Archive for the ‘MySQL DBA’ tag
Ruby+MySQL on Ubuntu
This post goes through installing and configuring Ruby and Ruby on Rails for MySQL. The first step requires updating the Ubuntu OS:
sudo apt-get update |
Interestingly, I found that the man-db service had inadvertently stopped. It raised the following error:
E: dpkg was interrupted, you must manually run 'sudo dpkg --configure -a' to correct the problem. |
You run this command to find the problem with the dpkg utility:
sudo dpkg --configure -a |
It returned:
Setting up man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Updating database of manual pages ... man-db.service is a disabled or a static unit not running, not starting it. |
The following command started the man-db service:
sudo systemctl start man-db.service |
Next, you install the prerequisite packages with this command:
sudo apt-get install -y git-core zlib1g-dev build-essential libssl-dev libreadline-dev libyaml-dev libsqlite3-dev sqlite3 libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev libcurl4-openssl-dev software-properties-common libffi-dev |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done Note, selecting 'git' instead of 'git-core' build-essential is already the newest version (12.9ubuntu3). build-essential set to manually installed. libreadline-dev is already the newest version (8.1.2-1). libreadline-dev set to manually installed. git is already the newest version (1:2.34.1-1ubuntu1.10). git set to manually installed. software-properties-common is already the newest version (0.99.22.9). zlib1g-dev is already the newest version (1:1.2.11.dfsg-2ubuntu9.2). zlib1g-dev set to manually installed. The following additional packages will be installed: libssl3 Suggested packages: libcurl4-doc libidn11-dev libkrb5-dev libldap2-dev librtmp-dev libssh2-1-dev sqlite3-doc libssl-doc libyaml-doc The following NEW packages will be installed: libcurl4-openssl-dev libffi-dev libsqlite3-dev libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev libyaml-dev sqlite3 The following packages will be upgraded: libssl-dev libssl3 2 upgraded, 7 newly installed, 0 to remove and 18 not upgraded. Need to get 7,426 kB of archives. After this operation, 12.8 MB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libssl-dev amd64 3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13 [2,374 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libssl3 amd64 3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13 [1,902 kB] Get:3 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libcurl4-openssl-dev amd64 7.81.0-1ubuntu1.15 [386 kB] Get:4 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libsqlite3-dev amd64 3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3 [846 kB] Get:5 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libxml2-dev amd64 2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.3 [804 kB] Get:6 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libxslt1-dev amd64 1.1.34-4ubuntu0.22.04.1 [219 kB] Get:7 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 sqlite3 amd64 3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3 [768 kB] Get:8 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libffi-dev amd64 3.4.2-4 [63.7 kB] Get:9 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 libyaml-dev amd64 0.2.2-1build2 [62.8 kB] Fetched 7,426 kB in 1s (5,467 kB/s) Preconfiguring packages ... (Reading database ... 246735 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libssl-dev_3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libssl-dev:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13) over (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.12) ... Preparing to unpack .../libssl3_3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libssl3:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13) over (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.12) ... Setting up libssl3:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13) ... Selecting previously unselected package libcurl4-openssl-dev:amd64. (Reading database ... 246735 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../0-libcurl4-openssl-dev_7.81.0-1ubuntu1.15_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libcurl4-openssl-dev:amd64 (7.81.0-1ubuntu1.15) ... Selecting previously unselected package libsqlite3-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../1-libsqlite3-dev_3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libsqlite3-dev:amd64 (3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxml2-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../2-libxml2-dev_2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxml2-dev:amd64 (2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libxslt1-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../3-libxslt1-dev_1.1.34-4ubuntu0.22.04.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libxslt1-dev:amd64 (1.1.34-4ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package sqlite3. Preparing to unpack .../4-sqlite3_3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3_amd64.deb ... Unpacking sqlite3 (3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3) ... Selecting previously unselected package libffi-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../5-libffi-dev_3.4.2-4_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libffi-dev:amd64 (3.4.2-4) ... Selecting previously unselected package libyaml-dev:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../6-libyaml-dev_0.2.2-1build2_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libyaml-dev:amd64 (0.2.2-1build2) ... Setting up libyaml-dev:amd64 (0.2.2-1build2) ... Setting up libffi-dev:amd64 (3.4.2-4) ... Setting up libxml2-dev:amd64 (2.9.13+dfsg-1ubuntu0.3) ... Setting up libsqlite3-dev:amd64 (3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3) ... Setting up libcurl4-openssl-dev:amd64 (7.81.0-1ubuntu1.15) ... Setting up libssl-dev:amd64 (3.0.2-0ubuntu1.13) ... Setting up sqlite3 (3.37.2-2ubuntu0.3) ... Setting up libxslt1-dev:amd64 (1.1.34-4ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for install-info (6.8-4build1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.6) ... |
Use the cd command to change to the student home directory. Clone the asdf as the multiple runtime version manager with this command:
git clone https://github.com/excid3/asdf.git ~/.asdf |
The following is the output of the git clone command:
Cloning into '/home/student/.asdf'... remote: Enumerating objects: 8756, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (829/829), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (476/476), done. remote: Total 8756 (delta 428), reused 657 (delta 334), pack-reused 7927 Receiving objects: 100% (8756/8756), 3.10 MiB | 4.29 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (5148/5148), done. |
Next, you fix your .bashrc file by adding the following components:
echo '. "$HOME/.asdf/asdf.sh"' >> ~/.bashrc echo '. "$HOME/.asdf/completions/asdf.bash"' >> ~/.bashrc echo 'legacy_version_file = yes' >> ~/.asdfrc echo 'export EDITOR="code --wait"' >> ~/.bashrc |
Source the modifies shell, which you can do like this:
exec $SHELL |
or, like:
. ${HOME}/.bashrc |
Add the following asdf plug-ins:
asdf plugin add ruby asdf plugin add nodejs |
Install Ruby with the following command:
asdf install ruby 3.3.0 |
Display detailed console log →
Downloading ruby-build...
==> Downloading ruby-3.3.0.tar.gz...
-> curl -q -fL -o ruby-3.3.0.tar.gz https://cache.ruby-lang.org/pub/ruby/3.3/ruby-3.3.0.tar.gz
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 21.0M 100 21.0M 0 0 10.1M 0 0:00:02 0:00:02 --:--:-- 10.1M
==> Installing ruby-3.3.0...
-> ./configure "--prefix=$HOME/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0" --enable-shared --with-ext=openssl,psych,+
-> make -j 2
-> make install
==> Installed ruby-3.3.0 to /home/student/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0
asdf: Warn: You have configured asdf to preserve downloaded files (with always_keep_download=yes or --keep-download). But
asdf: Warn: the current plugin (ruby) does not support that. Downloaded files will not be preserved. |
Install Ruby Global with this syntax:
asdf global ruby 3.3.0 |
Update the Ruby Gems with this command:
gem update --system |
Display detailed console log →
Updating rubygems-update Fetching rubygems-update-3.5.5.gem Successfully installed rubygems-update-3.5.5 Parsing documentation for rubygems-update-3.5.5 Installing ri documentation for rubygems-update-3.5.5 Done installing documentation for rubygems-update after 1 seconds Parsing documentation for rubygems-update-3.5.5 Done installing documentation for rubygems-update after 0 seconds Installing RubyGems 3.5.5 Successfully built RubyGem Name: bundler Version: 2.5.5 File: bundler-2.5.5.gem Bundler 2.5.5 installed RubyGems 3.5.5 installed Regenerating binstubs Regenerating plugins Parsing documentation for rubygems-3.5.5 Installing ri documentation for rubygems-3.5.5 # 3.5.5 / 2024-01-18 ## Enhancements: * Installs bundler 2.5.5 as a default gem. ## Bug fixes: * Fix `require` activation conflicts when requiring default gems under some situations. Pull request [#7379](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7379) by deivid-rodriguez * Use cache_home instead of data_home in default_spec_cache_dir. Pull request [#7331](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7331) by mrkn ## Documentation: * Use squiggly heredocs in `Gem::Specification#description` documentation, so it doesn't add leading whitespace. Pull request [#7373](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7373) by bravehager # 3.5.4 / 2024-01-04 ## Enhancements: * Always avoid "Updating rubygems-update" message. Pull request [#7335](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7335) by deivid-rodriguez * Installs bundler 2.5.4 as a default gem. ## Bug fixes: * Make `gem update --system` respect ruby version constraints. Pull request [#7334](https://github.com/rubygems/rubygems/pull/7334) by deivid-rodriguez ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ RubyGems installed the following executables: /home/student/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0/bin/gem /home/student/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0/bin/bundle /home/student/.asdf/installs/ruby/3.3.0/bin/bundler Ruby Interactive (ri) documentation was installed. ri is kind of like man pages for Ruby libraries. You may access it like this: ri Classname ri Classname.class_method ri Classname#instance_method If you do not wish to install this documentation in the future, use the --no-document flag, or set it as the default in your ~/.gemrc file. See 'gem help env' for details. RubyGems system software updated |
You can confirm your Ruby install with two commands. First, use the which utility to check the Ruby install:
which -a ruby |
It should return:
/home/student/.asdf/shims/ruby |
Then, check the Ruby version:
ruby -v |
It should return:
ruby 3.3.0 (2023-12-25 revision 5124f9ac75) [x86_64-linux] |
Assuming you’ve installed and configured MySQL 8 on Ubuntu, you need this additional library to support the necessary Ruby Gem:
sudo apt-get install -y libmysqlclient-dev |
Now, you can install the current MySQL Ruby Gem:
gem install mysql2 |
You can now write a mysql_connection.rb program to verify a connection to the MySQL 8 database, like:
# Include Ruby Gem libraries. require 'rubygems' require 'mysql2' begin # Create new database connection. db = Mysql2::Client.new( :host => 'localhost' \ , :username => 'student' \ , :password => 'student' \ , :database => 'studentdb') # Create a result set. stmt = db.query('SELECT version() AS version') # Read through the result set hash. stmt.each do | row | puts "#{row['version']}" end # Release the result set resources. stmt.free rescue Mysql2::Error => e # Print the error. puts "ERROR #{e.errno} (#{e.sqlstate}): #{e.error}" puts "Can't connect to the MySQL database specified." # Signal an error. exit 1 ensure # Close the connection when it is open. db.close if db end |
Call the program with this syntax:
ruby mysql_connection.rb |
It should return:
Connected to the MySQL database server. |
You can verify the version with this mysql_version.rb program:
# Include Ruby Gem libraries. require 'rubygems' require 'mysql2' begin # Create new database connection. db = Mysql2::Client.new( :host => 'localhost' \ , :username => 'student' \ , :password => 'student' \ , :database => 'studentdb') # Create a result set. rs = db.query('SELECT version() AS version') # Read through the result set hash. rs.each do | row | puts "#{row['version']}" end # Release the result set resources. rs.free rescue Mysql2::Error => e # Print the error. puts "ERROR #{e.errno} (#{e.sqlstate}): #{e.error}" puts "Can't connect to the MySQL database specified." # Signal an error. exit 1 ensure # Close the connection when it is open. db.close if db end |
On Ubuntu, it should return:
8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1 |
If you don’t know anything about the mysql2 Ruby Gem, you should read the documentation. It’s very concise and requires a basic understanding of Ruby programming. The two specific pages who may want to check for the next examples are:
- The Mysql2 Statement Class list.
- The Mysql2 Result Class List
The mysql_version.rb version uses the known string literal for columns or column aliases returned by the SQL statement, which becomes the stmt (or statement) in the program. The next program eliminates the need to enumerate with the text-based columns from the query by using the Statement#fields array values by use of a numeric index. The numeric index returns the field names from the Statement#fields class to use in as the name for values in the Result#fields value found in the row variable of the for loop.
# Include Ruby Gem libraries. require 'rubygems' require 'mysql2' # Begin block. begin # Create a new connection resource. db = Mysql2::Client.new( :host => 'localhost' \ , :username => 'student' \ , :password => 'student' \ , :database => 'studentdb') # Create a result set. stmt = db.query("SELECT DISTINCT i.item_title, ra.rating " + \ "FROM item i INNER JOIN rating_agency ra " + \ "ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id " + \ "WHERE ra.rating_agency = 'MPAA'" + \ "ORDER BY 1") # Read through the result set hash. stmt.each do | row | out = "" i = 0 while i < stmt.fields.count() # Check when not last column and use the: # - Hash returned by the result set for the value, and # - String array value returned by the statement object # as the name value of the hash by leveraging its # numeric index. if i < stmt.fields.count() - 1 out += "#{row[stmt.fields[i]]}" out += ", " else out += "#{row[stmt.fields[i]]}" end i += 1 end puts "#{out}" end # Release the result set resources. stmt.free rescue Mysql2::Error => e # Print the error. puts "ERROR #{e.errno} (#{e.sqlstate}): #{e.error}" puts "Can't connect to MySQL database specified." # Signal an error. exit 1 ensure # Close the connection when it is open. db.close if db end |
It returns the select two columns from the query:
A Man for All Seasons, G Around the World in 80 Days, G Beau Geste, PG Brave Heart, R Camelot, G Casino Royale, PG-13 ... Tomorrow Never Dies, PG-13 Tora! Tora! Tora!, G Tron, PG |
The following mysql_query_params.rb Ruby example accepts a single argument to leverage a wild card query in MySQL:
require 'rubygems' require 'mysql2' # Input external arguments. arguments = ARGV # Check for one input parameter and substitute an empty string # when one isn't found. if arguments.length == 1 argument = arguments[0] else argument = "" end # Begin block. begin # Create a new connection resource. db = Mysql2::Client.new( :host => 'localhost' \ , :username => 'student' \ , :password => 'student' \ , :database => 'studentdb') # Create a result set. stmt = db.prepare("SELECT DISTINCT i.item_title, ra.rating " + \ "FROM item i INNER JOIN rating_agency ra " + \ "ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id " + \ "WHERE ra.rating_agency = 'MPAA'" + \ "AND i.item_title LIKE CONCAT(?,'%')" + \ "ORDER BY 1") # Bind the variable into the query. rs = stmt.execute(argument) # Read through the result set hash. rs.each do | row | out = "" i = 0 while i < rs.fields.count() # Check when not last column and use the: # - Hash returned by the result set for the value, and # - String array value returned by the statement object # as the name value of the hash by leveraging its # numeric index. if i < rs.fields.count() - 1 out += "#{row[rs.fields[i]]}" out += ", " else out += "#{row[rs.fields[i]]}" end i += 1 end puts "#{out}" end # Release the result set resources. rs.free rescue Mysql2::Error => e # Print the error. puts "ERROR #{e.errno} (#{e.sqlstate}): #{e.error}" puts "Can't connect to MySQL database specified." # Signal an error. exit 1 ensure # Close the connection when it is open. db.close if db end |
If you call the mysql_query_params.rb program with this syntax:
ruby mysql_aquery_params.rb Harry |
It’ll return the following from the studentdb database:
Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, PG Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows, Part 1, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows, Part 2, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Half Blood Prince, PG Harry Potter and the Order of the Phoenix, PG-13 Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, PG Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone, PG |
After that, you should install Rails (check for current version beyond 1/2024). Install Ruby Global with this syntax:
gem install rails -v 7.1.3 |
Check the version installed:
rails -v |
It should return:
Rails 7.1.3 |
Run this command to enable Rails for MySQL 8:
rails new myapp -d mysql |
If you want to configure a username and password for MySQL, edit the config/database.yml file.
As always, I hope this helps somebody looking for step-by-step guide.
Ubuntu, Perl & MySQL
Configuring Perl to work with MySQL is straight forward. While Perl is installed generally, you may need to install the libdbd-mysql-perl library.
You install it as a sudoer user with this syntax:
sudo apt install -y libdbd-mysql-perl |
Display detailed console log →
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree... Done Reading state information... Done The following additional packages will be installed: libmysqlclient21 The following NEW packages will be installed: libdbd-mysql-perl libmysqlclient21 0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 12 not upgraded. Need to get 1,389 kB of archives. After this operation, 7,143 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 libmysqlclient21 amd64 8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1 [1,301 kB] Get:2 http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/universe amd64 libdbd-mysql-perl amd64 4.050-5ubuntu0.22.04.1 [87.6 kB] Fetched 1,389 kB in 1s (1,213 kB/s) Selecting previously unselected package libmysqlclient21:amd64. (Reading database ... 235085 files and directories currently installed.) Preparing to unpack .../libmysqlclient21_8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libmysqlclient21:amd64 (8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Selecting previously unselected package libdbd-mysql-perl:amd64. Preparing to unpack .../libdbd-mysql-perl_4.050-5ubuntu0.22.04.1_amd64.deb ... Unpacking libdbd-mysql-perl:amd64 (4.050-5ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Setting up libmysqlclient21:amd64 (8.0.35-0ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Setting up libdbd-mysql-perl:amd64 (4.050-5ubuntu0.22.04.1) ... Processing triggers for man-db (2.10.2-1) ... Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.35-0ubuntu3.5) ... |
You can find the Perl version with the following version.pl program:
1 2 3 4 | #!/usr/bin/perl -w # Print the version. print "Perl ".$]."\n"; |
The first line lets you call the program without prefacing the program name with perl. The first line invokes a subshell of perl by default. You just need to ensure the file has read and execute privileges to run by using the
chmod 755 version.pl |
You call it with this:
./version.pl |
It prints:
Perl 5.034000 |
The following static_query.pl Perl program uses the Perl DBI library to query and return a data set based on a static query.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | #!/usr/bin/perl -w # Use the DBI library. use DBI; use strict; use warnings; # Create a connection. my $dbh = DBI->connect("DBI:mysql:database=studentdb;host=localhost:3306" ,"student","student",{'RaiseError' => 1}); # Create SQL statement. my $sql = "SELECT i.item_title , ra.rating , cl.common_lookup_meaning FROM item i INNER JOIN common_lookup cl ON i.item_type = cl.common_lookup_id INNER JOIN rating_agency ra ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id WHERE i.item_title LIKE 'Harry%' AND cl.common_lookup_type = 'BLU-RAY'"; # Prepare SQL statement. my $sth = $dbh->prepare($sql); # Execute statement and read result set. $sth->execute() or die $DBI::errstr; # Read through returned rows, assign elements explicitly to match SELECT-list. while (my @row = $sth->fetchrow_array()) { my $item_title = $row[0]; my $rating = $row[1]; my $lookup_meaning = $row[2]; print "$item_title, $rating, $lookup_meaning\n"; } # Close resources. $sth->finish(); |
It returns the following rows from the sample database:
Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone, PG, Blu-ray Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, PG, Blu-ray Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, PG, Blu-ray Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, PG-13, Blu-ray |
The following dynamic_query.pl Perl program uses the Perl DBI library to prepare a query, bind a local variable into the query, and return a data set based on a dynamic query.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | #!/usr/bin/perl -w # Use the DBI library. use DBI; use strict; use warnings; # Mimic a function parameter by using a local variable. my $item_title_in = 'Star'; # Create a connection. my $dbh = DBI->connect("DBI:mysql:database=studentdb;host=localhost:3306" ,"student","student",{'RaiseError' => 1}); # Create SQL statement. my $sql = "SELECT i.item_title , ra.rating , cl.common_lookup_meaning FROM item i INNER JOIN common_lookup cl ON i.item_type = cl.common_lookup_id INNER JOIN rating_agency ra ON i.item_rating_id = ra.rating_agency_id WHERE i.item_title LIKE CONCAT(?,'%') AND cl.common_lookup_type = 'BLU-RAY'"; # Prepare SQL statement. my $sth = $dbh->prepare($sql); # Bind a variable to first parameter in the query string. $sth->bind_param(1, $item_title_in); # Execute statement and read result set. $sth->execute() or die $DBI::errstr; # Read through returned rows, assign elements explicitly to match SELECT-list. while (my @row = $sth->fetchrow_array()) { my $item_title = $row[0]; my $rating = $row[1]; my $lookup_meaning = $row[2]; print "$item_title, $rating, $lookup_meaning\n"; } # Close resources. $sth->finish(); |
It returns the following rows from the sample database:
Star Wars II, PG, Blu-ray |
You can replace lines 34 through 40 with the following to read any number of columns into a comma-delimited row return:
34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 | # Read through returned rows, assign elements explicitly to match SELECT-list. while (my @row = $sth->fetchrow_array()) { # Read through a dynamic column list for column separated display. my $result = ''; foreach(@row) { if (length($result) == 0) { $result = $_; } else { $result .= ", " . $_; } } # Print comma-separted values by row. print $result . "\n" } |
It returns the following rows from the sample database:
Star Wars II, PG, Blu-ray |
As always, I hope this helps the reader solve a problem.
MySQL on Ubuntu

Fresh install of Ubuntu on my MacBook Pro i7 because Apple said the OS X was no longer upgradable. Time to install and configure MySQL Server. These are the steps to install MySQL on the Ubuntu Desktop.
Installation
- Update the Ubuntu OS by checking for, inspecting, and upgrading any available updates with the following commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt list sudo apt upgrade
- Check for available MySQL Server packages with this command:
apt-cache search binaries | grep -i mysql
It should return:
mysql-server - MySQL database server binaries and system database setup mysql-server-8.0 - MySQL database server binaries and system database setup mysql-server-core-8.0 - MySQL database server binaries default-mysql-server - MySQL database server binaries and system database setup (metapackage) default-mysql-server-core - MySQL database server binaries (metapackage) mariadb-server-10.6 - MariaDB database core server binaries mariadb-server-core-10.6 - MariaDB database core server files
- Check for more details on the MySQL packages with this command:
apt info -a mysql-server-8.0
- Install MySQL Server packages with this command:
sudo apt install mysql-server-8.0
- Start the MySQL Server service with this command:
sudo systemctl start mysql.service - Before you can run the mysql_secure_installation script, you must set the root password. If you skip this step the mysql_secure_installation script will enter an infinite loop and lock your terminal session. Log in to the mysql monitor with the following command:
sudo mysqlEnter a password with the following command (password is an insecure example):
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'C4nGet1n!';
Quit the mysql monitor session:
quit; - Run the mysql_secure_installation script with this command:
sudo mysql_secure_installationHere’s the typical output from running the mysql_secure_installation script:
Securing the MySQL server deployment. Enter password for user root: VALIDATE PASSWORD COMPONENT can be used to test passwords and improve security. It checks the strength of password and allows the users to set only those passwords which are secure enough. Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD component? Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: Y There are three levels of password validation policy: LOW Length >= 8 MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 2 Using existing password for root. Estimated strength of the password: 100 Change the password for root ? ((Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : N ... skipping. By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y Success. Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y Success. By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y - Dropping test database... Success. - Removing privileges on test database... Success. Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y Success. All done!
Configuration
The next step is configuration. It requires setting up the sample sakila and studentdb database. The syntax has changed from prior releases. Here are the new three steps:
- Grant the root user the privilege to grant to others, which root does not have by default. You use the following syntax as the MySQL root user:
mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost';
- Download the sakila database, which you can download from this site. Click on the sakila database’s TGZ download.
When you download the sakila zip file it creates a sakila-db folder in the /home/student/Downloads directory. Copy the sakila-db folder into the /home/student/Data/sakila directory. Then, change to the /home/student/Data/sakila/sakila-db directory, connect to mysql as the root user, and run the following command:
mysql> SOURCE /home/student/Data/sakila/sakila-db/sakila-schema.sql mysql> SOURCE /home/student/Data/sakila/sakila-db/sakila-data.sql
- Create the studentdb database with the following command as the MySQL root user:
mysql> CREATE DATABASE studentdb; - Create the user with a clear English password and grant the user student full privileges on the sakila and studentdb databases:
mysql> CREATE USER 'student'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'Stud3nt!'; mysql> GRANT ALL ON studentdb.* TO 'student'@'localhost'; mysql> GRANT ALL ON sakila.* TO 'student'@'localhost';
You can now connect to a sandboxed sakila database with the student user’s credentials, like:
mysql -ustudent -p -Dsakila |
or, you can now connect to a sandboxed studentdb database with the student user’s credentials, like:
mysql -ustudent -p -Dstudentdb |
MySQL Workbench Installation
sudo snap install mysql-workbench-community |
You have now configure the MySQL Server 8.0.
MySQL @SQL_MODE
Installing MySQL Workbench 8 on Windows, we discovered that the default configuration no longer sets ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY as part of the default SQL_MODE parameter value. While I’ve written a stored function to set the SQL_MODE parameter value for a session, some students didn’t understand that such a call is only valid in the scope of a connection to the database server. They felt the function didn’t work because they didn’t understand the difference between connecting to the MySQL CLI and clicking the lightening bolt in MySQL Workbench.
So, here are the instructions to reset the default SQL_MODE parameter value for Windows. You need to edit the setting in the my.ini file, which is in the C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0 directory. The default installation will have the following:
# Set the SQL mode to strict sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION" |
You need to change it to the following in an editor with Administrative privileges:
# Set the SQL mode to strict sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY" |
Then, you need to connect to the services by launching services.msc from the command prompt. In the list of services find MYSQL80 service and restart it. You can verify it by connecting to the MySQL 8.0.* server and running the following SQL query:
SELECT @@SQL_MODE: |
That’s how you convert Windows to use only traditional group by behaviors in SQL. As always, I hope this helps those looking for a solution.
Updating SQL_MODE
This is an update for MySQL 8 Stored PSM to add the ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY mode to the global SQL_MODE variable when it’s not set during a session. Here’s the code:
/* Drop procedure conditionally on whether it exists already. */ DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS set_full_group_by; /* Reset delimter to allow semicolons to terminate statements. */ DELIMITER $$ /* Create a procedure to verify and set connection parameter. */ CREATE PROCEDURE set_full_group_by() LANGUAGE SQL NOT DETERMINISTIC SQL SECURITY DEFINER COMMENT 'Set connection parameter when not set.' BEGIN /* Check whether full group by is set in the connection and if unset, set it in the scope of the connection. */ IF EXISTS (SELECT TRUE WHERE NOT REGEXP_LIKE(@@SESSION.SQL_MODE,'ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY')) THEN SET @@GLOBAL.SQL_MODE := CONCAT(@@SESSION.sql_mode,',ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY'); END IF; END; $$ /* Reset the default delimiter. */ DELIMITER ; |
You can call the set_full_group_by procedure with the CALL command:
CALL set_full_group_by(); |
You can see the SQL_MODE variable with the following query:
SELECT @@GLOBAL.SQL_MODE; |
It’ll return:
+---------------------------------------------------------------+ | @@GLOBAL.SQL_MODE | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ | ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION | +---------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) |
As always, I hope this helps those looking to solve this type of problem.
GROUP BY Quirk
It’s always interesting to see how others teach SQL courses. It can be revealing as to whether they understand SQL or only understand a dialect of SQL. In this case, one of my old students was taking a graduate course in SQL and the teacher was using MySQL. The teacher made an issue of using ANSI SQL:1999 or SQL3 and asked the following question, which I suspect is a quiz bank question from a textbook:
“How would you get all students’ names and for each student the number of courses that the
student has registered for?”
They referenced the MySQL 5.7 documentation for the GROUP BY and SQL:1999 as if MySQL implemented the ANSI SQL:1999 specification defined the standard. I didn’t know whether to laugh or cry because they were referring to MySQL 5.7 when we’re all using MySQL 8 and anybody who’s worked in more than MySQL knows that the behavior for a GROUP BY in MySQL can work without listing the necessary non-aggregated columns in the SELECT-list.
For example, their working solution, which is from the instructor and the author of their MySQL textbook the correct perspective of ANSI:1999 behavior. It doesn’t matter that their solution is actually based on ANSI:1992 not ANSI:1999 because it will only succeed because of a quirk of MySQL:
SELECT a.studentname , COUNT(b.courseid) FROM students a INNER JOIN registeredcourses b ON a.studentid = b.studentid GROUP BY a.studentid; |
While it works in MySQL, it doesn’t work because it conforms to an ANSI standard. It works in MySQL, notwithstanding that standard because it violates the standard.
In Oracle, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server, it raises an exception. For example, Oracle raises the following exception:
SELECT a.studentname
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-00979: not a GROUP BY expression |
The correct way to write the GROUP BY is:
SELECT a.studentname , COUNT(b.courseid) FROM students a INNER JOIN registeredcourses b ON a.studentid = b.studentid INNER JOIN courses c ON b.courseid = c.courseid GROUP BY a.studentname; |
Then, it would return:
Student Name Course IDs ------------------------------ ---------- Montgomery Scott 1 Leonard McCoy 2 James Tiberus Kirk 3 |
For reference, here’s a complete test case for MySQL:
/* Drop table conditionally. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS students; /* Create table. */ CREATE TABLE students ( studentID int unsigned primary key auto_increment , studentName varchar(30)); /* Drop table conditionally. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS courses; /* Create table. */ CREATE TABLE courses ( courseid int unsigned primary key auto_increment , coursename varchar(40)); /* Drop table conditionally. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS registeredcourses; /* Create table. */ CREATE TABLE registeredcourses ( courseid int unsigned , studentid int unsigned ); /* Insert into students. */ INSERT INTO students ( studentName ) VALUES ('James Tiberus Kirk') ,('Leonard McCoy') ,('Montgomery Scott'); /* Insert into courses. */ INSERT INTO courses ( coursename ) VALUES ('English Literature') ,('Physics') ,('English Composition') ,('Botany') ,('Mechanical Engineering'); /* Insert into registeredcourses. */ INSERT INTO registeredcourses ( studentid , courseid ) VALUES (1,1) ,(1,3) ,(1,4) ,(2,2) ,(2,5) ,(3,4); /* Check global sql_mode to ensure only_full_group_by is set. */ SELECT @@GLOBAL.SQL_MODE; /* Query with a column not found in the SELECT-list. */ SELECT a.studentname , COUNT(b.courseid) FROM students a INNER JOIN registeredcourses b ON a.studentid = b.studentid GROUP BY a.studentid; /* Query consistent with ANSI SQL:1992 */ SELECT a.studentname , COUNT(b.courseid) FROM students a INNER JOIN registeredcourses b ON a.studentid = b.studentid INNER JOIN courses c ON b.courseid = c.courseid GROUP BY a.studentname; |
and, another complete test case for Oracle:
/* Drop tabhe unconditionallly. */ DROP TABLE students; /* Create table. */ CREATE TABLE students ( studentID NUMBER PRIMARY KEY , studentName VARCHAR(30)); /* Drop table unconditionally. */ DROP TABLE courses; /* Create table. */ CREATE TABLE courses ( courseid NUMBER PRIMARY KEY , coursename VARCHAR(40)); /* Drop table unconditionally. */ DROP TABLE registeredcourses; /* Create table. */ CREATE TABLE registeredcourses ( courseid NUMBER , studentid NUMBER ); /* Insert values in student. */ INSERT INTO students ( studentid, studentName ) VALUES (1,'James Tiberus Kirk'); INSERT INTO students ( studentid, studentName ) VALUES (2,'Leonard McCoy'); INSERT INTO students ( studentid, studentName ) VALUES (3,'Montgomery Scott'); /* Insert values in courses. */ INSERT INTO courses ( courseid, coursename ) VALUES (1,'English Literature'); INSERT INTO courses ( courseid, coursename ) VALUES (2,'Physics'); INSERT INTO courses ( courseid, coursename ) VALUES (3,'English Composition'); INSERT INTO courses ( courseid, coursename ) VALUES (4,'Botany'); INSERT INTO courses ( courseid, coursename ) VALUES (5,'Mechanical Engineering'); /* Insert values into registeredcourses. */ INSERT INTO registeredcourses ( studentid, courseid ) VALUES (1,1); INSERT INTO registeredcourses ( studentid, courseid ) VALUES (1,3); INSERT INTO registeredcourses ( studentid, courseid ) VALUES (1,4); INSERT INTO registeredcourses ( studentid, courseid ) VALUES (2,2); INSERT INTO registeredcourses ( studentid, courseid ) VALUES (2,5); INSERT INTO registeredcourses ( studentid, courseid ) VALUES (3,4); /* Non-ANSI SQL GROUP BY statement. */ SELECT a.studentname , COUNT(b.courseid) FROM students a INNER JOIN registeredcourses b ON a.studentid = b.studentid GROUP BY a.studentid; /* ANSI SQL GROUP BY statement. */ SELECT a.studentname AS "Student Name" , COUNT(b.courseid) AS "Course IDs" FROM students a INNER JOIN registeredcourses b ON a.studentid = b.studentid INNER JOIN courses c ON b.courseid = c.courseid GROUP BY a.studentname; |
I hope this helps those learning the correct way to write SQL.
MySQL PNG Files
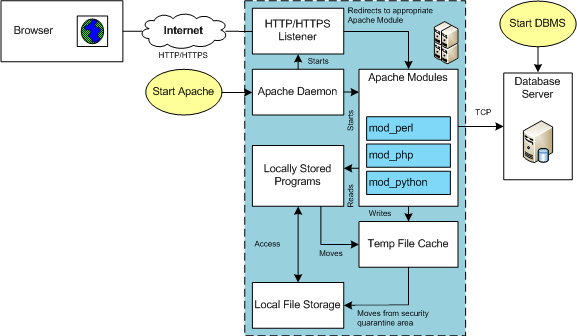
LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, Perl/PHP/Python) Architecture is very flexible. All the components can be positioned on the same server or different servers. The servers are divided into two types. The types are known as the Application or database tiers. Generally, the application tier holds the Apache Server, any Apache Modules, and local copies of Server Side Includes (SSI) programs.
In many development environments, you also deploy the client to the same machine. This means a single machine runs the database server, the application server, and the browser. The lab for this section assumes these configurations.
Before you test an installation, you should make sure that you’ve started the database and Apache server. In an Oracle LAMP configuration (known as an OLAP – Oracle, Linux, Apache, Perl/PHP/Python), you must start both the Oracle Listener and database. MySQL starts the listener when you start the database. You must also start the Apache Server. The Apache Server also starts an Apache Listener, which listens for incoming HTTP/HTTPS requests. It listens on Port 80 unless you override that setting in the httpd.conf file.
The URI reaches the server and is redirected to an Apache Module based on configuration information found in the httpd.conf file. Spawned or child processes of the Apache Module then read programs into memory from the file system and run them. If you’ve uploaded a file the locally stored program can move it from a secure cache location to another local area for processing. The started programs can run independently or include other files as libraries, and they can communicate to the database server.
Working though PHP test cases against the MySQL database for my AlmaLinux installation and configuration, I discovered that the php-gd library weren’t installed by default. I had to add it to get my PHP programs to upload and display PNG files.
The log file for applying the php-gd packages:
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 3:59:15 ago on Wed 28 Dec 2022 08:17:58 PM EST. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: php-gd x86_64 8.0.20-3.el9 appstream 43 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 43 k Installed size: 110 k Downloading Packages: php-gd-8.0.20-3.el9.x86_64.rpm 196 kB/s | 43 kB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 39 kB/s | 43 kB 00:01 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : php-gd-8.0.20-3.el9.x86_64 1/1 Running scriptlet: php-gd-8.0.20-3.el9.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : php-gd-8.0.20-3.el9.x86_64 1/1 Installed: php-gd-8.0.20-3.el9.x86_64 Complete! |
The balance of this page demonstrates how to upload, store, and manage Text (Character Large Data Streams) and BLOBs (Binary Large Objects). It provides MySQL equivalent instructions to those for manaing LOBs in an Oracle database. As covered in Chapter 8 in my Oracle Database 11g PL/SQL Programming book.
Before you begin these steps, you should have already installed Zend Server Community Edition. If you haven’t done so, please click here for instructions.
Create directories or folders, and position code →
This section provides you with instructions on how to position the code components in Windows, at least for the newbie. If you’re on Linux, you probably know how to do most if not all of this already. Likewise, if you already know how to put things in the right place, please choose your own locations.
- Create a
LOB(Large Object) directory for the PHP files inside thehtdocsdirectory.
![]()
- You can down the MySQL PHP Upload LOB Web Code zip file and unzip it into the directory you just created. It can co-exist with the Oracle equivalent if you’ve done that already.
Load a TEXT (like an Oracle CLOB) column to the MySQL database →
This is a copy of the three files required to load a large string to a MySQL database into a mediumtext data type. The code is in clear text because somebody asked for it. They’re nervous about zip files. Click the title above to expand all the code text.
MySQLCredentials.inc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <?php // Connection variables. define('HOSTNAME',"localhost"); define('USERNAME',"student"); define('PASSWORD',"student"); define('DATABASE',"sampledb"); ?> |
UploadItemDescMySQLForm.htm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | <html>
<head>
<title>
UploadItemDescMySQLForm.htm
</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="uploadForm"
action="UploadItemDescMySQL.php"
enctype="multipart/form-data"
method="post">
<table border=0 cellpadding=0 cellspacing=0>
<tr>
<td width=125>Item Number</td>
<td>
<input id="id" name="id" type="text">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width=125>Item Title</td>
<td>
<input id="title" name="title" type="text">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width=125>Select File</td>
<td>
<input id="uploadfilename" name="userfile" type="file">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width=125>Click Button to</td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Upload File"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html> |
UploadItemDescMySQL.php
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 | <?php // Set database credentials. include_once("MySQLCredentials.inc"); // Displayed moved file in web page. $item_desc = process_uploaded_file(); // Return successful attempt to connect to the database. if (!$c = @mysqli_connect(HOSTNAME,USERNAME,PASSWORD,DATABASE)) { // Print user message. print "Sorry! The connection to the database failed. Please try again later."; // Assign the mysqli_error() and format double and single quotes. print mysqli_error(); // Kill the resource. die(); } else { // Declare input variables. $id = (isset($_POST['id'])) ? (int) $_POST['id'] : $id = 21; $title = (isset($_POST['title'])) ? $_POST['title'] : $title = "Harry #1"; // Initialize a statement in the scope of the connection. $stmt = mysqli_stmt_init($c); // Declare a PL/SQL execution command. $sql = "Update item set item_desc = ? where item_id = ?"; // Prepate statement and link it to a connection. if (mysqli_stmt_prepare($stmt,$sql)) { mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt,"si",$item_desc,$id); // Execute it and print success or failure message. if (mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)) { query_insert($id,$title); } else { print "You're target row doesn't exist."; } } // Disconnect from database. mysqli_close($c); } // Query results afret an insert. function query_insert($id,$title) { // Return successful attempt to connect to the database. if (!$c = @mysqli_connect(HOSTNAME,USERNAME,PASSWORD,DATABASE)) { // Print user message. print "Sorry! The connection to the database failed. Please try again later."; // Assign the OCI error and format double and single quotes. print mysqli_error(); // Kill the resource. die(); } else { // Initialize a statement in the scope of the connection. $stmt = mysqli_stmt_init($c); // Declare a SQL SELECT statement returning a CLOB. $sql = "SELECT item_desc FROM item WHERE item_id = ?"; // Prepare statement. if (mysqli_stmt_prepare($stmt,$sql)) { mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt,"i",$id); // Execute it and print success or failure message. if (mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)) { // Bind result to local variable. mysqli_stmt_bind_result($stmt, $desc); // Read result. mysqli_stmt_fetch($stmt); // Format HTML table to display biography. $out = '<table border="1" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="0">'; $out .= '<tr>'; $out .= '<td align="center" class="e">'.$title.'</td>'; $out .= '</tr>'; $out .= '<tr>'; $out .= '<td class="v">'.$desc.'</td>'; $out .= '</tr>'; $out .= '</table>'; // Print the HTML table. print $out; } } // Disconnect from database. mysqli_close($c); } } // Manage file upload and return file as string. function process_uploaded_file() { // Declare a variable for file contents. $contents = ""; // Define the upload file name for Windows or Linux. if (preg_match(".Win32.",$_SERVER["SERVER_SOFTWARE"])) $upload_file = "C:\\temp\\".$_FILES['userfile']['name']; else $upload_file = "/tmp/".$_FILES['userfile']['name']; // Check for and move uploaded file. if (is_uploaded_file($_FILES['userfile']['tmp_name'])) move_uploaded_file($_FILES['userfile']['tmp_name'],$upload_file); // Open a file handle and suppress an error for a missing file. if ($fp = @fopen($upload_file,"r")) { // Read until the end-of-file marker. while (!feof($fp)) $contents .= fgetc($fp); // Close an open file handle. fclose($fp); } // Return file content as string. return $contents; } ?> |
Load a BLOB column to the MySQL database →
This is a copy of the four files required to load a large image to a MySQL database into a MEDIUMBLOB data type. The fourth file reads the binary image and translates it into an HTML header and image that can be read through a call to the src attribute of an img tag. You can find the call to the forth file in the UploadItemBlobMySQL.php.
The code is in clear text because somebody asked for it. They’re nervous about zip files. Click the title above to expand all the code text.
MySQLCredentials.inc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <?php // Connection variables. define('HOSTNAME',"localhost"); define('USERNAME',"student"); define('PASSWORD',"student"); define('DATABASE',"sampledb"); ?> |
UploadItemBlobMySQLForm.htm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | <html>
<head>
<title>
UploadItemBlobMySQLForm.htm
</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id="uploadForm"
action="UploadItemBlobMySQL.php"
enctype="multipart/form-data"
method="post">
<table border=0 cellpadding=0 cellspacing=0>
<tr>
<td width=125>Item Number</td>
<td>
<input id="id" name="id" type="text">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width=125>Item Title</td>
<td>
<input id="title" name="title" type="text">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width=125>Select File</td>
<td>
<input id="uploadfilename" name="userfile" type="file">
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width=125>Click Button to</td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Upload File"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html> |
UploadItemBlobMySQL.php
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 | <?php // Set database credentials. include_once("MySQLCredentials.inc"); // Displayed moved file in web page. $item_blob = process_uploaded_file(); // Return successful attempt to connect to the database. if (!$c = @mysqli_connect(HOSTNAME,USERNAME,PASSWORD,DATABASE)) { // Print user message. print "Sorry! The connection to the database failed. Please try again later."; // Assign the mysqli_error() error and format double and single quotes. print mysqli_error(); // Kill the resource. die(); } else { // Declare input variables. $id = (isset($_POST['id'])) ? (int) $_POST['id'] : 1021; $title = (isset($_POST['title'])) ? $_POST['title'] : "Harry #1"; // Initialize a statement in the scope of the connection. $stmt = mysqli_stmt_init($c); // Declare a PL/SQL execution command. $sql = "UPDATE item SET item_blob = ? WHERE item_id = ?"; // Prepare statement and link it to a connection. if (mysqli_stmt_prepare($stmt,$sql)) { mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt,"bi",$item_blob,$id); $start = 0; $chunk = 8192; while ($start < strlen($item_blob)) { mysqli_stmt_send_long_data($stmt,0,substr($item_blob,$start,$chunk)); $start += $chunk; } // Execute the PL/SQL statement. if (mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)) { query_insert($id,$title); } else { print "Your target row doesn't exist."; } } else { print "mysqli_stmt_prepare() failed."; } // Disconnect from database. mysqli_close($c); } // Query results afret an insert. function query_insert($id,$title) { // Return successful attempt to connect to the database. if (!$c = @mysqli_connect(HOSTNAME,USERNAME,PASSWORD,DATABASE)) { // Print user message. print "Sorry! The connection to the database failed. Please try again later."; // Assign the OCI error and format double and single quotes. print mysqli_error(); // Kill the resource. die(); } else { // Initialize a statement in the scope of the connection. $stmt = mysqli_stmt_init($c); // Declare a SQL SELECT statement returning a CLOB. $sql = "SELECT item_desc FROM item WHERE item_id = ?"; // Prepare statement and link it to a connection. if (mysqli_stmt_prepare($stmt,$sql)) { mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt,"i",$id); // Execute the PL/SQL statement. if (mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)) { // Bind result to local variable. mysqli_stmt_bind_result($stmt, $data); // Read result. mysqli_stmt_fetch($stmt); // Format HTML table to display BLOB photo and CLOB description. $out = '<table border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0">'; $out .= '<tr>'; $out .= '<td align="center" class="e">'.$title.'</td>'; $out .= '</tr>'; $out .= '<tr><td class="v">'; $out .= '<div>'; $out .= '<div style="margin-right:5px;float:left">'; $out .= '<img src="ConvertMySQLBlobToImage.php?id='.$id.'">'; $out .= '</div>'; $out .= '<div style="position=relative;">'.$data.'</div>'; $out .= '</div>'; $out .= '</td></tr>'; $out .= '</table>'; // Print the HTML table. print $out; } else { print "You're target row doesn't exist."; } } // Disconnect from database. mysqli_close($c); } } // Manage file upload and return file as string. function process_uploaded_file() { // Declare a variable for file contents. $contents = ""; // Define the upload file name for Windows or Linux. if (preg_match(".Win32.",$_SERVER["SERVER_SOFTWARE"])) $upload_file = "C:\\TEMP\\".$_FILES['userfile']['name']; else $upload_file = "/tmp/".$_FILES['userfile']['name']; // Check for and move uploaded file. if (is_uploaded_file($_FILES['userfile']['tmp_name'])) move_uploaded_file($_FILES['userfile']['tmp_name'],$upload_file); // Open a file handle and suppress an error for a missing file. if ($fp = @fopen($upload_file,"r")) { // Read until the end-of-file marker. while (!feof($fp)) $contents .= fgetc($fp); // Close an open file handle. fclose($fp); } // Return file content as string. return $contents; } ?> |
ConvertMySQLBlobToImage.php
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | <?php // Database credentials must be set manually because an include_once() function // call puts something ahead of the header, which causes a failure when rendering // an image. // Return successful attempt to connect to the database. if (!$c = @mysqli_connect("localhost","student","student","sampledb")) { // Print user message. print "Sorry! The connection to the database failed. Please try again later."; // Assign the OCI error and format double and single quotes. print mysqli_error(); // Kill the resource. die(); } else { // Declare input variables. $id = (isset($_GET['id'])) ? (int) $_GET['id'] : 1023; // Initialize a statement in the scope of the connection. $stmt = mysqli_stmt_init($c); // Declare a SQL SELECT statement returning a MediumBLOB. $sql = "SELECT item_blob FROM item WHERE item_id = ?"; // Prepare statement and link it to a connection. if (mysqli_stmt_prepare($stmt,$sql)) { mysqli_stmt_bind_param($stmt,"i",$id); // Execute the PL/SQL statement. if (mysqli_stmt_execute($stmt)) { // Bind result to local variable. mysqli_stmt_bind_result($stmt, $image); // Read result. mysqli_stmt_fetch($stmt); } } // Disconnect from database. mysqli_close($c); // Print the header first. header('Content-type: image/x-png'); imagepng(imagecreatefromstring($image)); } ?> |
- Create a
tempdirectory for the upload target location, as qualified in the PHP code. The PHP code works regardless of whether you’re on Windows or Linux, but it does depend on the creation of this directory.
- Create a directory or folder for the large file source directories. This directory is probably on your test machine (laptop) but it mimics a client laptop and would work if your server was on a different machine.
- Inside the Upload directory, you should create the following two directories:
- You should download the CLOB Text File zip file and unzip it into the
textfiles directory; then download the BLOB Image File zip file and unzip it into the imagefiles directory.Assuming you’ve downloaded the zip files and extracted them into the correct locations, this section is done.
Prepare the MySQL database →
This section provides you with instructions on how to ensure everything will work once the PHP programs call the database. Even if you have one of my sample Video Store databases, you should verify and add appropriate columns. This post assumes you’ve downloaded the one of my basic Video Store models
- Navigate to the directory that you created for SQL scripts, which should be
/home/student/Data/mysql. In that directory at the command prompt, connect as thestudentuser, which should be student. You connect to the MySQL database, with the following syntax as student (if you need more help, check this blog post on configuring MySQL).
mysql -ustudent -pstudent |
Once connected to the database, you run the files to create the database, like:
mysql> source /Data/mysql/create_mysql_store.sql mysql> source /Data/mysql/seed_mysql_store.sql |
- Navigate to the directory that you created for SQL scripts, which should be
/home/student/Data/mysql. In that directory at the command prompt, connect as thestudentuser, or whichever account you’re using. You should confirm that you have aitem_desccolumn ofTEXTdata type, and anitem_blobcolumn ofMEDIUMBLOBtype in theitemtable. If you don’t have those columns, you can add them with the following statement:
ALTER TABLE item ADD (item_desc TEXT, item_blob MEDIUMBLOB); |
After ensuring that you have those two columns, you’ve completed this section.
Test the Configuration →
This section shows you how to test all that you’ve done. It works provided you created the directories and extracted the zip file contents to their respective directories. The virtual URL actually maps to the /var/www/html/lob directory.
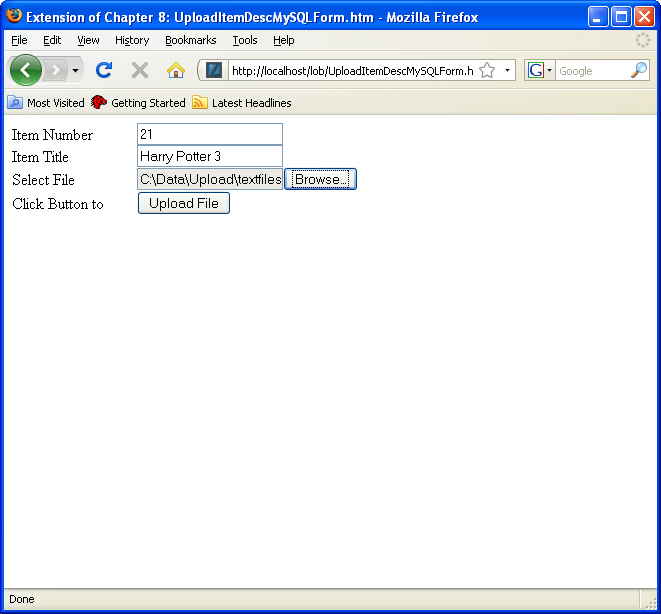
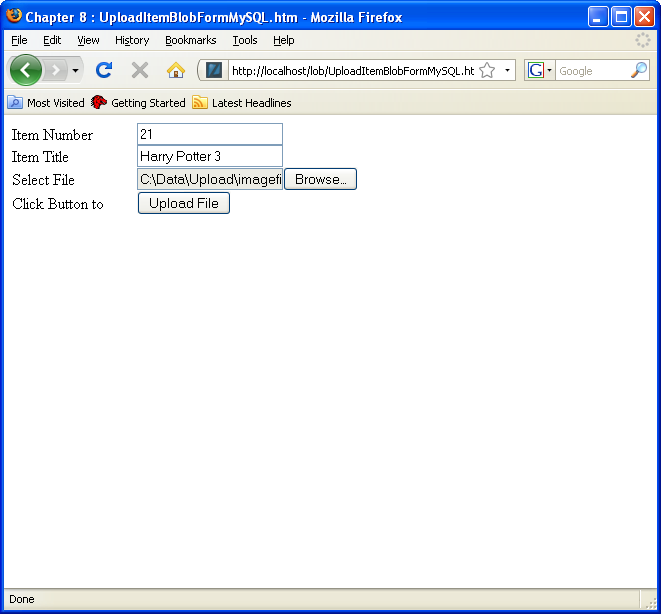
- Enter the
http://localhost/lob/UploadItemDescMySQLForm.htmURL, and complete the form by choosing a validitem_idcolumn value and text file from your/home/student/Upload/TextFilesdirectory. Then, click the Upload File button (you can see a larger version of the image by clicking on it).
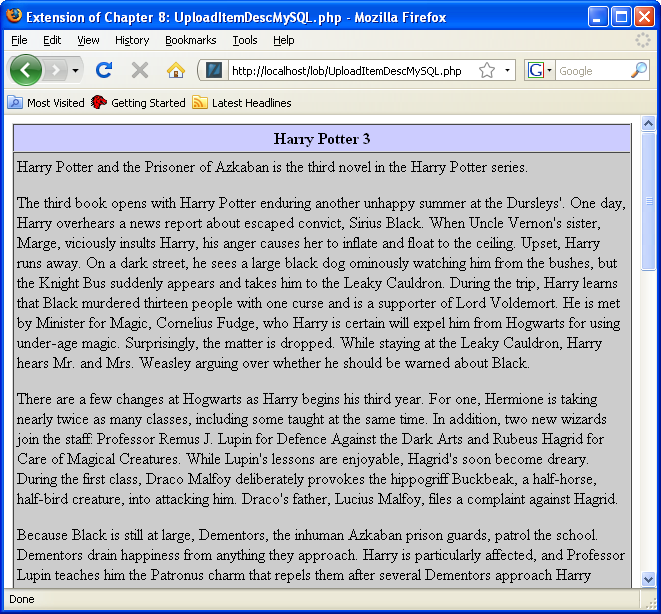
- This page displays after you successfully upload the text file to the database.
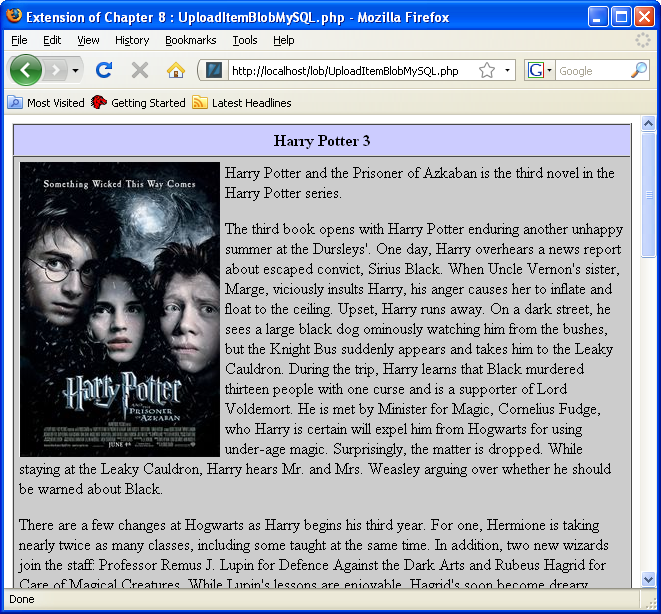
- Enter the
http://localhost/lob/UploadItemBlobFormMySQL.htmURL, and complete the form by choosing a validitem_idcolumn value and image file from your/home/student/Upload/ImageFilesdirectory. Then, click the Upload File button (you can see a larger version of the image by clicking on it).
- This page displays after you successfully upload the image file to the database.
Troubleshooting the Configuration →
This section shows you how to check why something isn’t working.
- The first thing to check are the credentials. They’re in the
MySQLCredentials.incfile. They’re posted with alocalhostmachine name,studentusername,studentpassword, andsampledbdatabase.
- Not to be funny, but the second thing to check are credentials. Specifically, you need to check the credentials in the
ConvertBlobToImage.phpfile. They’re individually entered in the connect string of this file because otherwise they put something in front of the header, which is disallowed to render the image.
- Check to see if the text or image file made it to the
/var/www/html/lob/tempdirectory. If they made it that far but no further, check to see if you have valid procedures in thestudentschema.
- Check whether the
TEXTandMEDIUMBLOBare loaded into the database. You use theLENGTHfunction, like this:
SELECT i.item_id , length(i.item_desc) , length(i.item_blob) FROM item i WHERE i.item_desc IS NOT NULL OR i.item_blob IS NOT NULL; |
- Check if the
item_idvalue is found in the list of values.
- If you’re stumped, add a comment and explain what’s up.
If you find any problems, please let me know. I’ll be happy to fix them.
AlmaLinux Install & Configuration

This is a collection of blog posts for installing and configuring AlmaLinux with the Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL databases and several programming languages. Sample programs show how to connect PHP and Python to the MySQL database.
- Installing AlmaLinux operating system
- Installing and configuring MySQL
- Installing Python-MySQL connector and provide sample programs
- Configuring Flask for Python on AlmaLinux with a complete software router instruction set.
- Installing Rust programming language and writing a sample program
- Installing and configuring LAMP stack with PHP and MySQL and a self-signed security key
- MySQL PNG Images in LAMP with PHP Programming
- Demonstration of how to write Perl that connects to MySQL
- Installing and configuring MySQL Workbench
- Installing and configuring PostgreSQL and pgAdmin4
- Identifying the required libnsl2-devel packages for SQL*Plus
- Writing and deploying a sqlplus function to use a read line wrapper
- Installing and configuring Visual Studio Code Editor
- Installing and configuring Java with connectivity to MySQL
- Installing and configuring Oracle SQL Developer
I used Oracle Database 11g XE in this instance to keep the footprint as small as possible. It required a few tricks and discovering the missing library that caused folks grief eleven years ago. I build another with a current Oracle Database XE after the new year.
If you see something that I missed or you’d like me to add, let me know. As time allows, I’ll try to do that. Naturally, the post will get updates as things are added later.
AlmaLinux MySQL Workbench
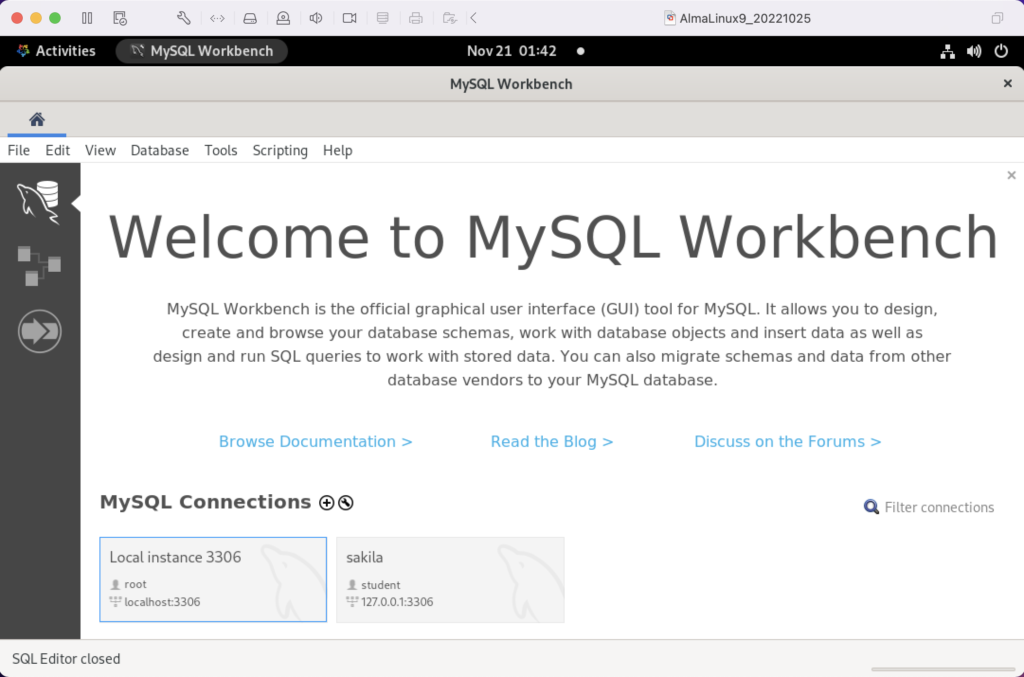
AlmaLinux doesn’t natively support MySQL Workbench but these notes will help you install it. The great news is that MySQL Workbench works perfectly once you’ve installed all the dependent libraries. It’ll look like the following:
Disclaimer of sorts:
AlmaLinux is an open-source, community-driven project that intends to fill the gap left by the demise of the CentOS stable release. AlmaLinux is a 1:1 binary compatible fork of RHEL® 9 and it is built by the AlmaLinux OS Foundation as a standalone, completely free OS. The AlmaLinux OS Foundation will support future RHEL® releases by updating AlmaLinux. Ongoing development efforts are governed by the members of the community.
You can download MySQL Workbench from the following website:
https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/workbench |
When you open this page, select the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 / Oracle Linux 9 (x86, 64-bit), RPM Package from the dropdown menu. Then, click the Download button. You may be prompted for your credentials or to create new credentials, but you can skip that by clicking on the No thanks, just start my download link.
When the download completes, open a terminal session as the student user. Navigate to the Downloads directory with the following command:
cd $HOME/Downloads |
List the files in the $HOME/Downloads directory and you should see:
mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.x86_64.rpm |
As the sudoer user or root, run the following command (naturally, exclude sudo if you’re the root user):
sudo dnf install -y mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.x86_64.rpm |
It will most likely fail with an error message like this:
Last metadata expiration check: 2:50:04 ago on Thu 17 Nov 2022 09:33:15 AM EST. Error: Problem: conflicting requests - nothing provides gtkmm30-devel needed by mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.src - nothing provides libzip-devel needed by mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.src - nothing provides proj-devel needed by mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.src - nothing provides swig >= 3.0 needed by mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.src (try to add '--skip-broken' to skip uninstallable packages or '--nobest' to use not only best candidate packages) |
AlmaLinux doesn’t install these prerequisite packages. You’ll need to resolve these dependencies by installing them in the right order and groups before you can run the MySQL Workbench packages.
You can discover missing packages at the pkgs.org website. You need to resolve all four prerequisites before installing MySQL Workbench.
- Let’s start with the gtkmm30-devel package, which has eight separate dependencies. Assuming you’re still in your $HOME/Downloads directory, you can run the following command to get the gtkmm30-devel for AlmaLinux 9:
wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
It downloads the following package:
gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
If you attempt to run it, the gtkmm30-devel package raises the following errors:
sudo dnf install -y gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64.rpm Last metadata expiration check: 0:41:13 ago on Thu 17 Nov 2022 02:39:59 PM EST. Error: Problem: conflicting requests - nothing provides pkgconfig(atkmm-1.6) >= 2.24.2 needed by gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64 - nothing provides pkgconfig(cairomm-1.0) >= 1.12.0 needed by gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64 - nothing provides pkgconfig(giomm-2.4) >= 2.54.0 needed by gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64 - nothing provides pkgconfig(pangomm-1.4) >= 1.12.0 needed by gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64 (try to add '--skip-broken' to skip uninstallable packages or '--nobest' to use not only best candidate packages)
While you only get four errors, there are more packages required. You need to use the wget utility to download these packages. I would recommend you create a temporary gtkmm30 subdirectory inside your $HOME/Downloads directory and change to that directory before downloading these files.
wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/atkmm-devel-2.28.2-2.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/cairomm-devel-1.14.2-10.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/gdk-pixbuf2-devel-2.42.6-2.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/glibmm24-devel-2.66.1-1.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/gtk3-devel-3.24.31-2.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/pangomm-devel-2.46.1-1.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/libsigc++20-devel-2.10.7-2.el9.x86_64.rpm
You need to run these as a set of prerequisites, so from your gtkmm30 subdirectory use the following dnf command as the sudoer user:
sudo dnf install -y *.rpm
The log file for this is:
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 0:09:20 ago on Sun 20 Nov 2022 12:52:28 AM EST. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: atkmm-devel x86_64 2.28.2-2.el9 @commandline 45 k cairomm-devel x86_64 1.14.2-10.el9 @commandline 62 k gdk-pixbuf2-devel x86_64 2.42.6-2.el9 @commandline 64 k glibmm24-devel x86_64 2.66.1-1.el9 @commandline 497 k gtk3-devel x86_64 3.24.31-2.el9 @commandline 4.1 M libsigc++20-devel x86_64 2.10.7-2.el9 @commandline 67 k pangomm-devel x86_64 2.46.1-1.el9 @commandline 65 k Upgrading: dbus-common noarch 1:1.12.20-6.el9 baseos 14 k dbus-daemon x86_64 1:1.12.20-6.el9 appstream 196 k dbus-libs x86_64 1:1.12.20-6.el9 baseos 151 k dbus-tools x86_64 1:1.12.20-6.el9 baseos 50 k fontconfig x86_64 2.14.0-1.el9 appstream 274 k freetype x86_64 2.10.4-9.el9 baseos 387 k fribidi x86_64 1.0.10-6.el9.2 appstream 84 k harfbuzz x86_64 2.7.4-8.el9 baseos 624 k harfbuzz-icu x86_64 2.7.4-8.el9 appstream 14 k libblkid x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 baseos 107 k libfdisk x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 baseos 154 k libmount x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 baseos 133 k libselinux x86_64 3.4-3.el9 baseos 85 k libselinux-utils x86_64 3.4-3.el9 baseos 158 k libsepol x86_64 3.4-1.1.el9 baseos 315 k libsmartcols x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 baseos 63 k libtiff x86_64 4.4.0-2.el9 appstream 195 k libuuid x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 baseos 27 k libxml2 x86_64 2.9.13-2.el9 baseos 746 k pcre2 x86_64 10.40-2.el9 baseos 236 k pcre2-syntax noarch 10.40-2.el9 baseos 143 k pcre2-utf16 x86_64 10.40-2.el9 appstream 216 k pcre2-utf32 x86_64 10.40-2.el9 appstream 205 k python3-libselinux x86_64 3.4-3.el9 appstream 185 k python3-libxml2 x86_64 2.9.13-2.el9 baseos 226 k util-linux x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 baseos 2.2 M util-linux-core x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 baseos 434 k util-linux-user x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 baseos 30 k Installing dependencies: at-spi2-atk-devel x86_64 2.38.0-4.el9 appstream 9.5 k at-spi2-core-devel x86_64 2.40.3-1.el9 appstream 134 k atk-devel x86_64 2.36.0-5.el9 appstream 172 k brotli x86_64 1.0.9-6.el9 appstream 313 k brotli-devel x86_64 1.0.9-6.el9 appstream 31 k bzip2-devel x86_64 1.0.8-8.el9 appstream 213 k cairo-devel x86_64 1.17.4-7.el9 appstream 190 k cairo-gobject-devel x86_64 1.17.4-7.el9 appstream 10 k dbus-devel x86_64 1:1.12.20-6.el9 appstream 33 k fontconfig-devel x86_64 2.14.0-1.el9 appstream 128 k freetype-devel x86_64 2.10.4-9.el9 appstream 1.1 M fribidi-devel x86_64 1.0.10-6.el9.2 appstream 25 k glib2-devel x86_64 2.68.4-5.el9 appstream 475 k graphite2-devel x86_64 1.3.14-9.el9 appstream 21 k harfbuzz-devel x86_64 2.7.4-8.el9 appstream 305 k libX11-devel x86_64 1.7.0-7.el9 appstream 940 k libXau-devel x86_64 1.0.9-8.el9 appstream 13 k libXcomposite-devel x86_64 0.4.5-7.el9 appstream 15 k libXcursor-devel x86_64 1.2.0-7.el9 appstream 21 k libXdamage-devel x86_64 1.1.5-7.el9 appstream 9.3 k libXext-devel x86_64 1.3.4-8.el9 appstream 72 k libXfixes-devel x86_64 5.0.3-16.el9 appstream 12 k libXft-devel x86_64 2.3.3-8.el9 appstream 18 k libXi-devel x86_64 1.7.10-8.el9 appstream 99 k libXinerama-devel x86_64 1.1.4-10.el9 appstream 13 k libXrandr-devel x86_64 1.5.2-8.el9 appstream 19 k libXrender-devel x86_64 0.9.10-16.el9 appstream 16 k libXtst-devel x86_64 1.2.3-16.el9 appstream 15 k libblkid-devel x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 appstream 17 k libdatrie-devel x86_64 0.2.13-4.el9 appstream 132 k libepoxy-devel x86_64 1.5.5-4.el9 appstream 133 k libffi-devel x86_64 3.4.2-7.el9 appstream 29 k libglvnd-core-devel x86_64 1:1.3.4-1.el9 appstream 17 k libglvnd-devel x86_64 1:1.3.4-1.el9 appstream 155 k libicu-devel x86_64 67.1-9.el9 appstream 830 k libmount-devel x86_64 2.37.4-9.el9 appstream 18 k libpng-devel x86_64 2:1.6.37-12.el9 appstream 290 k libselinux-devel x86_64 3.4-3.el9 appstream 113 k libsepol-devel x86_64 3.4-1.1.el9 appstream 40 k libthai-devel x86_64 0.1.28-8.el9 appstream 117 k libtiff-devel x86_64 4.4.0-2.el9 appstream 513 k libxcb-devel x86_64 1.13.1-9.el9 appstream 1.0 M libxkbcommon-devel x86_64 1.0.3-4.el9 appstream 61 k libxml2-devel x86_64 2.9.13-2.el9 appstream 828 k pango-devel x86_64 1.48.7-2.el9 appstream 141 k pcre-cpp x86_64 8.44-3.el9.3 appstream 26 k pcre-devel x86_64 8.44-3.el9.3 appstream 470 k pcre-utf16 x86_64 8.44-3.el9.3 appstream 184 k pcre-utf32 x86_64 8.44-3.el9.3 appstream 174 k pcre2-devel x86_64 10.40-2.el9 appstream 474 k perl-Filter x86_64 2:1.60-4.el9 appstream 81 k perl-encoding x86_64 4:3.00-462.el9 appstream 62 k perl-open noarch 1.12-479.el9 appstream 25 k pixman-devel x86_64 0.40.0-5.el9 appstream 17 k sysprof-capture-devel x86_64 3.40.1-3.el9 appstream 59 k wayland-devel x86_64 1.19.0-4.el9 appstream 132 k xorg-x11-proto-devel noarch 2021.4-2.el9 appstream 262 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 64 Packages Upgrade 28 Packages Total size: 23 M Total download size: 18 M Downloading Packages: (1/85): at-spi2-atk-devel-2.38.0-4.el9.x86_64.r 38 kB/s | 9.5 kB 00:00 (2/85): atk-devel-2.36.0-5.el9.x86_64.rpm 334 kB/s | 172 kB 00:00 (3/85): brotli-devel-1.0.9-6.el9.x86_64.rpm 354 kB/s | 31 kB 00:00 (4/85): at-spi2-core-devel-2.40.3-1.el9.x86_64. 167 kB/s | 134 kB 00:00 (5/85): cairo-devel-1.17.4-7.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.9 MB/s | 190 kB 00:00 (6/85): cairo-gobject-devel-1.17.4-7.el9.x86_64 179 kB/s | 10 kB 00:00 (7/85): brotli-1.0.9-6.el9.x86_64.rpm 413 kB/s | 313 kB 00:00 (8/85): dbus-devel-1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64.rpm 549 kB/s | 33 kB 00:00 (9/85): bzip2-devel-1.0.8-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 505 kB/s | 213 kB 00:00 (10/85): fribidi-devel-1.0.10-6.el9.2.x86_64.rp 492 kB/s | 25 kB 00:00 (11/85): fontconfig-devel-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64.r 891 kB/s | 128 kB 00:00 (12/85): graphite2-devel-1.3.14-9.el9.x86_64.rp 316 kB/s | 21 kB 00:00 (13/85): glib2-devel-2.68.4-5.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.1 MB/s | 475 kB 00:00 (14/85): harfbuzz-devel-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 850 kB/s | 305 kB 00:00 (15/85): freetype-devel-2.10.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.7 MB/s | 1.1 MB 00:00 (16/85): libXau-devel-1.0.9-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 170 kB/s | 13 kB 00:00 (17/85): libXcomposite-devel-0.4.5-7.el9.x86_64 273 kB/s | 15 kB 00:00 (18/85): libXcursor-devel-1.2.0-7.el9.x86_64.rp 344 kB/s | 21 kB 00:00 (19/85): libXdamage-devel-1.1.5-7.el9.x86_64.rp 133 kB/s | 9.3 kB 00:00 (20/85): libXfixes-devel-5.0.3-16.el9.x86_64.rp 256 kB/s | 12 kB 00:00 (21/85): libXext-devel-1.3.4-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 768 kB/s | 72 kB 00:00 (22/85): libXft-devel-2.3.3-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 324 kB/s | 18 kB 00:00 (23/85): libXinerama-devel-1.1.4-10.el9.x86_64. 205 kB/s | 13 kB 00:00 (24/85): libXi-devel-1.7.10-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 913 kB/s | 99 kB 00:00 (25/85): libXrender-devel-0.9.10-16.el9.x86_64. 295 kB/s | 16 kB 00:00 (26/85): libXrandr-devel-1.5.2-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 289 kB/s | 19 kB 00:00 (27/85): libXtst-devel-1.2.3-16.el9.x86_64.rpm 261 kB/s | 15 kB 00:00 (28/85): libblkid-devel-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 284 kB/s | 17 kB 00:00 (29/85): libX11-devel-1.7.0-7.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.4 MB/s | 940 kB 00:00 (30/85): libepoxy-devel-1.5.5-4.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 133 kB 00:00 (31/85): libdatrie-devel-0.2.13-4.el9.x86_64.rp 876 kB/s | 132 kB 00:00 (32/85): libffi-devel-3.4.2-7.el9.x86_64.rpm 426 kB/s | 29 kB 00:00 (33/85): libglvnd-core-devel-1.3.4-1.el9.x86_64 233 kB/s | 17 kB 00:00 (34/85): libmount-devel-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 280 kB/s | 18 kB 00:00 (35/85): libglvnd-devel-1.3.4-1.el9.x86_64.rpm 976 kB/s | 155 kB 00:00 (36/85): libpng-devel-1.6.37-12.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.9 MB/s | 290 kB 00:00 (37/85): libselinux-devel-3.4-3.el9.x86_64.rpm 801 kB/s | 113 kB 00:00 (38/85): libsepol-devel-3.4-1.1.el9.x86_64.rpm 636 kB/s | 40 kB 00:00 (39/85): libthai-devel-0.1.28-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 630 kB/s | 117 kB 00:00 (40/85): libicu-devel-67.1-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.3 MB/s | 830 kB 00:00 (41/85): libtiff-devel-4.4.0-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.6 MB/s | 513 kB 00:00 (42/85): libxkbcommon-devel-1.0.3-4.el9.x86_64. 710 kB/s | 61 kB 00:00 (43/85): pango-devel-1.48.7-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 914 kB/s | 141 kB 00:00 (44/85): pcre-cpp-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64.rpm 425 kB/s | 26 kB 00:00 (45/85): pcre-devel-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64.rpm 1.8 MB/s | 470 kB 00:00 (46/85): pcre-utf16-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64.rpm 1.5 MB/s | 184 kB 00:00 (47/85): libxml2-devel-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 828 kB 00:00 (48/85): libxcb-devel-1.13.1-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 1.0 MB 00:00 (49/85): pcre-utf32-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64.rpm 1.4 MB/s | 174 kB 00:00 (50/85): perl-Filter-1.60-4.el9.x86_64.rpm 704 kB/s | 81 kB 00:00 (51/85): perl-encoding-3.00-462.el9.x86_64.rpm 916 kB/s | 62 kB 00:00 (52/85): perl-open-1.12-479.el9.noarch.rpm 476 kB/s | 25 kB 00:00 (53/85): pixman-devel-0.40.0-5.el9.x86_64.rpm 272 kB/s | 17 kB 00:00 (54/85): sysprof-capture-devel-3.40.1-3.el9.x86 797 kB/s | 59 kB 00:00 (55/85): pcre2-devel-10.40-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.3 MB/s | 474 kB 00:00 (56/85): wayland-devel-1.19.0-4.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.0 MB/s | 132 kB 00:00 (57/85): xorg-x11-proto-devel-2021.4-2.el9.noar 1.3 MB/s | 262 kB 00:00 (58/85): dbus-daemon-1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.3 MB/s | 196 kB 00:00 (59/85): fontconfig-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.7 MB/s | 274 kB 00:00 (60/85): harfbuzz-icu-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 217 kB/s | 14 kB 00:00 (61/85): fribidi-1.0.10-6.el9.2.x86_64.rpm 700 kB/s | 84 kB 00:00 (62/85): libtiff-4.4.0-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.5 MB/s | 195 kB 00:00 (63/85): pcre2-utf32-10.40-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 205 kB 00:00 (64/85): python3-libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64.rp 1.5 MB/s | 185 kB 00:00 (65/85): pcre2-utf16-10.40-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 995 kB/s | 216 kB 00:00 (66/85): dbus-common-1.12.20-6.el9.noarch.rpm 203 kB/s | 14 kB 00:00 (67/85): dbus-tools-1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64.rpm 856 kB/s | 50 kB 00:00 (68/85): dbus-libs-1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.3 MB/s | 151 kB 00:00 (69/85): libblkid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.6 MB/s | 107 kB 00:00 (70/85): libfdisk-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.6 MB/s | 154 kB 00:00 (71/85): freetype-2.10.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.5 MB/s | 387 kB 00:00 (72/85): libmount-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.3 MB/s | 133 kB 00:00 (73/85): libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64.rpm 820 kB/s | 85 kB 00:00 (74/85): harfbuzz-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.4 MB/s | 624 kB 00:00 (75/85): libselinux-utils-3.4-3.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.4 MB/s | 158 kB 00:00 (76/85): libuuid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 448 kB/s | 27 kB 00:00 (77/85): libsmartcols-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 793 kB/s | 63 kB 00:00 (78/85): libsepol-3.4-1.1.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.6 MB/s | 315 kB 00:00 (79/85): pcre2-syntax-10.40-2.el9.noarch.rpm 1.2 MB/s | 143 kB 00:00 (80/85): pcre2-10.40-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.6 MB/s | 236 kB 00:00 (81/85): python3-libxml2-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64.rp 1.4 MB/s | 226 kB 00:00 (82/85): libxml2-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.5 MB/s | 746 kB 00:00 (83/85): util-linux-user-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rp 618 kB/s | 30 kB 00:00 (84/85): util-linux-core-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rp 1.1 MB/s | 434 kB 00:00 (85/85): util-linux-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64.rpm 1.9 MB/s | 2.2 MB 00:01 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 2.4 MB/s | 18 MB 00:07 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : xorg-x11-proto-devel-2021.4-2.el9.noarch 1/120 Upgrading : libuuid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 2/120 Upgrading : libblkid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 3/120 Running scriptlet: libblkid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 3/120 Upgrading : harfbuzz-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 4/120 Upgrading : freetype-2.10.4-9.el9.x86_64 5/120 Upgrading : libxml2-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 6/120 Upgrading : pcre2-syntax-10.40-2.el9.noarch 7/120 Upgrading : pcre2-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 8/120 Upgrading : libsepol-3.4-1.1.el9.x86_64 9/120 Upgrading : libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 10/120 Running scriptlet: libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 10/120 Upgrading : libmount-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 11/120 Upgrading : dbus-libs-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 12/120 Installing : libpng-devel-2:1.6.37-12.el9.x86_64 13/120 Installing : dbus-devel-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 14/120 Installing : libxml2-devel-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 15/120 Upgrading : libsmartcols-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 16/120 Installing : libsigc++20-devel-2.10.7-2.el9.x86_64 17/120 Installing : libffi-devel-3.4.2-7.el9.x86_64 18/120 Installing : wayland-devel-1.19.0-4.el9.x86_64 19/120 Upgrading : util-linux-core-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 20/120 Running scriptlet: util-linux-core-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 20/120 Installing : libxkbcommon-devel-1.0.3-4.el9.x86_64 21/120 Upgrading : dbus-tools-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 22/120 Installing : libsepol-devel-3.4-1.1.el9.x86_64 23/120 Upgrading : pcre2-utf16-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 24/120 Upgrading : pcre2-utf32-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 25/120 Installing : pcre2-devel-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 26/120 Installing : libselinux-devel-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 27/120 Upgrading : fontconfig-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64 28/120 Running scriptlet: fontconfig-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64 28/120 Upgrading : harfbuzz-icu-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 29/120 Installing : libblkid-devel-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 30/120 Installing : libmount-devel-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 31/120 Upgrading : libfdisk-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 32/120 Upgrading : util-linux-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 33/120 Installing : libXau-devel-1.0.9-8.el9.x86_64 34/120 Installing : libxcb-devel-1.13.1-9.el9.x86_64 35/120 Installing : libX11-devel-1.7.0-7.el9.x86_64 36/120 Installing : libXext-devel-1.3.4-8.el9.x86_64 37/120 Installing : libXfixes-devel-5.0.3-16.el9.x86_64 38/120 Installing : libXrender-devel-0.9.10-16.el9.x86_64 39/120 Installing : libXi-devel-1.7.10-8.el9.x86_64 40/120 Installing : libXtst-devel-1.2.3-16.el9.x86_64 41/120 Installing : libXcursor-devel-1.2.0-7.el9.x86_64 42/120 Installing : libXrandr-devel-1.5.2-8.el9.x86_64 43/120 Installing : libXcomposite-devel-0.4.5-7.el9.x86_64 44/120 Installing : libXdamage-devel-1.1.5-7.el9.x86_64 45/120 Installing : libXinerama-devel-1.1.4-10.el9.x86_64 46/120 Upgrading : dbus-common-1:1.12.20-6.el9.noarch 47/120 Running scriptlet: dbus-common-1:1.12.20-6.el9.noarch 47/120 Upgrading : libtiff-4.4.0-2.el9.x86_64 48/120 Installing : libtiff-devel-4.4.0-2.el9.x86_64 49/120 Upgrading : fribidi-1.0.10-6.el9.2.x86_64 50/120 Installing : fribidi-devel-1.0.10-6.el9.2.x86_64 51/120 Installing : sysprof-capture-devel-3.40.1-3.el9.x86_64 52/120 Installing : pixman-devel-0.40.0-5.el9.x86_64 53/120 Installing : perl-Filter-2:1.60-4.el9.x86_64 54/120 Installing : perl-encoding-4:3.00-462.el9.x86_64 55/120 Installing : perl-open-1.12-479.el9.noarch 56/120 Installing : pcre-utf32-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 57/120 Installing : pcre-utf16-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 58/120 Installing : pcre-cpp-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 59/120 Installing : pcre-devel-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 60/120 Installing : glib2-devel-2.68.4-5.el9.x86_64 61/120 Installing : atk-devel-2.36.0-5.el9.x86_64 62/120 Installing : glibmm24-devel-2.66.1-1.el9.x86_64 63/120 Installing : at-spi2-core-devel-2.40.3-1.el9.x86_64 64/120 Installing : at-spi2-atk-devel-2.38.0-4.el9.x86_64 65/120 Installing : gdk-pixbuf2-devel-2.42.6-2.el9.x86_64 66/120 Installing : libicu-devel-67.1-9.el9.x86_64 67/120 Installing : libglvnd-core-devel-1:1.3.4-1.el9.x86_64 68/120 Installing : libglvnd-devel-1:1.3.4-1.el9.x86_64 69/120 Installing : libepoxy-devel-1.5.5-4.el9.x86_64 70/120 Installing : libdatrie-devel-0.2.13-4.el9.x86_64 71/120 Installing : libthai-devel-0.1.28-8.el9.x86_64 72/120 Installing : graphite2-devel-1.3.14-9.el9.x86_64 73/120 Installing : bzip2-devel-1.0.8-8.el9.x86_64 74/120 Installing : brotli-1.0.9-6.el9.x86_64 75/120 Installing : brotli-devel-1.0.9-6.el9.x86_64 76/120 Installing : harfbuzz-devel-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 77/120 Installing : freetype-devel-2.10.4-9.el9.x86_64 78/120 Installing : fontconfig-devel-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64 79/120 Installing : cairo-devel-1.17.4-7.el9.x86_64 80/120 Installing : cairo-gobject-devel-1.17.4-7.el9.x86_64 81/120 Installing : cairomm-devel-1.14.2-10.el9.x86_64 82/120 Installing : libXft-devel-2.3.3-8.el9.x86_64 83/120 Installing : pango-devel-1.48.7-2.el9.x86_64 84/120 Installing : gtk3-devel-3.24.31-2.el9.x86_64 85/120 Installing : pangomm-devel-2.46.1-1.el9.x86_64 86/120 Installing : atkmm-devel-2.28.2-2.el9.x86_64 87/120 Running scriptlet: dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 88/120 Upgrading : dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 88/120 Running scriptlet: dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 88/120 Upgrading : util-linux-user-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 89/120 Upgrading : python3-libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 90/120 Upgrading : libselinux-utils-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 91/120 Upgrading : python3-libxml2-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 92/120 Cleanup : python3-libxml2-2.9.13-1.el9_0.1.x86_64 93/120 Running scriptlet: dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-5.el9.x86_64 94/120 Cleanup : dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-5.el9.x86_64 94/120 Running scriptlet: dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-5.el9.x86_64 94/120 Cleanup : libselinux-utils-3.3-2.el9.x86_64 95/120 Cleanup : fontconfig-2.13.94-2.el9.x86_64 96/120 Running scriptlet: fontconfig-2.13.94-2.el9.x86_64 96/120 Cleanup : dbus-tools-1:1.12.20-5.el9.x86_64 97/120 Cleanup : python3-libselinux-3.3-2.el9.x86_64 98/120 Cleanup : util-linux-user-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 99/120 Cleanup : util-linux-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 100/120 Cleanup : util-linux-core-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 101/120 Cleanup : libmount-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 102/120 Cleanup : libfdisk-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 103/120 Cleanup : libselinux-3.3-2.el9.x86_64 104/120 Cleanup : harfbuzz-icu-2.7.4-5.el9.x86_64 105/120 Cleanup : pcre2-10.37-5.el9_0.x86_64 106/120 Cleanup : libblkid-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 107/120 Cleanup : freetype-2.10.4-6.el9.x86_64 108/120 Cleanup : pcre2-utf32-10.37-5.el9_0.x86_64 109/120 Cleanup : pcre2-utf16-10.37-5.el9_0.x86_64 110/120 Cleanup : pcre2-syntax-10.37-5.el9_0.noarch 111/120 Running scriptlet: dbus-common-1:1.12.20-5.el9.noarch 112/120 Cleanup : dbus-common-1:1.12.20-5.el9.noarch 112/120 Running scriptlet: dbus-common-1:1.12.20-5.el9.noarch 112/120 Cleanup : harfbuzz-2.7.4-5.el9.x86_64 113/120 Cleanup : libuuid-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 114/120 Cleanup : libsepol-3.3-2.el9.x86_64 115/120 Cleanup : libsmartcols-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 116/120 Cleanup : dbus-libs-1:1.12.20-5.el9.x86_64 117/120 Cleanup : libxml2-2.9.13-1.el9_0.1.x86_64 118/120 Cleanup : libtiff-4.2.0-3.el9.x86_64 119/120 Cleanup : fribidi-1.0.10-6.el9.x86_64 120/120 Running scriptlet: fontconfig-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64 120/120 Running scriptlet: fribidi-1.0.10-6.el9.x86_64 120/120 Regex version mismatch, expected: 10.40 2022-04-14 actual: 10.37 2021-05-26 Regex version mismatch, expected: 10.40 2022-04-14 actual: 10.37 2021-05-26 Regex version mismatch, expected: 10.40 2022-04-14 actual: 10.37 2021-05-26 Regex version mismatch, expected: 10.40 2022-04-14 actual: 10.37 2021-05-26 Verifying : at-spi2-atk-devel-2.38.0-4.el9.x86_64 1/120 Verifying : at-spi2-core-devel-2.40.3-1.el9.x86_64 2/120 Verifying : atk-devel-2.36.0-5.el9.x86_64 3/120 Verifying : brotli-1.0.9-6.el9.x86_64 4/120 Verifying : brotli-devel-1.0.9-6.el9.x86_64 5/120 Verifying : bzip2-devel-1.0.8-8.el9.x86_64 6/120 Verifying : cairo-devel-1.17.4-7.el9.x86_64 7/120 Verifying : cairo-gobject-devel-1.17.4-7.el9.x86_64 8/120 Verifying : dbus-devel-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 9/120 Verifying : fontconfig-devel-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64 10/120 Verifying : freetype-devel-2.10.4-9.el9.x86_64 11/120 Verifying : fribidi-devel-1.0.10-6.el9.2.x86_64 12/120 Verifying : glib2-devel-2.68.4-5.el9.x86_64 13/120 Verifying : graphite2-devel-1.3.14-9.el9.x86_64 14/120 Verifying : harfbuzz-devel-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 15/120 Verifying : libX11-devel-1.7.0-7.el9.x86_64 16/120 Verifying : libXau-devel-1.0.9-8.el9.x86_64 17/120 Verifying : libXcomposite-devel-0.4.5-7.el9.x86_64 18/120 Verifying : libXcursor-devel-1.2.0-7.el9.x86_64 19/120 Verifying : libXdamage-devel-1.1.5-7.el9.x86_64 20/120 Verifying : libXext-devel-1.3.4-8.el9.x86_64 21/120 Verifying : libXfixes-devel-5.0.3-16.el9.x86_64 22/120 Verifying : libXft-devel-2.3.3-8.el9.x86_64 23/120 Verifying : libXi-devel-1.7.10-8.el9.x86_64 24/120 Verifying : libXinerama-devel-1.1.4-10.el9.x86_64 25/120 Verifying : libXrandr-devel-1.5.2-8.el9.x86_64 26/120 Verifying : libXrender-devel-0.9.10-16.el9.x86_64 27/120 Verifying : libXtst-devel-1.2.3-16.el9.x86_64 28/120 Verifying : libblkid-devel-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 29/120 Verifying : libdatrie-devel-0.2.13-4.el9.x86_64 30/120 Verifying : libepoxy-devel-1.5.5-4.el9.x86_64 31/120 Verifying : libffi-devel-3.4.2-7.el9.x86_64 32/120 Verifying : libglvnd-core-devel-1:1.3.4-1.el9.x86_64 33/120 Verifying : libglvnd-devel-1:1.3.4-1.el9.x86_64 34/120 Verifying : libicu-devel-67.1-9.el9.x86_64 35/120 Verifying : libmount-devel-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 36/120 Verifying : libpng-devel-2:1.6.37-12.el9.x86_64 37/120 Verifying : libselinux-devel-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 38/120 Verifying : libsepol-devel-3.4-1.1.el9.x86_64 39/120 Verifying : libthai-devel-0.1.28-8.el9.x86_64 40/120 Verifying : libtiff-devel-4.4.0-2.el9.x86_64 41/120 Verifying : libxcb-devel-1.13.1-9.el9.x86_64 42/120 Verifying : libxkbcommon-devel-1.0.3-4.el9.x86_64 43/120 Verifying : libxml2-devel-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 44/120 Verifying : pango-devel-1.48.7-2.el9.x86_64 45/120 Verifying : pcre-cpp-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 46/120 Verifying : pcre-devel-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 47/120 Verifying : pcre-utf16-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 48/120 Verifying : pcre-utf32-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 49/120 Verifying : pcre2-devel-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 50/120 Verifying : perl-Filter-2:1.60-4.el9.x86_64 51/120 Verifying : perl-encoding-4:3.00-462.el9.x86_64 52/120 Verifying : perl-open-1.12-479.el9.noarch 53/120 Verifying : pixman-devel-0.40.0-5.el9.x86_64 54/120 Verifying : sysprof-capture-devel-3.40.1-3.el9.x86_64 55/120 Verifying : wayland-devel-1.19.0-4.el9.x86_64 56/120 Verifying : xorg-x11-proto-devel-2021.4-2.el9.noarch 57/120 Verifying : atkmm-devel-2.28.2-2.el9.x86_64 58/120 Verifying : cairomm-devel-1.14.2-10.el9.x86_64 59/120 Verifying : gdk-pixbuf2-devel-2.42.6-2.el9.x86_64 60/120 Verifying : glibmm24-devel-2.66.1-1.el9.x86_64 61/120 Verifying : gtk3-devel-3.24.31-2.el9.x86_64 62/120 Verifying : libsigc++20-devel-2.10.7-2.el9.x86_64 63/120 Verifying : pangomm-devel-2.46.1-1.el9.x86_64 64/120 Verifying : dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 65/120 Verifying : dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-5.el9.x86_64 66/120 Verifying : fontconfig-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64 67/120 Verifying : fontconfig-2.13.94-2.el9.x86_64 68/120 Verifying : fribidi-1.0.10-6.el9.2.x86_64 69/120 Verifying : fribidi-1.0.10-6.el9.x86_64 70/120 Verifying : harfbuzz-icu-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 71/120 Verifying : harfbuzz-icu-2.7.4-5.el9.x86_64 72/120 Verifying : libtiff-4.4.0-2.el9.x86_64 73/120 Verifying : libtiff-4.2.0-3.el9.x86_64 74/120 Verifying : pcre2-utf16-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 75/120 Verifying : pcre2-utf16-10.37-5.el9_0.x86_64 76/120 Verifying : pcre2-utf32-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 77/120 Verifying : pcre2-utf32-10.37-5.el9_0.x86_64 78/120 Verifying : python3-libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 79/120 Verifying : python3-libselinux-3.3-2.el9.x86_64 80/120 Verifying : dbus-common-1:1.12.20-6.el9.noarch 81/120 Verifying : dbus-common-1:1.12.20-5.el9.noarch 82/120 Verifying : dbus-libs-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 83/120 Verifying : dbus-libs-1:1.12.20-5.el9.x86_64 84/120 Verifying : dbus-tools-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 85/120 Verifying : dbus-tools-1:1.12.20-5.el9.x86_64 86/120 Verifying : freetype-2.10.4-9.el9.x86_64 87/120 Verifying : freetype-2.10.4-6.el9.x86_64 88/120 Verifying : harfbuzz-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 89/120 Verifying : harfbuzz-2.7.4-5.el9.x86_64 90/120 Verifying : libblkid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 91/120 Verifying : libblkid-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 92/120 Verifying : libfdisk-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 93/120 Verifying : libfdisk-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 94/120 Verifying : libmount-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 95/120 Verifying : libmount-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 96/120 Verifying : libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 97/120 Verifying : libselinux-3.3-2.el9.x86_64 98/120 Verifying : libselinux-utils-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 99/120 Verifying : libselinux-utils-3.3-2.el9.x86_64 100/120 Verifying : libsepol-3.4-1.1.el9.x86_64 101/120 Verifying : libsepol-3.3-2.el9.x86_64 102/120 Verifying : libsmartcols-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 103/120 Verifying : libsmartcols-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 104/120 Verifying : libuuid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 105/120 Verifying : libuuid-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 106/120 Verifying : libxml2-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 107/120 Verifying : libxml2-2.9.13-1.el9_0.1.x86_64 108/120 Verifying : pcre2-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 109/120 Verifying : pcre2-10.37-5.el9_0.x86_64 110/120 Verifying : pcre2-syntax-10.40-2.el9.noarch 111/120 Verifying : pcre2-syntax-10.37-5.el9_0.noarch 112/120 Verifying : python3-libxml2-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 113/120 Verifying : python3-libxml2-2.9.13-1.el9_0.1.x86_64 114/120 Verifying : util-linux-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 115/120 Verifying : util-linux-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 116/120 Verifying : util-linux-core-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 117/120 Verifying : util-linux-core-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 118/120 Verifying : util-linux-user-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 119/120 Verifying : util-linux-user-2.37.4-3.el9.x86_64 120/120 Upgraded: dbus-common-1:1.12.20-6.el9.noarch dbus-daemon-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 dbus-libs-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 dbus-tools-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 fontconfig-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64 freetype-2.10.4-9.el9.x86_64 fribidi-1.0.10-6.el9.2.x86_64 harfbuzz-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 harfbuzz-icu-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 libblkid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 libfdisk-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 libmount-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 libselinux-utils-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 libsepol-3.4-1.1.el9.x86_64 libsmartcols-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 libtiff-4.4.0-2.el9.x86_64 libuuid-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 libxml2-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 pcre2-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 pcre2-syntax-10.40-2.el9.noarch pcre2-utf16-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 pcre2-utf32-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 python3-libselinux-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 python3-libxml2-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 util-linux-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 util-linux-core-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 util-linux-user-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 Installed: at-spi2-atk-devel-2.38.0-4.el9.x86_64 at-spi2-core-devel-2.40.3-1.el9.x86_64 atk-devel-2.36.0-5.el9.x86_64 atkmm-devel-2.28.2-2.el9.x86_64 brotli-1.0.9-6.el9.x86_64 brotli-devel-1.0.9-6.el9.x86_64 bzip2-devel-1.0.8-8.el9.x86_64 cairo-devel-1.17.4-7.el9.x86_64 cairo-gobject-devel-1.17.4-7.el9.x86_64 cairomm-devel-1.14.2-10.el9.x86_64 dbus-devel-1:1.12.20-6.el9.x86_64 fontconfig-devel-2.14.0-1.el9.x86_64 freetype-devel-2.10.4-9.el9.x86_64 fribidi-devel-1.0.10-6.el9.2.x86_64 gdk-pixbuf2-devel-2.42.6-2.el9.x86_64 glib2-devel-2.68.4-5.el9.x86_64 glibmm24-devel-2.66.1-1.el9.x86_64 graphite2-devel-1.3.14-9.el9.x86_64 gtk3-devel-3.24.31-2.el9.x86_64 harfbuzz-devel-2.7.4-8.el9.x86_64 libX11-devel-1.7.0-7.el9.x86_64 libXau-devel-1.0.9-8.el9.x86_64 libXcomposite-devel-0.4.5-7.el9.x86_64 libXcursor-devel-1.2.0-7.el9.x86_64 libXdamage-devel-1.1.5-7.el9.x86_64 libXext-devel-1.3.4-8.el9.x86_64 libXfixes-devel-5.0.3-16.el9.x86_64 libXft-devel-2.3.3-8.el9.x86_64 libXi-devel-1.7.10-8.el9.x86_64 libXinerama-devel-1.1.4-10.el9.x86_64 libXrandr-devel-1.5.2-8.el9.x86_64 libXrender-devel-0.9.10-16.el9.x86_64 libXtst-devel-1.2.3-16.el9.x86_64 libblkid-devel-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 libdatrie-devel-0.2.13-4.el9.x86_64 libepoxy-devel-1.5.5-4.el9.x86_64 libffi-devel-3.4.2-7.el9.x86_64 libglvnd-core-devel-1:1.3.4-1.el9.x86_64 libglvnd-devel-1:1.3.4-1.el9.x86_64 libicu-devel-67.1-9.el9.x86_64 libmount-devel-2.37.4-9.el9.x86_64 libpng-devel-2:1.6.37-12.el9.x86_64 libselinux-devel-3.4-3.el9.x86_64 libsepol-devel-3.4-1.1.el9.x86_64 libsigc++20-devel-2.10.7-2.el9.x86_64 libthai-devel-0.1.28-8.el9.x86_64 libtiff-devel-4.4.0-2.el9.x86_64 libxcb-devel-1.13.1-9.el9.x86_64 libxkbcommon-devel-1.0.3-4.el9.x86_64 libxml2-devel-2.9.13-2.el9.x86_64 pango-devel-1.48.7-2.el9.x86_64 pangomm-devel-2.46.1-1.el9.x86_64 pcre-cpp-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 pcre-devel-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 pcre-utf16-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 pcre-utf32-8.44-3.el9.3.x86_64 pcre2-devel-10.40-2.el9.x86_64 perl-Filter-2:1.60-4.el9.x86_64 perl-encoding-4:3.00-462.el9.x86_64 perl-open-1.12-479.el9.noarch pixman-devel-0.40.0-5.el9.x86_64 sysprof-capture-devel-3.40.1-3.el9.x86_64 wayland-devel-1.19.0-4.el9.x86_64 xorg-x11-proto-devel-2021.4-2.el9.noarch Complete!
Now return to your $HOME/Downloads directory and run the following command. You’ll notice that it installs and upgrades many more packages than you might expect.
sudo dnf install -y gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
The log file for this is:
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 1:22:32 ago on Sun 20 Nov 2022 12:52:28 AM EST. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: gtkmm30-devel x86_64 3.24.5-1.el9 @commandline 605 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total size: 605 k Installed size: 4.7 M Downloading Packages: Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Regex version mismatch, expected: 10.40 2022-04-14 actual: 10.37 2021-05-26 Regex version mismatch, expected: 10.40 2022-04-14 actual: 10.37 2021-05-26 Preparing : 1/1 Installing : gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64 1/1 Running scriptlet: gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64 1/1 Installed: gtkmm30-devel-3.24.5-1.el9.x86_64 Complete!
All that done and you’ve only got the first of four dependencies resovled.
- Next, start with the libzip-devel package, which has a couple dependencies. Assuming you’re still in your $HOME/Downloads directory, you can run the following command to get the libzip-devel and its prerequisite packages for AlmaLinux 9:
wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/libzip-devel-1.7.3-7.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/cmake-filesystem-3.20.2-7.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/AppStream/x86_64/os/Packages/libzip-1.7.3-7.el9.x86_64.rpm
You can run the prerequisites with the following command:
sudo dnf install -y cmake*.rpm libzip-1.7.3*.rpm
Now, you can run the libzip-devel package with this syntax:
sudo dnf install -y libzip-devel*.rpm
Having resolved the two dependencies, you can install the compression development kit. This completes the second step.
-
Next, you need to apply the proj_devel package for AlmaLinux 9:
wget https://download-ib01.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/9/Everything/x86_64/Packages/p/proj-devel-8.2.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
Now, you can run the proj-devel package with this syntax:
sudo dnf install -y proj-devel-8.2.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
-
Next, you need to apply the swig packages for AlmaLinux 9:
wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/swig-4.0.2-8.el9.x86_64.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/swig-doc-4.0.2-8.el9.noarch.rpm wget https://repo.almalinux.org/almalinux/9/CRB/x86_64/os/Packages/swig-gdb-4.0.2-8.el9.x86_64.rpm
sudo dnf install -y swig*.rpm
-
Next, you need to apply the mysql-community-workbench packages for AlmaLinux 9. The download instructions where provided above. You apply the packages with the following command.
sudo dnf install -y mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
Display detailed console log →
Last metadata expiration check: 1:06:04 ago on Sun 20 Nov 2022 03:28:30 PM EST. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: mysql-workbench-community x86_64 8.0.31-1.el9 @commandline 39 M Upgrading: proj x86_64 8.2.0-1.el9 epel 2.5 M Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Upgrade 1 Package Total size: 41 M Total download size: 2.5 M Downloading Packages: proj-8.2.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm 388 kB/s | 2.5 MB 00:06 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 354 kB/s | 2.5 MB 00:07 Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 9 - x86_64 1.6 MB/s | 1.6 kB 00:00 Importing GPG key 0x3228467C: Userid : "Fedora (epel9) <epel@fedoraproject.org>" Fingerprint: FF8A D134 4597 106E CE81 3B91 8A38 72BF 3228 467C From : /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-9 Key imported successfully Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Regex version mismatch, expected: 10.40 2022-04-14 actual: 10.37 2021-05-26 Regex version mismatch, expected: 10.40 2022-04-14 actual: 10.37 2021-05-26 Preparing : 1/1 Upgrading : proj-8.2.0-1.el9.x86_64 1/3 Installing : mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.x86_64 2/3 Running scriptlet: mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.x86_64 2/3 Cleanup : proj-4.8.0-4.el7.x86_64 3/3 Running scriptlet: proj-4.8.0-4.el7.x86_64 3/3 Verifying : mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.x86_64 1/3 Verifying : proj-8.2.0-1.el9.x86_64 2/3 Verifying : proj-4.8.0-4.el7.x86_64 3/3 Upgraded: proj-8.2.0-1.el9.x86_64 Installed: mysql-workbench-community-8.0.31-1.el9.x86_64 Complete!
After applying the dependent and mysql-community-workbench packages, you can launch MySQL Workbench by clicking the Activities symbol in the upper left hand corner. That displays the nine-dots for Show Applications icon. Click the Show Applications icon and choose the MySQL Workbench icon to launch MySQL Workbench.
You’ll be prompted with the following dialog. Just click Don’t show this message again checkbox and the OK button to launch MySQL Workbench.
As always, I hope this helps those looking to solve a real problem.
AlmaLinux LAMP

After installing and configuring MySQL 8.0.30, I installed the Apache Web Server, PHP and the MySQLi packages. Here are the step-by-step instructions after installing and configuring the MySQL Server and provisioning a student user and the sakila and studentdb databases (blog for those steps). After installing the major components, I completed the HTTPS configuration steps for Apache 2.
The installation steps are:
- Install the Apache packages as the sudoer user with this command:
sudo dnf install -y httpd
- Enable Apache as the sudoer user with this command:
chkconfig httpd on
This returns the following completion message:
Note: Forwarding request to 'systemctl enable httpd.service'. Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.
A quick Linux syntax note in the event you want to confirm the link or link target later. You can use the following syntax as a sudoer user to find the link:
ls `find /etc -type l | grep httpd.service 2>/dev/null`
and the following syntax as a sudoer user to find the link’s target:
readlink `find /etc -type l | grep httpd.service 2>/dev/null`
- You still need to start the Apache service unless you reboot the operating system as the sudoer user with this command:
apachectl start - At this point, you need to check the firewall settings because Apache can’t even read localhost at this point. If you’re new to these firewall commands, you should consider reviewing Korbin Brown’s tutorial. As the sudoer user check the Apache available services with this command:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-services
It should return:
cockpit dhcpv6-client sshAdd the following services and ports with these commands:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port 80/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port 443/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port 8080/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=http --permanent firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=https --permanent
Check the open ports with the following command:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
It should return:
80/tcp 443/tcp 8080/tcp
Check the open services with the following command:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-services
It should return:
cockpit dhcpv6-client http https ssh - Create the hello.htm file in the /var/www/html directory as the root user:
Restart the Apache service as the sudoer user:
apache restart
<html> <body> Hello World! </body> </html>
Then, you can launch the Firefox browser and type the following:
localhost/hello.htmIt should print “Hello World!” in the browser.
- Install the php package as the sudoer user with the following command:
sudo dnf install -y php
Create the info.php file in the /var/www/html directory as the root user:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
apache restart
Then, you can launch the Firefox browser and type the following:
localhost/info.php
It should return the following in the browser.
- Install the php_mysqli package as the sudoer user with the following command:
dnf install -y php-mysqli
Create the mysqli_check.php file in the /var/www/html directory as the root user:
<html> <header> <title>Static Query Object Sample</title> </header> <body> <?php if (!function_exists('mysqli_init') && !extension_loaded('mysqli')) { print 'mysqli not installed.'; } else { print 'mysqli installed.'; } if (!function_exists('pdo_init') && !extension_loaded('pdo')) { print '<p>pdo not installed.</p>'; } else { print '<p>pdo installed.</p>'; } ?> </script> </body> </html>
apache restart
Then, you can launch the Firefox browser and type the following:
localhost/mysqli_check.php
It should print the following in the browser.
mysqli installed. pdo installed.
- Check if the mod_ssl module is installed. You can use the following command::
rpm -qa | grep mod_ssl
Assuming it’s not installed, you install it like this:
dnf install -y mod_ssl
Recheck after installing mod_ssl with the following command::
rpm -qa | grep mod_ssl
It should print:
mod_ssl-2.4.51-7.el9_0.x86_64
- AlmaLinux and Apache require you to resolve the ServerName values and the public and private keys. Run this command on AlmaLinux to begin verifying and configuring the ServerName values and the public and private keys:
httpd -M | grep ssl
Assuming a new installation consistent with were MySQL and Apache were just configured, you should get the following message:
AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using localhost.localdomain. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress this message ssl_module (shared)
Recheck the failure for more detail with this command:
sudo systemctl status httpd.service -l --no-pager
It should print:
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.d └─php-fpm.conf Active: active (running) since Sun 2022-11-13 22:39:07 EST; 1h 37min ago Docs: man:httpd.service(8) Main PID: 1351 (httpd) Status: "Total requests: 0; Idle/Busy workers 100/0;Requests/sec: 0; Bytes served/sec: 0 B/sec" Tasks: 213 (limit: 23280) Memory: 43.1M CPU: 2.733s CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service ├─1351 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1443 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1452 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1456 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND └─1459 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND Nov 13 22:39:06 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server... Nov 13 22:39:07 localhost.localdomain httpd[1351]: AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using localhost.localdomain. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress this message Nov 13 22:39:07 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server. Nov 13 22:39:07 localhost.localdomain httpd[1351]: Server configured, listening on: port 80It takes the next set of steps to fix the ServerName values.
- Generically, on Linux you need to find the files to modify. You can use the following command from within the /etc directory to find the configuration files in the /etc directory that include ServerName in them. Their values will be proceeded by a # symbol because they’re comments by default.
find /etc -type f | xargs grep -i ServerName
It should return the following:
./httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf:#ServerName www.example.com:443 ./httpd/conf/httpd.conf:# ServerName gives the name and port that the server uses to identify itself. ./httpd/conf/httpd.conf:#ServerName www.example.com:80 ./dnsmasq.conf:# tftp_servername (the third option to dhcp-boot) and in that
- Add the following line to the ssl.conf file as the root user:
ServerName localhost:443 - Add the following line to the httpd.conf file as the root user:
ServerName localhost:443 - After adding the two values, restart Apache with the following command:
sudo apachectl restart
- Rerun the systemctl command to get the status of the httpd service with this command:
sudo systemctl status httpd.service -l --no-pager
It should print:
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Drop-In: /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service.d └─php-fpm.conf Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-11-14 00:37:03 EST; 3min 23s ago Docs: man:httpd.service(8) Main PID: 53596 (httpd) Status: "Total requests: 0; Idle/Busy workers 100/0;Requests/sec: 0; Bytes served/sec: 0 B/sec" Tasks: 213 (limit: 23280) Memory: 34.0M CPU: 183ms CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service ├─53596 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─53597 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─53598 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─53599 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND └─53600 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND Nov 14 00:37:03 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP Server... Nov 14 00:37:03 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP Server. Nov 14 00:37:03 localhost.localdomain httpd[53596]: Server configured, listening on: port 443, port 80
- Generically, on Linux you need to find the files to modify. You can use the following command from within the /etc directory to find the configuration files in the /etc directory that include ServerName in them. Their values will be proceeded by a # symbol because they’re comments by default.
- Your next step requires setting up an SSL Certificate. Consistent with the design to build a standalone test system that uses a DHCP assigned IP address to resolve a localhost server name, you require the following two tasks to create an openssl self-signed certificate.
- On the new instance, you create a private subdirectory with this command:
sudo mkdir /etc/ssl/private
- Then, you can build a self-signed certificate with this command:
sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/apache-selfsigned.key -out /etc/ssl/certs/apache-selfsigned.crt
The openssl command will prompt you for these values to create a private key:
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]: State or Province Name (full name) []: Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]: Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []: Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []: Email Address []:
- On the new instance, you create a private subdirectory with this command:
- Your last step requires three tasks to configure Apache to use SSL.
- You need to create the following sites-available directory with the following command as the root user:
mkdir /etc/httpd/sites-available
- Add the following localhost.conf/etc/httpd/sites-available directory:
<VirtualHost *:443> ServerName localhost DocumentRoot /var/www/html SSLEngine on SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/localhost.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/apache-selfsigned.key </VirtualHost>
- Restart Apache with the following command:
sudo apachectl restart
- You need to create the following sites-available directory with the following command as the root user:
- After configuring everything, let’s test our self-signed HTTPS skunkworks. Launch the default Firefox browser and enter the following URL, which uses the mysql_check.php file from step #7:
https://localhost/mysqli_check.php
It will raise a warning message about a potential security risk, which is caused by our self-signed certificate. Click the Advanced… button and will see the option to Accept the Risk and Continue. If you want to use the self-signed and contained AlmaLinux LAMP stack for developer testing, accept the risk.
Having assumed the risk, the confirmation of the configuration will be displayed as follows:
As always, I hope this helps those looking to install MySQL, PHP, on AlmaLinux.