in unexpected behavior such as time-outs. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-03T01:20:19.592589+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Time drifts can result in unexpected behavior such as time-outs. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-03T01:25:01.817094+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):Resize operation completed for file# 13, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/FREEPDB1/sysaux01.dbf, old size 389120K, new size 399360K 2023-12-03T01:25:11.199280+00:00 TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTHEAD_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P553 (45262) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-04 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTGRM_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P556 (45262) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-04 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) 2023-12-03T01:25:13.434023+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTHEAD_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P502 (45262) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-04 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) FREEPDB1(3):TABLE SYS.WRI$_OPTSTAT_HISTGRM_HISTORY: ADDED INTERVAL PARTITION SYS_P505 (45262) VALUES LESS THAN (TO_DATE(' 2023-12-04 00:00:00', 'SYYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS', 'NLS_CALENDAR=GREGORIAN')) 2023-12-03T01:26:29.620704+00:00 FREEPDB1(3):cellip.ora not found. 2023-12-03T01:26:36.758289+00:00 cellip.ora not found. 2023-12-03T02:25:52.946809+00:00 Warning: VKTM detected a forward time drift. Time drifts can result in unexpected behavior such as time-outs. Please see the VKTM trace file for more details: /opt/oracle/diag/rdbms/free/FREE/trace/FREE_vktm_46.trc 2023-12-03T02:27:56.055089+00:00 --ATTENTION-- Heavy swapping observed on system WARNING: Heavy swapping observed on system in last 5 mins. Heavy swapping can lead to timeouts, poor performance, and instance eviction. 2023-12-03T02:32:47.996105+00:00 Resize operation completed for file# 3, fname /opt/oracle/oradata/FREE/sysaux01.dbf, old size 665600K, new size 675840K
You can connect to the Oracle Database 23c Free container with the following syntax:
docker exec -it -u root oracle23c bash |
At the command-line, you connect to the Oracle Database 23c Free container with the following syntax:
sqlplus system/cangetin@free |
You have arrived at the Oracle SQL prompt:
SQL*Plus: Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Production on Fri Dec 1 00:13:55 2023 Version 23.3.0.23.09 Copyright (c) 1982, 2023, Oracle. All rights reserved. Last Successful login time: Thu Nov 30 2023 23:27:54 +00:00 Connected to: Oracle Database 23c Free Release 23.0.0.0.0 - Develop, Learn, and Run for Free Version 23.3.0.23.09 SQL> |
As always, I hope this helps those trying to work with the newest Oracle stack.
SQL Developer & PostgreSQL
I had a request from one of the adjunct professors to connect SQL Developer to the PostgreSQL database. This is in support of our database programming class that teaches students how to write PL/SQL against the Oracle database and pgPL/SQL against the PostgreSQL database. We also demonstrate transactional management through Node.js, Python and Java.
Naturally, this is also a frequent step taken by those required to migrate PostgreSQL data models to an Oracle database. While my final solution requires mimicking Oracle’s database user to schema, it does work for migration purposes. I’ll update this post when I determine how to populate the database drop-down list.
The first step was figuring out where to put the PostgreSQL JDBC Java ARchive (.jar) file on a Linux distribution. You navigate to the end-user student account in a Terminal and change to the .sqldeveloper directory. Then, create a jdbc subdirectory as the student user with the following command:
mkdir /home/student/.sqldeveloper/jdbc |
Then, download the most current PostgreSQL JDBC Java ARchive (.jar) file and copy it into the /home/student/.sqldeveloper/jdbc, which you can see afterward with the following command:
ll /home/student/.sqldeveloper/jdbc |
It should display:
-rw-r--r--. 1 student student 1041081 Aug 9 13:46 postgresql-42.3.7.jar |
The next series of steps are done within SQL Developer. Launch SQL Developer and navigate to Tools and Preferences, like this:
Inside the Preferences dialog, navigate to Database and Third Party JDBC Drivers like shown and click the Add Entry button to proceed:
Inside the Select Path Entry dialog, select the current PostgreSQL JDBC Java ARchive (.jar) file, which is postgresql-42-3.7.jar in this example. Then, click the Select button.
You are returned to the Preferences dialog as shown below. Click the OK button to continue.
After completing the 3rd Party Java Driver setup, you attempt to create a new connection to the PostgreSQL database. You should see that you now have two available Database Type values: Oracle and PostgreSQL, as shown below:
When you click on the PostgreSQL Database Type, the dialog updates to the following view. Unfortunately, I couldn’t discover how to set the values in the list for the Choose Database drop down. Naturally, a sandboxed user can’t connect to the PostgreSQL database without qualifying the database name.
Unless you qualify the PostgreSQL database or connect as the postgres user with a privileged password, SQL Developer translates the absence of a database selection to a database name equivalent to the user’s name. That’s the default behavior for the Oracle database but differs from the behavior for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server. It returns the following
Status: Failure - Test failed: FATAL: database "student" does not exist |
As seen in the diaglog’s result when testing the connection:
Based on my hunch and not knowing how to populate the database field for the connection, I did the following:
- Created a Linux OS videodb user.
- Copied the .bashrc file with all the standard Oracle environment variables.
- Created the /home/videodb/.sqldeveloper/jdbc directory.
- Copied the postgresql-42.3.7.jar into the new jdbc directory.
- Connected as the postgres super user and created the PostgreSQL videodb user with this syntax:
CREATE USER videodb WITH ROLE dba ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'cangetin';
- As the postgres super user, granted the following privileges:
-- Grant privileges on videodb database videodb user. GRANT ALL ON DATABASE "videodb" TO "videodb"; -- Connect to the videodb database. \c -- Grant privileges. GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO videodb; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA public TO videodb;
- Added the following line to the pg_hba.conf file in the /var/lib/pgsql/15/data directory as the postgres user:
local all videodb peer - Connected as the switched from the student to videodb Linux user, and launched SQL Developer. Then, I used the Tools menu to create the 3rd party PostgreSQL JDBC Java ARchive (.jar) file in context of the SQL Developer program. Everything completed correctly.
- Created a new PostgreSQL connection in SQL Developer and tested it with success as shown:
- Saving the new PostgreSQL connection, I opened the connection and could run SQL statements and display the catalog information, as shown:
Connected as the videodb user to the videodb database I can display tables owned by student and videodb users:
-- List tables. \d List of relations Schema | Name | Type | Owner --------+--------------------------+----------+--------- public | new_hire | table | student public | new_hire_new_hire_id_seq | sequence | student public | oracle_test | table | videodb (3 rows)
In SQL Developer, you can also inspect the tables, as shown:
At this point, I’m working on trying to figure out how to populate the database drop-down table. However, I’ve either missed a key document or it’s unfortunate that SQL Developer isn’t as friendly as MySQL Workbench in working with 3rd Party drivers.