Archive for the ‘PostgreSQL’ Category
AlmaLinux Install & Configuration

This is a collection of blog posts for installing and configuring AlmaLinux with the Oracle, PostgreSQL, MySQL databases and several programming languages. Sample programs show how to connect PHP and Python to the MySQL database.
- Installing AlmaLinux operating system
- Installing and configuring MySQL
- Installing Python-MySQL connector and provide sample programs
- Configuring Flask for Python on AlmaLinux with a complete software router instruction set.
- Installing Rust programming language and writing a sample program
- Installing and configuring LAMP stack with PHP and MySQL and a self-signed security key
- MySQL PNG Images in LAMP with PHP Programming
- Demonstration of how to write Perl that connects to MySQL
- Installing and configuring MySQL Workbench
- Installing and configuring PostgreSQL and pgAdmin4
- Identifying the required libnsl2-devel packages for SQL*Plus
- Writing and deploying a sqlplus function to use a read line wrapper
- Installing and configuring Visual Studio Code Editor
- Installing and configuring Java with connectivity to MySQL
- Installing and configuring Oracle SQL Developer
I used Oracle Database 11g XE in this instance to keep the footprint as small as possible. It required a few tricks and discovering the missing library that caused folks grief eleven years ago. I build another with a current Oracle Database XE after the new year.
If you see something that I missed or you’d like me to add, let me know. As time allows, I’ll try to do that. Naturally, the post will get updates as things are added later.
PL/pgSQL Transactions
There are many nuances that I show students about PL/pgSQL because first I teach them how to use PL/SQL. These are some of the differences:
- PL/SQL declares the function or procedure and then uses the IS keyword; whereas, PL/pgSQL uses the AS keyword.
- PL/SQL uses the RETURN keyword for functions declarations, like:
RETURN [data_type} IS
Whereas, PL/pgSQL uses the plural RETURNS keyword in the function declaration, like:
RETURNS [data_type] AS
- PL/SQL considers everything after the function or procedure header as the implicit declaration section; whereas, PL/pgSQL requires you block the code with something like $$ (double dollar symbols) and explicitly use the DECLARE keyword.
- PL/SQL supports local functions (inside the DECLARE block of a function or procedure); whereas, PL/pgSQL doesn’t.
- PL/SQL puts the variable modes (IN, INOUT, OUT) between the parameter name and type; whereas, PL/pgSQL puts them before the variable name.
- PL/SQL declares cursors like:
CURSOR cursor_name (parameter_list) IS
Whereas, PL/pgSQL declares them like
cursor_name CURSOR (parameter_list) FOR
- PL/SQL terminates and runs the block by using an END keyword, an optional module name, a semicolon to terminate the END; statement, and a forward slash to dispatch the program to PL/SQL statement engine:
END [module_name]; /
Whereas, PL/pgSQL terminates and runs the block by using an END keyword, a semicolon to terminate the END; statement, two dollar signs to end the PL/pgSQL block, and a semicolon to dispatch the program.
END LANGUAGE plpgsql; $$;
After all that basic syntax discussion, we try to create a sample set of tables, a function, a procedure, and a test case in PL/pgSQL. They’ve already done a virtually equivalent set of tasks in PL/SQL.
Here are the steps:
- Create the grandma and tweetie_bird tables:
/* Conditionally drop grandma table and grandma_s sequence. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS grandma CASCADE; /* Create the table. */ CREATE TABLE GRANDMA ( grandma_id SERIAL , grandma_house VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (grandma_id) ); /* Conditionally drop a table and sequence. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS tweetie_bird CASCADE; /* Create the table with primary and foreign key out-of-line constraints. */ SELECT 'CREATE TABLE tweetie_bird' AS command; CREATE TABLE TWEETIE_BIRD ( tweetie_bird_id SERIAL , tweetie_bird_house VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL , grandma_id INTEGER NOT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (tweetie_bird_id) , CONSTRAINT tweetie_bird_fk FOREIGN KEY (grandma_id) REFERENCES grandma (grandma_id) );
- Create a get_grandma_id function that returns a number, which should be a valid primary key value from the grandma_id column of the grandma table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_grandma_id ( IN pv_grandma_house VARCHAR ) RETURNS INTEGER AS $$ /* Required for PL/pgSQL programs. */ DECLARE /* Local return variable. */ lv_retval INTEGER := 0; -- Default value is 0. /* Use a cursor, which will not raise an exception at runtime. */ find_grandma_id CURSOR ( cv_grandma_house VARCHAR ) FOR SELECT grandma_id FROM grandma WHERE grandma_house = cv_grandma_house; BEGIN /* Assign a value when a row exists. */ FOR i IN find_grandma_id(pv_grandma_house) LOOP lv_retval := i.grandma_id; END LOOP; /* Return 0 when no row found and the ID # when row found. */ RETURN lv_retval; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
- Create a Warner_brother procedure that writes data across two tables as a transaction. You con’t include any of the following in your functions or procedures because all PostgreSQL PL/pgSQL functions and procedures are transaction by default:
- SET TRANSACTION
- START TRANSACTION
- SAVEPOINT
- COMMIT
A ROLLBACK should be placed in your exception handler as qualified on lines #33 thru #36. The warner_brother procedure inserts rows into the grandma and tweetie_bird tables.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
/* Create or replace procedure warner_brother. */ CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE warner_brother ( pv_grandma_house VARCHAR , pv_tweetie_bird_house VARCHAR ) AS $$ /* Required for PL/pgSQL programs. */ DECLARE /* Declare a local variable for an existing grandma_id. */ lv_grandma_id INTEGER; BEGIN /* Check for existing grandma row. */ lv_grandma_id := get_grandma_id(pv_grandma_house); IF lv_grandma_id = 0 THEN /* Insert grandma. */ INSERT INTO grandma ( grandma_house ) VALUES ( pv_grandma_house ) RETURNING grandma_id INTO lv_grandma_id; END IF; /* Insert tweetie bird. */ INSERT INTO tweetie_bird ( tweetie_bird_house , grandma_id ) VALUES ( pv_tweetie_bird_house , lv_grandma_id ); EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN ROLLBACK; RAISE NOTICE '[%] [%]', SQLERRM, SQLSTATE; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
You should take note of the RETURNING-INTO statement on line #22. The alternative to this clause isn’t pretty if you know that PostgreSQL uses a table name, column name, and the literal seq value separated by underscores (that is, snake case), like:
/* Assign current value to local variable. */ lv_grandma_id := CURRVAL('grandma_grandma_id_seq');
It would be even uglier if you had to look up the sequence name, like:
/* Assign current value to local variable. */ lv_grandma_id := CURRVAL(pg_get_serial_sequence('grandma','grandma_id'));
- You can test the combination of these two stored procedures with the following DO-block:
/* Test the warner_brother procedure. */ DO $$ BEGIN /* Insert the yellow house. */ CALL warner_brother( 'Yellow House', 'Cage'); CALL warner_brother( 'Yellow House', 'Tree House'); /* Insert the red house. */ CALL warner_brother( 'Red House', 'Cage'); CALL warner_brother( 'Red House', 'Tree House'); END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
Then, query the results:
SELECT * FROM grandma g INNER JOIN tweetie_bird tb ON. g.grandma_id = tb.grandma_id;
It should return:
grandma_id | grandma_house | tweetie_bird_id | tweetie_bird_house | grandma_id ------------+---------------+-----------------+--------------------+------------ 1 | Red House | 1 | Cage | 1 1 | Red House | 2 | Tree House | 1 2 | Yellow House | 3 | Cage | 2 2 | Yellow House | 4 | Tree House | 2 (4 rows)
As always, I hope writing a clear and simple examples helps those looking for sample code.
Logging Table Function
It is interesting when somebody remembers a presentation from 10 years ago. They asked if it was possible in PL/pgSQL to write an autonomous procedure to log data when calling a table view function. The answer is two fold. PL/pgSQL doesn’t support autonomous functions or procedures like the Oracle database but it doesn’t need to because unless you invoke a transaction it auto commits writes.
Logging table functions are important for security auditing and compliance management against laws, like SOX, HIPAA, and FERPA. All too many systems lack the basic ability to audit who queries records without raising an error and blocking the access. That means the bad actor or actress gains the ability to probe the system for weaknesses before determining an attack vector. It’s often better to capture the unauthorized access and take direct action to protect both the the data and systems.
While the example lets an unauthorized person access the information in the first version of the student_query, it blocks access by reporting no rows returned in the latter. Both versions of the query log the data and thereby collect the evidence necessary to act against the hack.
This blog post shows you how to write it and test it. Follow the following steps:
- Create the necessary tables and data to work with a logging PL/pgSQL table view function:
/* Conditionally drop and create table. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS student; CREATE TABLE student ( student_id SERIAL , first_name VARCHAR(20) , last_name VARCHAR(20) , hogwarts_house VARCHAR(10)); /* Conditionally drop and create table. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS logger; CREATE TABLE logger ( logger_id SERIAL , app_user VARCHAR(30) , queried_student VARCHAR(30) , query_time TIMESTAMP ); /* Insert one record into table. */ INSERT INTO student ( first_name, last_name, hogwarts_house ) VALUES ( 'Harry', 'Potter', 'Gryffindor' ) ,( 'Hermione', 'Granger', 'Gryffindor' ) ,( 'Ronald', 'Weasily', 'Gryffindor' ) ,( 'Draco', 'Malfoy', 'Slytherin' ) ,( 'Vincent', 'Crabbe', 'Slytherin' ) ,( 'Susan', 'Bones', 'Hufflepuff' ) ,( 'Hannah', 'Abbott', 'Hufflepuff' ) ,( 'Luna', 'Lovegood', 'Ravenclaw' ) ,( 'Cho', 'Chang', 'Ravenclaw' ) ,( 'Gilderoy', 'Lockhart', 'Ravenclaw' );
- While not necessary if you’re very familiar with PL/pgSQL, it may be helpful to review:
- The SET command that lets you assign a value to a session-level variable, which you can later use in a PL/pgSQL block.
- The SELECT-INTO statement in a DO-block.
Here’s a test script that demonstrates both:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
/* Set a session-level variable. */ SET credential.app_user = 'Draco Malfoy'; /* Secure the value from a session-level variable. */ SELECT current_setting('credential.app_user'); /* DO $$ DECLARE input VARCHAR(30) := 'Hermione'; output VARCHAR(30); BEGIN /* Sample for partial name construction of full name. */ SELECT CONCAT(s.first_name, ' ', s.last_name) AS student_name INTO output FROM student s WHERE CONCAT(s.first_name, ' ', s.last_name) LIKE '%'||input||'%'; /* Show result of local assignment via a query. */ RAISE NOTICE '[%][%]', current_setting('credential.app_user'), output; END; $$;
There’s an important parsing trick to this sample program. It uses the LIKE operator rather than the SIMILAR TO operator because the parser fails to recognize the SIMILAR TO operator.
The DO-block returns the following output:
NOTICE: [Draco Malfoy][Hermione Granger]
- This creates the student_query logging table function, which takes a partial portion of a students first and last name to return the student information. While the example only returns the name and the Hogwarts House it lays a foundation for a more complete solution.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION student_query (partial_name VARCHAR) RETURNS TABLE ( first_naem VARCHAR(20) , last_name VARCHAR(20) , hogwarts_house VARCHAR(10) ) AS $$ DECLARE queried VARCHAR; by_whome VARCHAR; BEGIN /* Query separately because embedding in insert statement fails. */ SELECT CONCAT(s.first_name, ' ', s.last_name) AS student_name FROM student s INTO queried WHERE CONCAT(s.first_name, ' ', s.last_name) LIKE '%'||partial_name||'%'; /* Log the query with the credentials of the user. */ INSERT INTO logger ( app_user , queried_student , query_time ) VALUES ( current_setting('credential.app_user') , queried , NOW()); /* Return the result set without disclosing the query was recorded. */ RETURN QUERY SELECT s.first_name , s.last_name , s.hogwarts_house FROM student s WHERE CONCAT(s.first_name, ' ', s.last_name) LIKE '%'||partial_name||'%'; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
- You can test the function by calling it, like this:
SELECT * FROM student_query('Hermione');
It displays:
first_naem | last_name | hogwarts_house ------------+-----------+---------------- Hermione | Granger | Gryffindor (1 row)
You can check the logging table and discover who looked up another student’s records.
SELECT * FROM logger;
It displays:
logger_id | app_user | queried_student | query_time -----------+--------------+------------------+---------------------------- 1 | Draco Malfoy | Hermione Granger | 2022-05-29 22:51:50.398987 (1 row) - Assuming you’ve built an authorized_user function that returns a Boolean, you can add a call to it in the WHERE clause. For simplicity, let’s implement the function to deny all users, like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION authorized_user (user_name VARCHAR) RETURNS BOOLEAN AS $$ DECLARE lv_retval BOOLEAN := FALSE; BEGIN RETURN lv_retval; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
You can now replace the query on lines 28 through 32 with the new one below. The added clause on line 33 denies access to unauthorized users because there aren’t any.
28 29 30 31 32 33
SELECT s.first_name , s.last_name , s.hogwarts_house FROM student s WHERE CONCAT(s.first_name, ' ', s.last_name) LIKE '%'||partial_name||'%' AND authorized_user(current_setting('credential.app_user'));
While it returns:
first_naem | last_name | hogwarts_house ------------+-----------+---------------- (0 rows)
The logger table shows two entries. One for the query that returned a value and one for the version that didn’t.
logger_id | app_user | queried_student | query_time -----------+--------------+------------------+---------------------------- 1 | Draco Malfoy | Hermione Granger | 2022-05-29 23:23:39.82063 2 | Draco Malfoy | Hermione Granger | 2022-05-29 23:23:40.736945 (2 rows)In both cases the bad actor Draco Malfoy’s unauthorized access is captured and he was denied any information without alerting him to the security precaution in a logging table function.
As always, I hope this helps those looking for this type of solution.
PostgreSQL Table Function
A quick tutorial on how to write a PL/pgSQL Table function. The functions is simple. It returns the list of conquistadors that were originally German. It does that by filtering on the lang column in the table. For example, you use ‘de‘ for German.
I’ll stage this with the same conquistador table used in the last post. Don’t forget to use the chcp command to the Active Console Code Page to 4-byte Unicode before you run the script file, like:
chcp 65001 |
Then, connect to the psql shell and run the following script file:
/* Conditionally drop the conquistador table. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS conquistador; /* Create the conquistador table. */ CREATE TABLE conquistador ( conquistador_id SERIAL , conquistador VARCHAR(30) , actual_name VARCHAR(30) , nationality VARCHAR(30) , lang VARCHAR(2)); /* Insert some conquistadors into the table. */ INSERT INTO conquistador ( conquistador , actual_name , nationality , lang ) VALUES ('Juan de Fuca','Ioánnis Fokás','Greek','el') ,('Nicolás de Federmán','Nikolaus Federmann','German','de') ,('Sebastián Caboto','Sebastiano Caboto','Venetian','it') ,('Jorge de la Espira','Georg von Speyer','German','de') ,('Eusebio Francisco Kino','Eusebius Franz Kühn','Italian','it') ,('Wenceslao Linck','Wenceslaus Linck','Bohemian','cs') ,('Fernando Consag','Ferdinand Konšcak','Croatian','sr') ,('Américo Vespucio','Amerigo Vespucci','Italian','it') ,('Alejo García','Aleixo Garcia','Portuguese','pt'); |
Now, you can build another script file to create the getConquistador function, like:
/* Drop the funciton conditionally. */ DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS getConquistador; |
Create the getConquistador function:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | CREATE FUNCTION getConquistador (IN lang_in VARCHAR(2)) RETURNS TABLE ( conquistador VARCHAR(30) , actual_name VARCHAR(30) , nationality VARCHAR(30)) AS $$ BEGIN RETURN QUERY SELECT c.conquistador , c.actual_name , c.nationality FROM conquistador c WHERE c.lang = lang_in; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; |
Then, you can test it like:
SELECT * FROM getConquistador('de'); |
It will return the following:
conquistador | actual_name | nationality -----------------------+--------------------+------------- Nicolás de Federmán | Nikolaus Federmann | German Jorge de la Espira | Georg von Speyer | German (2 rows) |
As always, I hope this helps with a technique that’s useful.
PostgreSQL Unicode
It seems unavoidable to use Windows. Each time I’m compelled to run tests on the platform I find new errors. For example, they don’t use 4-byte unicode and as a result when you want to use Unicode in PostgreSQL there’s a mismatch.
For example, change the Active Console Code Page with the chcp (change code page) to match the one PostgreSQL uses, like:
chip 1252 |
It lets you avoid this warning message:
Password for user postgres:
psql (14.1)
WARNING: Console code page (437) differs from Windows code page (1252)
8-bit characters might not work correctly. See psql reference
page "Notes for Windows users" for details.
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# |
However, it won’t avoid display issues with real Unicode values. For example, let’s use a small international table like the following:
/* Conditionally drop the conquistador table. */ DROP TABLE IF EXISTS conquistador; /* Create the conquistador table. */ CREATE TABLE conquistador ( conquistador_id SERIAL , conquistador VARCHAR(30) , actual_name VARCHAR(30) , nationality VARCHAR(30) , lang VARCHAR(2)); /* Insert some conquistadors into the table. */ INSERT INTO conquistador ( conquistador , actual_name , nationality , lang ) VALUES ('Juan de Fuca','Ioánnis Fokás','Greek','el') ,('Nicolás de Federmán','Nikolaus Federmann','German','de') ,('Sebastián Caboto','Sebastiano Caboto','Venetian','it') ,('Jorge de la Espira','Georg von Speyer','German','de') ,('Eusebio Francisco Kino','Eusebius Franz Kühn','Italian','it') ,('Wenceslao Linck','Wenceslaus Linck','Bohemian','cs') ,('Fernando Consag','Ferdinand Konšcak','Croatian','sr') ,('Américo Vespucio','Amerigo Vespucci','Italian','it') ,('Alejo García','Aleixo Garcia','Portuguese','pt'); /* Query the values from the conquistador table. */ SELECT * FROM conquistador; |
When you call the script to load it, like:
\i testScript.sql |
It’ll display the following, which you can check against the strings in the VALUES clause above. There are encoding issues on lines 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, and 8 below.
conquistador_id | conquistador | actual_name | nationality | lang
-----------------+------------------------+----------------------+-------------+------
1 | Juan de Fuca | Ioánnis Fokás | Greek | el
2 | Nicolás de Federmán | Nikolaus Federmann | German | de
3 | Sebastián Caboto | Sebastiano Caboto | Venetian | it
4 | Jorge de la Espira | Georg von Speyer | German | de
5 | Eusebio Francisco Kino | Eusebius Franz Kühn | Italian | it
6 | Wenceslao Linck | Wenceslaus Linck | Bohemian | cs
7 | Fernando Consag | Ferdinand Konšcak | Croatian | sr
8 | Américo Vespucio | Amerigo Vespucci | Italian | it
9 | Alejo GarcÃa | Aleixo Garcia | Portuguese | pt
(9 rows) |
If you’re like me, it was annoying. The problem is that the native 2-byte Unicode of Microsoft sends values into PostgreSQL that are invalid. Those codes are read back with unintended values from other character encoding sets.
While you can’t set Windows generic encoding to 65001 without causing the system problems, you can set Active Console Code Page value in the scope of a Command-Line session before running the script.
The chcp command lets you set it to 4-byte Unicode, like:
chcp 65001 |
Now, rerun the script and PostgreSQL will display the correct character encoding set with some spacing irregularities. However, that’s not what’s important when you call table from another programming language through the ODBC-layer. The data will be returned in a 4-byte Unicode encoding stream.
conquistador_id | conquistador | actual_name | nationality | lang
-----------------+------------------------+----------------------+-------------+------
1 | Juan de Fuca | Ioánnis Fokás | Greek | el
2 | Nicolás de Federmán | Nikolaus Federmann | German | de
3 | Sebastián Caboto | Sebastiano Caboto | Venetian | it
4 | Jorge de la Espira | Georg von Speyer | German | de
5 | Eusebio Francisco Kino | Eusebius Franz Kühn | Italian | it
6 | Wenceslao Linck | Wenceslaus Linck | Bohemian | cs
7 | Fernando Consag | Ferdinand Konšcak | Croatian | sr
8 | Américo Vespucio | Amerigo Vespucci | Italian | it
9 | Alejo García | Aleixo Garcia | Portuguese | pt
(9 rows) |
A similar error to what I encountered testing MySQL Workbench’s ability to export SQL Server databases 10 years ago. I thought giving a solution to get coerce correct 4-byte Unicode data insertion may help those who also may be surprised by the behavior.
PL/pgSQL List to Struct
This blog post addresses how to convert a list of values into a structure (in C/C++ its a struct, in Java its an ArrayList, and PL/pgSQL it’s an array of a type). The cast_strings function converts a list of strings into a record data structure. It calls the verify_date function to identify a DATE data type and uses regular expressions to identify numbers and strings.
You need to build the struct type below first.
CREATE TYPE struct AS ( xnumber DECIMAL , xdate DATE , xstring VARCHAR(100)); |
The cast_strings function is defined below:
CREATE FUNCTION cast_strings ( pv_list VARCHAR(10)[] ) RETURNS struct AS $$ DECLARE /* Declare a UDT and initialize an empty struct variable. */ lv_retval STRUCT := (null, null, null); BEGIN /* Loop through list of values to find only the numbers. */ FOR i IN 1..ARRAY_LENGTH(pv_list,1) LOOP /* Order if statements by evaluation. */ CASE /* Check for a value with only digits. */ WHEN lv_retval.xnumber IS NULL AND REGEXP_MATCH(pv_list[i],'^[0-9]+$') IS NOT NULL THEN lv_retval.xnumber := pv_list[i]; /* Check for a valid date. */ WHEN lv_retval.xdate IS NULL AND verify_date(pv_list[i]) IS NOT NULL THEN lv_retval.xdate := pv_list[i]; /* Check for a string with characters, whitespace, and digits. */ WHEN lv_retval.xstring IS NULL AND REGEXP_MATCH(pv_list[i],'^[A-Za-z 0-9]+$') IS NOT NULL THEN lv_retval.xstring := pv_list[i]; ELSE NULL; END CASE; END LOOP; /* Print the results. */ RETURN lv_retval; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; |
There are two test cases for the cast_strings function. One uses a DO-block and the other a query.
- The first use-case checks with a DO-block:
DO $$ DECLARE lv_list VARCHAR(11)[] := ARRAY['86','1944-04-25','Happy']; lv_struct STRUCT; BEGIN /* Pass the array of strings and return a record type. */ lv_struct := cast_strings(lv_list); /* Print the elements returned. */ RAISE NOTICE '[%]', lv_struct.xnumber; RAISE NOTICE '[%]', lv_struct.xdate; RAISE NOTICE '[%]', lv_struct.xstring; END; $$;
It should return:
psql:verify_pg.SQL:263: NOTICE: [86] psql:verify_pg.SQL:263: NOTICE: [1944-04-25] psql:verify_pg.SQL:263: NOTICE: [Happy]
The program returns a structure with values converted into their appropriate data type.
- The second use-case checks with a query:
WITH get_struct AS (SELECT cast_strings(ARRAY['99','2015-06-14','Agent 99']) AS mystruct) SELECT (mystruct).xnumber , (mystruct).xdate , (mystruct).xstring FROM get_struct;
It should return:
xnumber | xdate | xstring ---------+------------+---------- 99 | 2015-06-14 | Agent 99 (1 row)
The query defines a call to the cast_strings function with a valid set of values and then displays the elements of the returned structure.
As always, I hope this helps those looking for how to solve this type of problem. Just a quick reminder that this was written and tested in PostgreSQL 14.
PL/pgSQL Date Function
This post provides an example of using PostgreSQL’s REGEXP_MATCH function, which works very much like the REGEXP_LIKE function in Oracle and a verify_date function that converts a string data type to date data type.
Here’s a basic function to show how to use a generic REGEXP_MATCH function:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | DO $$ DECLARE lv_date_in DATE := '2022-10-22'; BEGIN IF (REGEXP_MATCH('2022-10-02','^[0-9]{4,4}-[0-9]{2,2}-[0-9]{2,2}$') IS NOT NULL) THEN RAISE NOTICE '[%]', 'Truth'; END IF; END; $$; |
The following is a verify_date function, which takes a string with the ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ or ‘YY-MM-DD’ format and returns a BOOLEAN true or false value.
CREATE FUNCTION verify_date ( IN pv_date_in VARCHAR(10)) RETURNS BOOLEAN AS $$ DECLARE /* Local return variable. */ lv_retval BOOLEAN := FALSE; BEGIN /* Check for a YYYY-MM-DD or YYYY-MM-DD string. */ IF REGEXP_MATCH(pv_date_in,'^[0-9]{2,4}-[0-9]{2,2}-[0-9]{2,2}$') IS NOT NULL THEN /* Case statement checks for 28 or 29, 30, or 31 day month. */ CASE /* Valid 31 day month date value. */ WHEN (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 10 AND SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,6,2) IN ('01','03','05','07','08','10','12') AND TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,9,2),'99') BETWEEN 1 AND 31) OR (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 8 AND SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,4,2) IN ('01','03','05','07','08','10','12') AND TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,7,2),'99') BETWEEN 1 AND 31) THEN lv_retval := TRUE; /* Valid 30 day month date value. */ WHEN (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 10 AND SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,6,2) IN ('04','06','09','11') AND TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,9,2),'99') BETWEEN 1 AND 30) OR (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 8 AND SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,4,2) IN ('04','06','09','11') AND TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,7,2),'99') BETWEEN 1 AND 30) THEN lv_retval := TRUE; /* Valid 28 or 29 day month date value. */ WHEN (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 10 AND SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,6,2) = '02') OR (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 8 AND SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,4,2) = '02') THEN /* Verify 4-digit year. */ IF (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 10 AND MOD(TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,1,4),'99'),4) = 0 AND TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,9,2),'99') BETWEEN 1 AND 29) OR (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 8 AND MOD(TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(TO_CHAR(TO_DATE(pv_date_in,'YYYY-MM-DD'),'YYYY-MM-DD'),1,4),'99'),4) = 0 AND TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,7,2),'99') BETWEEN 1 AND 29) THEN lv_retval := TRUE; ELSE /* Not a leap year. */ IF (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 10 AND TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,9,2),'99') BETWEEN 1 AND 28) OR (LENGTH(pv_date_in) = 8 AND TO_NUMBER(SUBSTRING(pv_date_in,7,2),'99') BETWEEN 1 AND 28)THEN lv_retval := TRUE; END IF; END IF; NULL; END CASE; END IF; /* Return date. */ RETURN lv_retval; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; |
The following four SQL test cases:
SELECT verify_date('2020-07-04') AS "verify_date('2020-07-04')"; SELECT verify_date('71-05-31') AS "verify_date('71-05-31')"; SELECT verify_date('2024-02-29') AS "verify_date('2024-02-29')"; SELECT verify_date('2019-04-31') AS "verify_date('2019-04-31')"; |
Return the following:
verify_date('2020-07-04')
---------------------------
t
(1 row)
verify_date('71-05-31')
-------------------------
t
(1 row)
verify_date('2024-02-29')
---------------------------
t
(1 row)
verify_date('2019-04-31')
---------------------------
f
(1 row) |
As always, I hope the example code fills somebody’s need.
Record Type Arrays
Another question that I was asked today: “Can you create an array of a record type in PL/pgSQL?” The answer is yes.
You first have to create a type, which is what you do when you want to create a table with an embedded table. This is a simple full_name record type:
CREATE TYPE full_name AS ( first_name VARCHAR(20) , middle_name VARCHAR(20) , last_name VARCHAR(20)); |
The following DO block shows you how to create a record type array and then print it’s contents in a FOR-LOOP:
DO $$ DECLARE -- An array of full_name records. list full_name[] = array[('Harry','James','Potter') ,('Ginevra','Molly','Potter') ,('James','Sirius','Potter') ,('Albus','Severus','Potter') ,('Lily','Luna','Potter')]; BEGIN -- Loop through the integers. FOR i IN 1..CARDINALITY(list) LOOP RAISE NOTICE '%, % %', list[i].last_name, list[i].first_name, list[i].middle_name; END LOOP; END; $$; |
Since you typically only have a single dimension array with record-type structure, using CARDINALITY is clearer than ARRAY_LENGTH(list,1). If you don’t agree use the latter.
It prints the following:
NOTICE: Potter, Harry James
NOTICE: Potter, Ginevra Molly
NOTICE: Potter, James Sirius
NOTICE: Potter, Albus Severus
NOTICE: Potter, Lily Luna
DO |
As always, I hope this helps those looking for a solution to this type of problem.
Multidimension Arrays
Picking up where I left off on yesterday’s post on PostgreSQL arrays, you can also write multidimensional arrays provided all the nested arrays are equal in size. You can’t use the CARDINALITY function to determine the length of nested arrays, you must use the ARRAY_LENGTH to determine the length of subordinate arrays.
Here’s an example file with a multidimensional array of integers:
DO $$ DECLARE /* Declare an array of integers with a subordinate array of integers. */ list int[][] = array[array[1,2,3,4] ,array[1,2,3,4] ,array[1,2,3,4] ,array[1,2,3,4] ,array[1,2,3,4]]; row varchar(20) = ''; BEGIN /* Loop through the first dimension of integers. */ <<Outer>> FOR i IN 1..ARRAY_LENGTH(list,1) LOOP row = ''; /* Loop through the second dimension of integers. */ <<Inner>> FOR j IN 1..ARRAY_LENGTH(list,2) LOOP IF LENGTH(row) = 0 THEN row = row || list[i][j]; ELSE row = row || ',' || list[i][j]; END IF; END LOOP; /* Exit outer loop. */ RAISE NOTICE 'Row [%][%]', i, row; END LOOP; END; $$; |
It prints:
NOTICE: Row [1][1,2,3,4] NOTICE: Row [2][1,2,3,4] NOTICE: Row [3][1,2,3,4] NOTICE: Row [4][1,2,3,4] NOTICE: Row [5][1,2,3,4] DO |
Multidimensional arrays are unique to PostgreSQL but you can have nested lists of tables or varrays inside an Oracle database. Oracle also supports nested lists that are asynchronous.
As always, I hope this helps those trying sort out the syntax.
PostgreSQL+PowerShell
This post explains and demonstrates how to install, configure, and use the psqlODBC (32-bit) and psqlODBC (64-bit) libraries to connect your Microsoft PowerShell programs to a locally installed PostgreSQL 14 database. It relies on you previously installing and configuring a PostgreSQL 14 database. This post is a step-by-step guide to installing PostgreSQL 14 on Windows 10, and this post shows you how to configure the PostgreSQL 14 database.
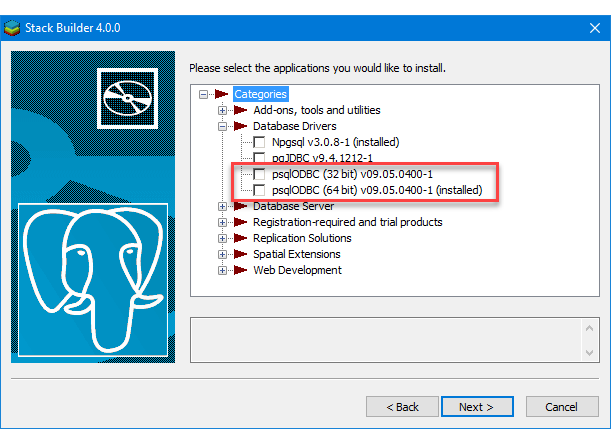
If you didn’t follow the instructions to get the psqlODBC libraries in the installation blog post, you will need to get those libraries, as qualified by Microsoft with the PostgreSQL Stack Builder.
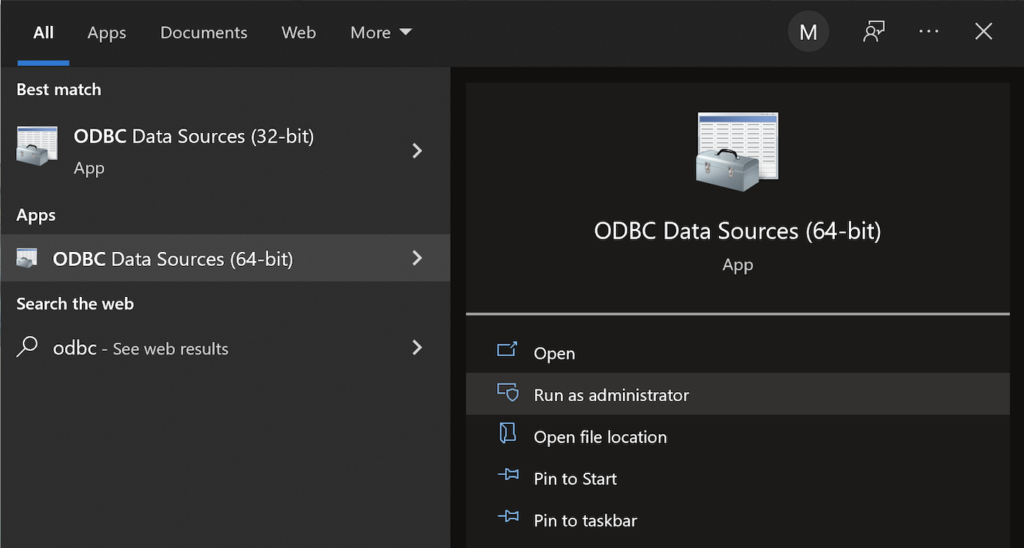
You can launch PostgreSQL Stack Builder after the install by clicking on Start -> PostgreSQL -> Stack Builder. Choose to enable Stack Builder to change your system and install the psqlODBC libraries. After you’ve installed the psqlODBC library, use Windows search field to find the ODBC Data Sources dialog and run it as administrator.
There are six steps to setup, test, and save your ODBC Data Source Name (DSN). You can click on the images on the right to launch them in a more readable format or simply read the instructions.
PostgreSQL ODBC Setup Steps
- The Microsoft DSN (Data Source Name) dialog automatically elects the User DSN tab. Click on the System DSN tab.
- The view under the System DSN is exactly like the User DSN tab. Click the Add button to start the workflow.
- The Create New Data Source dialog requires you select the PostgreSQL ODBC Driver(UNICODE) option from the list and click the Finish button to proceed.
- The PostgreSQL Unicode ODBC Driver Setup dialog should complete the prompts as follows below and consistent with the PostgreSQL 14 Configuration blog. If you opt for localhost as the server value because you have a DCHP IP address, make sure you’ve configured your hosts file in the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc directory. You should enter the following two lines in the hosts file:
127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost
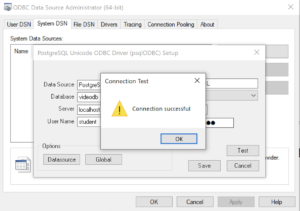
These are the string values you should enter in the PostgreSQL Unicode ODBC Driver Setup dialog:
Data Source: PostgreSQL35W Database: videodb Server: localhost User Name: student Description: PostgreSQL SSL Mode: disable Port: 5432 Password: student
After you complete the entry, click the Test button.
- The Connection Test dialog should return a “Connection successful” message. Click the OK button to continue.
- The ODBC Data Source Administrator dialog should show the PostgreSQL35W System Data Source. Click the OK button to continue.
After you have created the System PostgreSQL ODBC Setup, it’s time to build a PowerShell Cmdlet (or, Commandlet). Some documentation and blog notes incorrectly suggest you need to write a connection string with a UID and password, like:
$ConnectionString = 'DSN=PostgreSQL35W;Uid=student;Pwd=student' |
The UID and password is unnecessary in the connection string. As a rule, the UID and password are only necessary in the ODBC DSN, like:
$ConnectionString = 'DSN=PostgreSQL35W' |
You can create a readcursor.ps1 Cmdlet like the following:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | # Define a ODBC DSN connection string. $ConnectionString = 'DSN=PostgreSQL35W' # Define a MySQL Command Object for a non-query. $Connection = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcConnection; $Connection.ConnectionString = $ConnectionString # Attempt connection. try { $Connection.Open() # Create a SQL command. $Command = $Connection.CreateCommand(); $Command.CommandText = "SELECT current_database();"; # Attempt to read SQL command. try { $Reader = $Command.ExecuteReader(); # Read while records are found. while ($Reader.Read()) { Write-Host "Current Database [" $Reader[0] "]"} } catch { Write-Error "Message: $($_.Exception.Message)" Write-Error "StackTrace: $($_.Exception.StackTrace)" Write-Error "LoaderExceptions: $($_.Exception.LoaderExceptions)" } finally { # Close the reader. $Reader.Close() } } catch { Write-Error "Message: $($_.Exception.Message)" Write-Error "StackTrace: $($_.Exception.StackTrace)" Write-Error "LoaderExceptions: $($_.Exception.LoaderExceptions)" } finally { $Connection.Close() } |
Line 14 assigns a SQL query that returns a single row with one column as the CommandText of a Command object. Line 22 reads the zero position of a row or record set with only one column.
You call the readcursor.ps1 Cmdlet with the following syntax:
powershell .\readcursor.ps1 |
It returns:
Current Database [ videodb ] |
A more realistic way to write a query would return multiple rows with a set of two or more columns. The following program queries a table with multiple rows of two columns, but the program logic can manage any number of columns.
# Define a ODBC DSN connection string. $ConnectionString = 'DSN=PostgreSQL35W' # Define a MySQL Command Object for a non-query. $Connection = New-Object System.Data.Odbc.OdbcConnection; $Connection.ConnectionString = $ConnectionString # Attempt connection. try { $Connection.Open() # Create a SQL command. $Command = $Connection.CreateCommand(); $Command.CommandText = "SELECT last_name, first_name FROM contact ORDER BY 1, 2"; # Attempt to read SQL command. try { $row = $Command.ExecuteReader(); # Read while records are found. while ($row.Read()) { # Initialize output for each row. $output = "" # Navigate across all columns (only two in this example). for ($column = 0; $column -lt $row.FieldCount; $column += 1) { # Mechanic for comma-delimit between last and first name. if ($output.length -eq 0) { $output += $row[$column] } else { $output += ", " + $row[$column] } } # Write the output from the database. Write-Host $output } } catch { Write-Error "Message: $($_.Exception.Message)" Write-Error "StackTrace: $($_.Exception.StackTrace)" Write-Error "LoaderExceptions: $($_.Exception.LoaderExceptions)" } finally { # Close the reader. $row.Close() } } catch { Write-Error "Message: $($_.Exception.Message)" Write-Error "StackTrace: $($_.Exception.StackTrace)" Write-Error "LoaderExceptions: $($_.Exception.LoaderExceptions)" } finally { $Connection.Close() } |
You call the readcontact.ps1 Cmdlet with the following syntax:
powershell .\readcontact.ps1 |
It returns an ordered set of comma-separated values, like
Clinton, Goeffrey Gretelz, Simon Moss, Wendy Royal, Elizabeth Smith, Brian Sweeney, Ian Sweeney, Matthew Sweeney, Meaghan Vizquel, Doreen Vizquel, Oscar Winn, Brian Winn, Randi |
As always, I hope this helps those looking for a complete concrete example of how to make Microsoft Powershell connect and query results from a PostgreSQL database.